* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fetal Development
Prenatal testing wikipedia , lookup
Anovulation wikipedia , lookup
Embryo transfer wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Egg donation wikipedia , lookup
Female infertility wikipedia , lookup
Semen quality wikipedia , lookup
Infertility wikipedia , lookup
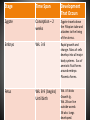
Fetal Development Prenatal development • The period from conception moving through the 3 stages (Zygote, Embryo, Fetus) • Physical changes that take place before the baby is born. Fetal Development Terms • • • • Ovum: A female cell or egg – for reproduction Uterus: A female organ where baby develops Sperm: A male cell for reproduction Conception: A union of ovum and sperm resulting in the beginning of pregnancy. • Zygote: A fertilized egg. Stage Time Span Stages, Time Span and Development That Occurs Development Zygote travels down the Fillopian tube and attaches to the lining of the uterus. Zygote Conception – 2 weeks Embryo Wk. 3-8 Rapid growth and change. Mass of cells develop into all major body systems. Sac of amniotic fluid forms around embryo. Placenta Forms. Fetus Wk. 8-9 (begins) Until birth Wk. 4-5 kicks Growth lg. Wk. 28 can live outside womb. 36 wks lungs developed. Important Terms • Placenta: A tissue in the uterus of a pregnant woman that is rich in blood vessels and plays a role in bringing food and oxygen from the mother’s body to a developing fetus. Amniotic Fluid: Liquid that surrounds and protects the developing baby in the uterus during pregnancy. Umbilical cord: A long tube that connects the placenta to the developing baby; carries food and oxygen to the baby. More Terms • Quickening: Signs (kicking , fluttering etc. ) telling a pregnant woman that she has a live baby developing in her body. (4-5 wks) • Lightening: The baby shifting down. The pregnant woman feels lighter in the upper abdomen and heavier in the lower abdomen. The baby is dropping into the birth canal in preparation for delivery. (usually in the 9th month) Heredity • The passing on of certain characteristics from earlier generations. • Characteristic that can be hereditary: • Physical build; skin color; hair texture and color; colour and shape of eyes; shape and size of the ears, hands and feet; and blood type. Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes consist of many genes • At conception every human baby receives 46 chromosomes. These chromosomes come in 23 pairs. The father’s sperm and the mother’s ovum both contribute a chromosome to each pair. Each chromosome has thousands of genes, the units that determine the child’s inherited characteristics. Genes make up chromosomes as like beads make up a necklace. Dominant and Recessive Genes • What happens if a baby has a mother with blue eyes and a father with brown eyes? - The way the characteristic (brown or blue eyes) is expressed will be controlled by the DOMINANT or stronger gene. The RECESSIVE or weaker gene will be lost. • In this example BROWN EYES ARE DOMINANT so what colour eyes will the baby most likely have? Answer • The baby would most likely have brown eyes because BROWN is DOMINANT however there would be a slight chance he/she would have BLUE eyes IF both parents had RECESSIVE blue eye genes. More precisely if the person with the brown dominant also had a blue recessive then the baby could have blue eyes. What determines the sex of a baby? • At conception, gender is determined by chromosome characteristics - and it is the male's sperm that dictates whether the baby will be a boy or a girl. Prior to conception, the unfertilized egg carries an X chromosome while the sperm can carry either an X or a Y chromosome. The gender of the baby comes down to one simple event: • If the sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, a girl will be conceived. • If the sperm carrying a Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, a boy will be conceived. Multiple Births • Fraternal Twins: 2 eggs fertilized resulting in non indentical twins (siblings but different genetics) - could be same sex or opposite sex .Fraternal twins are hereditary. They do not always “skip a generation”. • Identical Twins: 1 eggs is fertilized and splits. No one really knows why the egg splits. It is considered a “fluke of nature”. Identical twins have the same genetic make up since they come from the same fertilized egg. The later the egg splits, the more dis-similar the twins will be. Identical twins are always same sex twins due to the identical genetics. Identical twins are not hereditary. • Both Fraternal and Identical Twin pregnancies are considered high risk pregnancies however identical twin pregnancies are slightly greater risk due to the fact that most of the time identical twins share a placenta and sometime this can cause problem. Eg. Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome. Triplets • More common as twins are now due to fertility treatments such as in-vitro fertilization whereby three or more embryos are implanted. • Usually fraternal triplets. In rare cases you may have triplets as a result of two eggs being fertilized and the one of the eggs splits to create and identical set. • Higher order multiples are very rare unless fertility treatments are involved and pose ethical questions that can not be ignored. Eg. selective reduction. Infertility • Infertility is the inability to become pregnant • It is estimated that one in six couples has trouble conceiving. • Some reasons for females infertility are: • - Ovulation problems: her ovaries are not releasing eggs each month • - endometriosis (the endometrial tissue or uterine lining grows outside of the uterus) • Other causes: polycystic ovary syndrome, poor egg quality, fallopian tube blockages. Infertility options • Adoption: A couple is given the legal rights to a child already born. • Artificial Insemination: Sperm is injected into a woman. • In vitro fertilization: A egg from the woman is removed and fertilized with sperm from the man. The resulting zygote is placed in the woman’s uterus. • Ovum transfer: A female donor is used for in-vitro. In this case a woman may not have working ovaries or may have an inherited disease so they use a donor. • Surrogate mother: A woman gets pregnant for a couple. The couple’s fertilized eggs can be used or artificial insemination can be done. • NB: Fertility drugs can be used to stimulate ovulation or treat infertility. These medications can cause serious side effects such as lung probbems, abdominal pain etc. Another side effect can be multiple births. Infertility • Male Infertility • - Some causes for male infertility are: - Male tube blockages - Sperm problems (low sperm count or a motilty problem) - Sperm allergy – woman develops antibodies that kills sperm.(diagnosis is controversial)