* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Notes
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
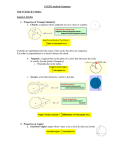
Chapter 11 Notes Section 11.1 • Polygon Interior Angles Theorem: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex n-gon is (n 2) 180 where n is the number of sides. • Corollary: The measure of each interior angle of a regular n-gon is 1 (n 2) (n 2) 180 or 180 n n • Polygon Exterior Angles Theorem: The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a convex polygon, one angle at each vertex, is 360 • Converse: The measure of each exterior angle of a regular n-gon is 1 360 360 or . n n Section 11.2 • Area of an Equilateral Triangle: The area of an equilateral triangle is one fourth the square of the length of the side times 3. A 1 1 3 s 2 or s 2 4 4 3. • The center of a polygon and radius of a polygon are the center and radius of its circumscribed circle, respectively. • Apothem The apothem of a polygon is the distance from its center to any side. • Central Angle: The central angle of a regular polygon is an angle whose vertex is the center and whose sides contain two consecutive vertices of the polygon. • Area of a regular Polygon: The area of a regular n-gon with side length s is half the product of the apothem, a, and the perimeter P, so A 1 1 aP or A a ns. 2 2 Section 11.3 • Areas of Similar Polygons: If two polygons are similar with the lengths of corresponding sides in the ratio of a:b, then the ratio of their areas is a 2 b 2 . Side length of Quad . I a . Side length of Quad . II b Section 11.4 • Circumference: is the distance around a circle. • Circumference of a Circle: The circumference C of a circle is C 2 r , or C d where d is the diameter and r is the radius of the circle. • Arc Length: An arc length is a portion of the circumference of a circle. • Arc Length Corollary: In a circle, the ratio of the length of a given arc to the circumference is equal to the ratio of the measure of the arc to 360 . Arc length of AB m AB , 2 r 360 or Arc length of AB m AB 2 r 360 Section 11.5 • Area of a Circle: The area of a circle is times the radius, or A r 2 . • Area of a Sector: The ratio of the area A of a sector of a circle to the area of the circle is equal to the ratio of the measure of the intercepted arc to 360 . A mAB mAB , or A r2 2 r 360 360 Section 11.6 • Probability: A number from 0 to 1 that represents the chance that an event will occur. • Probability and Length: Let AB be a segment that contains the segment CD . If a point K on AB is chosen at random, then the probability (P) that it is on CD is as Length of CD follows: P (Point K is on CD ) = A C D B Length of AB. • Probability and Area: Let J be a region that contains region M. If a point K in J is chosen at random, then the probability that it is in region M is as follows: Area of M P(Point K is in region M) = . Area of J