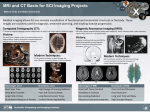
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Systems Counseling Practice Exam - 2009 - LIOS-2010
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Postpartum depression wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Systems Counseling Practice Exam - 2009 1. In structural therapy, the therapist a. directs b. joins with the family c. is in charge d. all of the above 2. Most depressed patients do not have medically unexplained somatic complaints. False. 3. Which is not an SSRI? a. Paxil b. Wellbutrin c. Lexapro d. Zoloft e. Prozac 4. Erickson is known for a. Video taping b. Hierarchy c. Dominos d. Hypnosis 5. According to Gottman, which of the following is a form of a stable relationship? a. No arguing b. Arguing c. Enmeshment 6. In MRI/Strategic Therapy, the therapist would use a paradoxical intervention with the family member who is: d. Defiant e. Resistant f. Over-confident g. The one who perceives the “problem behavior.” 7. Match the following disorders with the side effects of the medications used to treat them: a. Psychosis a. Sexual Dysfunction b. Depression b. Dependence(‘addiction’ is the answer in a different test) c. Anxiety c. Muscle stiffness/shaking 8. In structural theory which of the following is used to unbalance a stable family? a. The therapist joins with the family member who she/he thinks is right b. The therapist joins with the one most external (weakest) in the family. c. All of the above d. None of the above. 9. The definition of depression includes 5 criteria: must have either dysphoria or anhedonia and at least 4 of the following: (T/F) -sleep problems, -appetite/weight increase or decrease, -impaired concentration/decision making, -suicidal thoughts or actions, -feelings of guilt, self blame, worthlessness, -low energy-fatigue, -psychomotor agitation or retardation. 10. Which of the following rules and functions will be the most atypical for structural family therapists? a. Joining the family in a position of leadership. b. Giving voice to the therapist’s impulses c. Mapping the underlying structure of the family. d. Intervening in a way designed to transform an ineffective family structure. e. Being a stage director 11. From a social constructionist perspective, change begins with a. Understanding the roots of the problem. b. Therapist skill in using confrontational techniques. c. Deconstructing the power of cultural narrative. 12. Bowen believes that people generally choose mates with _______level of differentiation than their own. a. slightly lower b. slightly higher c. about the same d. considerably higher e. considerably lower 13. Structuralists claim that dysfunctional families require a change in the: a. covert rules that govern family transactions b. Resolving problems with each parent family of origin c. Increase togetherness d. Discovery e. All of the above 14. What do Strategic (MRI) therapists believe behavior is determined by? a. DNA and cannot be changed b. Most behavior is volitional and therapists must simply get the clients to admit to it. c. Behavior is communication and the challenge is to understand what is being communicated and to whom. d. One need not focus on the behavior but rather the beliefs that keep the behavior in place. 15. In structural theory, which of the following describe complementarity: a. One’s leniency is balanced by the other’s strictness b. When one has the flu and feels lousy, the other takes over c. Ed is the bread-winner and Mary is the dependent housewife d. All of the above 16. In solution-focused therapy the role of the miracle question is to: a. Identify who has the negative outlook b. See the future without problems, create possible goals c. Identify who in the past would not be surprised by client’s accomplishment. 17. Epistemology is: a. Exploring ways of knowing, how we know what we know. b. A family map c. Study of the sex organs of flowers d. All of the above e. None of the above 18. When talking about Gottman’s 4 horsemen, what do the following letters stand for? a. C –criticism b. C-contempt c. S –stonewalling d. D-defensiveness 19. Which of the following would not enhance therapeutic maneuverability? a. Using qualifying language b. Managing own anxiety c. Taking a firm stand early on in the session d. B & C e. All of the above 20. The miracle question allows the client to: a. Speculate on their future once the problem is gone. b. Put their faith in the therapeutic process. c. Disassociate from the present d. Join with the therapist e. None of the above 21. Solution oriented therapists offer insights a. Through their interpretations b. Orient families toward solutions to their problems. c. Create a collaborative dialogue with the family d. Rely on reflecting team to offer solutions 22. The reflection question is found in: a. Narrative therapy b. MRI/Strategic c. Solution focused d. None of the above 23. Post modern thought supports the following idea: a. There are multiple realities b. Truth is an objective reality c. Behavior as pathology d. Nature/nurture debate 24. Axis II measures personality disorders and _______ a. clinical disorders b. psychosocial problems c. V-codes d. mental retardation 25. The GAF scale measures: a. Eligibility for treatment services b. Ability to carry out activities of daily living c. Occupational functioning d. Overall level of functioning e. a and c d. All of the above 26. Describing how the problem has been helpful in some ways to a client is an example of: a. Dealing with resistance b. Enhancing maneuverability c. Reframing d. All of the above 27. One of the main MRI/Brief Therapy tenets is that: a. Family’s dysfunction is the result of unclear hierarchy and rules b. People who are organized by their own and other’s emotions are emotional dominoes c. Families pass down patterns of behavior from generation to generation d. Problems develop when difficulties are mishandled and the more of the same solution is applied 28. Delusions are: a. Auditory perceptions of stimuli not present b. Phobic attacks c. Manifestations of a multiple personality disorder d. Fixed, false and powerful beliefs 29. Which assumption is not a hallmark of SFT? a. Agenda or goals, if it ain’t broke don’t ix it b. Clients are viewed as competent c. Clients are resistant needing motivation d. Reality is subjective 30. The intervention in solution focused therapy a. the miracle question b. choosing which family member identifies the solution c. the interview d. externalizing the problem 31. Who is associated with SFT? a. Madanes, Erickson, White, Epston b. Erickson, Berg, Weiner-Davis, O’hanlon, and DeShazer c. Haley, Madanes, Dejong, Nagy 32. Which theory does not work with paradox? a. Solution focused b. Narrative c. MRI/Strategic d. Contextual 33. The maximum number of sessions for Brief Therapy is: a. 10 b. 12 c. 6 d. None, no maximum 34. Etiology is a. lack of pathology b. cause or development of the problem c. the family map d. an intervention 35. Over/Under functioning apply to what theory a. Narrative b. Contextual c. Structural d. Bowen 36. What is a sparkling event? a. Event where dysfunction is most evident b. Moment when exception becomes reality c. Removing the right domino from a sequence 37. Which theory has “customers”? a. MRI/Strategic b. Narrative c. Structural d. Solution Focused e. One or more of the above 38. Which theory uses a reflecting team? a. Bowen family systems therapy b. Narrative c. Strategic d. Solution Focused 39. What is historicizing? a. documenting medications taken in the past b. retelling of a story from different perspectives c. identifying people from the past who wouldn’t be surprised by a successful outcome. d. linking personality traits in common with past generations 40. Who is a constructionist? a. Von Forester b. Bateson c. Watzlawick d. All of the above 41. Which theories are both influenced by Erickson? a. Structural and Bowenian b. Solution focused and Narrative c. Structural and MRI/Strategic d. Solution focused and MRI/Strategic 42. The goal of Solution Focused Therapy is: a. focus on the solution b. client understands why they have the problem c. focus on the past d. resolve the problem 43. Which theory uses complementarity? a. Structural b. Solution Focused c. Strategic d. MRI 44. Maneuverability is referred to in: a. Bowen theory b. Solution Focused therapy c. Structural therapy d. MRI/Strategic therapy 45. Anhedonia is a. Inappropriate affect b. Inability to experience pleasure c. Being cut off from primary family group d. Developmental delays caused by lack of oxygen at birth 46. Who would NOT want to focus on the etiology of a problem? a. DeShazer b. Nagy c. Epston d. Haley 47. Which theory uses reciprocity? a. Structural b. MRI/Strategic c. Bowen 48. What are the MRI – Prescriptives? a. more of the same. b. something different. c. restraining. d. paradox. 49. What is the intervention in Narrative Therapy? a. the questions b. externalizing the problem c. identifying the sparkling event d. none of the above 50. Who are the founders of Narrative Therapy? a. White b. Foucalt c. Epston d. All of the above 51. Who uses amplifying to get exceptions? a) White/Narrative b) Berg/Solution Focused c) Minuchin/Structural d) Nagy/Contextual 52. Which theorist uses the term Social Regression? a) David White b) Murray Bowen c) Salvador Minuchin d) Jay Haley 53. Which theorist is connected to both MRI/Strategic and Solution-Focused? a) Erickson b) Bateson c) Haley 54. Which theory talks about client position? a) Narrative b) Structural c) MRI/Strategic d) Bowen 55. Narrative Therapy directs the family to pay attention to: a) The problem saturated story b) Meaning of the problem in the family’s life c) The reflecting team’s response d) Experiences of the problem in the family’s life 56. Michael White and Steve DeShazer would both agree on all but one of the following: a) Intention was important to the therapy b) The client’s past would reveal an exception c) The client’s situation is non-pathological 57. Who mentions scapegoat in the family system? a) Bowen b) Minuchin c) Berg d) White 58. Transaction questions refer to: a) Bowen Family Systems theory b) Narrative therapy c) Structural d) MRI/Strategic 59. Which theory sees problems as repeating unsuccessful behaviors? a) Solution Focused b) MRI/Strategic c) Bowen d) Narrative 60. Who refers to the family projection process? a) Minuchin b) Bowen c) White d) Erickson 61. The person with low differentiation would tend to be bound up by: a) the family hierarchy b) the family boundaries c) the emotions of others 62. Which of the following is NOT a known neurotransmitter? a) Norepinephrine b) Serotonin c) Lithium d) Dopamine 63. Which of the following antidepressants has a different mechanism of action than the others? a) Paxil b) Prozac c) Zoloft d) Wellbutrin e) Luvox 64. Which is not an anxiolytic? a) Valium b) Benzodiazepines c) Buspar d) Propranolol e) Depakote 65. Which is NOT a potential complication of the use of hypnotic agents? a) Dependence b) Tolerance c) Abuse d) Daytime Sedation e) All are potential complications 66. Which is not a mood-stabilizing agent? a) Lithium b) Depakote c) Trilafon d) Tegretol e) Gabapentin 67. Which neuroleptic has shown effectiveness against the negative symptoms of schizophrenia? a) Haldol b) Zyprexa c) Risperdol d) Prolixin e) Both Zyprexa and Risperdol 68. Which is good advice when discussing medications with the prescribing MD? a) Always let him/her know that you know as much about psychopharmacology as he/she does because you have taken a course. b) Never present any clinical psychological information since prescribing MDs mostly only care about side effects and efficacy c) Confidentiality does not apply when discussing the case with a co-treating prescribing physician d) Give a brief presentation of your patient and give supporting data for your recommendations 69. Malpractice claims are being upheld against MFCCs and psychologists for treating depression without referring the client for a medical evaluation. True. 70. Depression is the most widely diagnosed psychiatric problem currently being treated in the outpatient office. True. 71. According to DSM-IV, sadness is essential to making the diagnosis of major depression. False. 72. The DSM-IV requires at least four of the following neuro-vegetative symptoms to be present for diagnosis of major depression: (T/F) Ture. a. insomnia or oversleeping b. appetite changes or weight gain or loss c. suicidal ideas or plans d. guilt, self-blame, worthlessness feelings e. low energy f. psychomotor agitation or retardation g. difficulty concentrating h. impaired decision making 73. Dysthymia describes a mood disorder lasting less than one year. False. 74. Psychological depression should be treated even though it is clear that it is caused by a medical condition. True. 75. Drugs, which cause depression, include the following: a) alcohol b) anti-hypertensives c) anti-anxiety d) anti-parkinsonian e) birth control pills f) corticoid steroids g) all of the above 76. Differential diagnosis of depression must be mindful of: a) Grief reactions b) Adjustment disorder due to situational problems c) Substance abuse due to situational problems c) All of the above 77. The DSM-IV lists the following types of depression; a) Dysthymia b) Double depression c) Recurrent with full recovery d) Single episode e) All of the above 78. Treatment of depression usually results in relief of all somatic pain complaints. True. 79. Comorbidity of anxiety and depression is easily and successfully treated with antidepressants. False. 80. Drug/drug interactions must be carefully considered, particularly in the elderly. True. 81. Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder is an exacerbation of PMS, identifiable by the intensity of the symptoms. True. 82. The diagnosis of PMDD is appropriate for a client who does not find the symptoms severe enough to interfere with social and vocational functioning. False. 83. What percentage of patients diagnosed with PMDD meet the criteria for Dysthymia? ____25%__ 84. Apparently, estrogen exerts its effect on mood through serotonin. True. 85. Scaling questions are used in which theory? a) Structural b) Solution-focused c) Bowenian d) MRI 86. Discussion of depression does not need to include the risk factor for suicide. False. 87. The risk for suicide is highest for the older adult male who lives alone and abuses alcohol and/or substances. True. 88. Serotonin affects which of the following part of the patient’s life? a) Eating b) Sleeping c) Sexual function d) Aggression e) Activity f) All of the above 89. Dopamine is responsible for pleasure. True. 90. The incidence of sexual dysfunction in connection with antidepressants is: a) 35% b) 25% c) 15% d) 5% 91. It is always necessary to taper when changing antidepressant medication. a) Always b) Yes, except when the change involves medications with long half-lives, such as Prozac c) No 92. The goal of antidepressant medication is: a) Mitigation of symptoms b) Full remission of symptoms c) Neither of the above 93. Patients who elect to discontinue medication are at risk for: a) A relapse of depression b) Vulnerability to relapse c) Return of somatic symptoms d) All of the above 94. Antidepressant treatment interruption is also referred to as discontinuation syndrome. True. 95. Psychopharmacology is the study of drug-induced changes in mood, sensation, thinking and behavior. 96. Sleeping pills themselves can be the cause of insomnia 97. In failing to consider psychotropic medications in treatment, we are possibly failing our client. 98. When psychotropic medications are used, it is necessary to consider their impact beyond the patient’s biological system. 99. A majority of depressed patients suffer from anxiety as part of their symptomatology. 100. In general, when the efficacy of antidepressants is compared, all seem to perform equally.