* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Accelerated Math I - Harrison High School
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
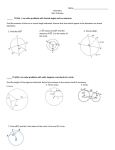
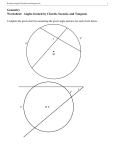
CCGPS Analytic Geometry Unit 3 Circles & Volume: Lesson 1-Circles 1) Properties of Triangle Similarity: a. Chords: a segment whose endpoints are on a circle or a sphere If chords are equidistant from the center of the circle, then they are congruent. If a radius is perpendicular to a chord it bisects the chord. b. Tangents: a segment/line in the plane of a circle that intersects the circle in exactly 1 point (point of tangency) i. Perpendicular to the radius c. Secants: a line that intersects a circle in 2 points 2) Properties of Angles: a. Inscribed Angles: angle whose vertex is on a circle & sides are chords b. Central Angles: angle with vertex at center of circle & sides are radii i. Intercepted arc is the same as the angle measure c. Other: 3) Properties of Circles: a. Arc: a continuous part of the circle i. Intercepted Arc: portion of a circle that is in the interior of an inscribed angle & endpoints are on sides of angle 1. Major Arc: larger than semicircle 2. Minor Arc: smaller than semicircle ii. Length of an Arc: Lesson 2-Area Sector b. Sector: the region bounded by 2 radii of the circle & the arc they intercept i. Area of a Sector: Lesson 3-Volume 1) Measurement: a. Spheres: i. The Great Circle: cross section with the diameter ii. Effect of changing radius 1. Factor changing the radius is cubed to change the volume b. Cylinders: c. Pyramids: d. Cones: