* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Notes
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
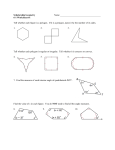
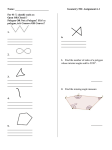
Chapter 11 Notes Mrs. Myers – Geometry Name ______________________________ Period ______ 11.1 Angle Measures in Polygons Polygon # of Sides Number of Triangles Sum of Measures of Interior Angles Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon … N-gon * Theorem 11.1: Polygon Interior Angles = the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex n-gon is n 2 180 * Corollary to Theorem 11.1: the measure of each interior angle of a regular n-gon is n 2 180 n * Theorem 11.2: Polygon Exterior Angles = the sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a convex polygon, one angle at each vertex is 360 . * Corollary to Theorem 11.2: the measure of each interior angle of a regular n-gon is 360 n Ex. 1 Find x. 114 105 102 x 135 Ex. 2 The measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon is 165 . How many sides does the polygon have? Ex. 3 Find y. 2y y y 2y Ex. 4 Find x. 11.2 Areas of Regular Polygons * Theorem 11.3: Area of an Equilateral Triangle = A 1 2 s 3 4 Center of Polygon: center of its circumscribed circle. Radius of the Polygon: radius of its circumscribed circle. Apothem of the Polygon: the distance from the center to any side of the polygon (it is also the height of a triangle between the center and 2 consecutive vertices of the polygon…so it must hit at a right angle). * Theorem 11.4: Area of a Regular Polygon = A 1 ap 2 a apothem p perimeter of the polygon Central Angle of a Regular Polygon: is an angle whose vertex is the center and whose sides contain 2 consecutive vertices of the polygon. Measure of Each Central Angle: 360 n Ex. 1 Find the area of the triangle. Ex. 2 Find the area of an equilateral triangle whose perimeter is 6 in. Ex. 3 The bottom of a glass is a regular 12-gon with a side length of 1.2 cm and a radius of 2.3 cm. What is the area of the bottom of the glass? Ex. 4 A regular octagon is inscribed in a circle with a radius of 4 units. Find the area of the octagon. 11.3 Perimeters and Areas of Similar Figures * Theorem 11.5: Areas of Similar Polygons = if 2 polygons are similar with the lengths of corresponding sides in the ratio a : b , then the ratio of their areas is a 2 :b 2 . ka kb I II If I II , then side length of I ka a and side length of II kb b Perimeter of I a and Perimeter of II b area of I a2 2 area of II b Ex. 1 The ratio of corresponding sides of 2 similar hexagons is 8:2 . A) Find the ratio of their perimeters B) Find the ratio of their areas. Ex. 2 A rectangular tablecloth is 60 in by 120 in. A rectangular place mat made from the same cloth is 12 in. by 24 in. and cost $5.00. Compare the areas of the place mat and table cloth to find a reasonable cost for the tablecloth. Ex. 3 A store sells trampolines that are all regular hexagons. One trampoline has a side length of 4.5 ft and an area of 52.6 ft 2 . Find the area of the trampoline whose perimeter is 67.5 ft. 11.4 Circumference and Arc Length Circumference: of a circle is the distance around the circle. * Theorem 11.6: Circumference of a Circle = C d or C 2r Ex. 1 Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 9 in. Ex. 2 Find the radius of a circle with a circumference of 52 in. Arc Length: is a portion of the circumference of a circle. * Arc Length Corollary: arc length of AB m AB 2r 360 Ex. 2 Find the length of each arc. A) B) 16 in M 60 7 cm 100 M K B Ex. 3 Find the indicated measure. A) mLM B) Circumference 8 in. L 45 M 16. 76 in 10.2 cm 11.5 Areas of Circles and Sectors * Theorem 11.7: Area of a Circle = A r 2 Ex. 1 A) Find the area of a circle with a radius of 3 m. B) Find the diameter of circle B when the area is 254.5 ft 2 . Sector of a Circle: is the region bounded by two radii of the circle and their intercepted arc. * Theorem 11.8: Area of a Sector = m AB r A 2 360 Ex. 2 Find the area of the sector. Ex. 3 L and M are two points on circle R with radius of 50 cm and m LRM 150 . Find the area of the sectors formed by LRM . Ex. 4 Find the area of the shaded region. A) B) 11.6 Geometric Probability Probability: a number from 0 to 1 that represents the chance that an event will occur. Geometric Probability: o Probability and Length: A C D B P Po int K is on CD length of CD length of AB o Probability and Area: M J P po int K is in region M area of M area of J Ex. 1 On the number line AF : The probability of a point landing in: A) P AB B) P BD C) P BF Ex. 2 Find the P hitting the bull ' s eye 17 in 3 in 17 in Ex. 3 Find the M 13 m 9 m 3 m B 14 m B) P placing a po int in M C) P Placing a po int not in M