* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adrenal Glands
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
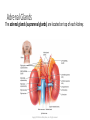
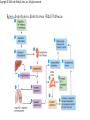
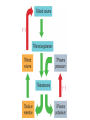
Adrenal Glands Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands (suprarenal glands) are located on top of each kidney. Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Adrenal Gland – 2 Glands in 1 Cortex (outer) – bulk of gland (75%); glandular tissue Medulla (inner) – nervous tissue; SNS Cortex vs. Medulla • Glandular vs. Nervous tissue • Remind you of another endocrine gland?? • Blood flows from outside of adrenals inward Adrenal Cortex Zones Cortex - divided histologically into 3 regions: • ZG - “salt” • Mineralcorticoids • ZF – “sugar” • Glucocorticoids • ZR – “sex” • Gonadocorticoids Adrenal Cortex Hormones • The zona glomerulosa secretes: • Mineralocorticoids - used to regulate mineral homeostasis (electrolytes), Na2+ K+ • Aldosterone • The zona fasciculata secretes: • Glucocorticoids - affect glucose homeostasis • Cortisol • The zona reticularis secretes: • Weak androgens • DHEA, androstenedione Zona Glomerulosa - Mineralcorticoids • Aldosterone is the major mineralocorticoid. • Regulates sodium (Na2+) and potassium (K+) homeostasis. • Controlled by renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) pathway • A.k.a. Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone (RAA) Pathway Zona Fasciculata - Glucocorticoids • Stimulated by ACTH • Secretion of cortisol is regulated by negative feedback. Glucocorticoids help control: • • • • • • Protein breakdown Glucose formation Lipolysis Resistance to stress Inflammation Immune responses Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Glucocorticoids Mostly permissive to actions of other hormones. • Epi is ineffective w/out cortisol • Under stress, w/out glucocorts, there is vascular collapse. • Maintain cardiac output; increase arteriolar tone; decrease endothelial permeability; maintain normal vascular resistance • • • • • Maintains normal BP (angiotensin II) Modulate emotional tone, wakefulness; memory High cortisol will ↓ muscle mass and bone formation Inhibit inflammatory and immune response Facilitate maturation of the fetus • Develops fetal enzyme systems • Growth and development Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Glucocorticoid Feedback Loop Zona Reticularis - Gonadocorticoids • Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) – major androgen secreted. • In males, after puberty the hormone testosterone is secreted in much larger quantities so DHEA has virtually no effect. • In females, DHEA and other adrenal androgens play a major role in promoting libido and are converted to estrogens. • In menopausal women, all female estrogens come from adrenal androgens. Adrenal Medulla • Stimulated by sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). • Chromaffin cells store and secrete 2 catecholamines: • epinephrine (adrenaline) • norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Both of which are involved in the fight-or-flight response. Catecholamines & Thyroid Hormone • Sympathoadrenal activity is enhanced under conditions of hyperthyroidism and depressed under conditions of low levels of thyroid hormones. • Major symptoms of patients with thyroid dysfunction relate to functional alterations of those organs regulated by the sympathetic nervous system.