* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz 4 Review (Blank)
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
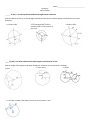
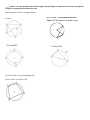
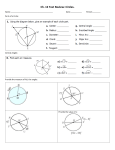
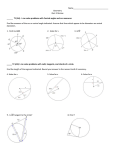
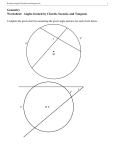
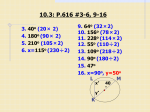
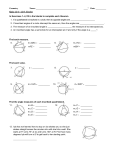
Name__________________________________ Geometry Quiz 4 Review ______ T1 (A4) - I can solve problems with Central angles and arc measures Find the measure of the arc or central angle indicated. Assume that lines which appear to be diameters are actual diameters. ̂ 1. Find the m𝐷𝐹 ̂ measures 100⁰, find the 2. 𝑆𝐷 ̂ . Q is the center of measure of 𝑅𝐸 the circle. 3. Find m∠GDH _____ T2 (A2): I can solve problems with radii, tangents, and chords of a circle. Find the length of the segment indicated. Round your answer to the nearest tenth if necessary. 5. Find x and y. 6. Find x 4. Find x ̂ , and AB, if the radius of the circle is 5cm and XY is 1cm. 7. Find m𝐴𝐵 _____ T3 (A4) : I can solve problems with Inscribed angles, inscribed angles on a diameter, and I can prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. Find the measure of the arc or angle indicated. 9. m O = 38°. O is the center of the circle. Find m R. (The diagram is not drawn to scale.) 8. Find x. N O x Q R 10. Find m∠EFG 11. Find m∠VXW x x 12. Given: DUCK is an inscribed quadrilateral. Prove: m∠DUC + m∠CKD = 180. ____ T4 (A3): I can solve problems with intersecting chords, secants, tangents, and their segment lengths, as well as intersecting chords, secants, tangents and their angle measures. T4a (Angles): Find the value of x. 13. 14. x x 15. x 85⁰ 16. 17. 18. T4b (sides): Solve for x. Assume that lines which appear tangent are tangent. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. T5 (A1): Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.3 25. Go to http://mathopenref.com/tocs/constructionstoc.html and learn how to construct the incenter and circumcenter. 26. The incenter of a triangle is the point where all three ________________________________ always intersect. 27. The circumcenter of a triangle is the point where the __________________________________________ of the sides intersect. _____ T6 (A1): Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.B.5 28. The circle with center F is divided into sectors. In circle F, is a diameter. The length of the radius is 3 units. Find the ̂. arc length of 𝐵𝐶 29. Find the measure of x in radians 30. Find the area of the shaded region.