* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Third Six Weeks SFA/Energy Transformation Review
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
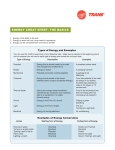
Energy Unit Part II Test Review KEY At what point is potential and kinetic energy the highest? 1. Potential energy ___A__________ A 2. Kinetic energy ____C_________ At what point is potential and kinetic energy the lowest? 3. Potential energy ____C______ B 4. Kinetic energy ______A_____ 5. The horse has ___gravitational______ potential energy. 6. The horse has _mechanical__________ kinetic energy. List the 6 types of potential energy and an example of each. Answers will vary on #7-17 Type of Potential Energy Examples 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. List the 4 types of kinetic energy and an example of each. Type of Kinetic Energy 13. 14. 15. 16. Light Energy Examples 17. Examples C D Directions: Match the following key words to their definition. 18. ____A_____ Conduction A. Transfer of thermal energy through direct contact between particles of matter 19. ____C_____ Convection B. Transfer of thermal energy by electromagnetic waves that can travel through space 20. ____B_______ Radiation C. Transfer of thermal energy by movements of a fluid (gas or liquid) Identify the method of heat transfer: Conduction (CD), Convection (CV), Radiation (R). _____R_______21. Microwave _____CD______22. Frying egg in skillet. _____CD______23. Hair Straightener _____CV______24. Hot Air Balloon _____CV______25. Air Popcorn Popper _____R_______26. Car getting hot sitting outside. _____CV______27. Lava Lamp _____CV______28. Movement in earth’s mantle causing plates to move. _____R______29. Roasting marshmallows by a fire. _____CD_____30. Metal spoon sitting in hot soup. Fill in the blanks with the correct word. 31. Thermal energy always flows from __HOT_________ to ___COLD___________. 32. The sun transfers heat to the earth through __RADIATION___________________________. 33. ___SOLIDS___________ cannot transfer heat through convection because they do not have ___FLUID_____________ motion. 34. Copper is used on the bottom of pots and pans because it is one of the best __CONDUCTOR___________________ of heat. Cool Times B 35. At what point, (A, B, or C), is thermal equilibrium reached in the Cool Times lab? _____C_________ C A 36. Explain what is happening to the thermal energy in the hot beaker compared to the thermal energy in the tap water beaker, according to the graph. Thermal energy of the hot beaker is decreasing while the thermal energy of the tap water beaker is increasing. 37. 38. 39. 40. What is it called when one form of energy changes to another form of energy? Energy Transformation What energy transformation happens when you turn on a light? Electrical to Light What energy transformation occurs when wood is burned in a fireplace? Chemical to Thermal What energy transformation happens in a battery powered toy car? Chemical to Mechanical Kinetic 41. Directions: Match the energy transformation to its example. May be used more than once or not at all. __G___ 1. Turning on the lights in the classroom. __A___ 2. An electric space heater. __E___ 3. Battery operated remote controlled car. __C___ 4. Nuclear power plant providing energy for a community. __E___ 5. Driving your ethanol powered car. __H___ 6. Plants producing sugar and oxygen by photosynthesis. __B___ 7. A hydroelectric dam producing energy for a town. __E___ 8. Eating a banana and then going for a walk. __I___ 9. Burning wood in a fireplace. __F___ 10. Playing the guitar. __D___ 11. Using a solar powered calculator. A. Electrical to Thermal B. Mechanical to Electrical C. Nuclear to Electrical D. Radiant to Electrical E. Chemical to Mechanical F. Mechanical to Sound G. Electrical to Radiant H. Radiant to Chemical I. Chemical to Thermal