* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Toxoplasma gondii
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Echinococcosis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
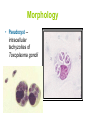
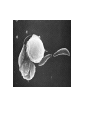
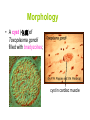
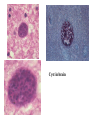
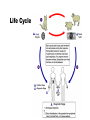
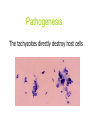
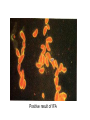
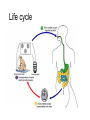
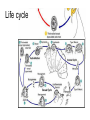
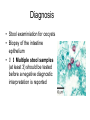
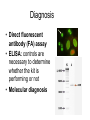
Opportunistic protozoa Pathogens Disease Sites parasitized Toxoplasma gondii toxoplasmosis All cells except RBC Cryptosporidium spp. cryptosporidiosis Intestinal epithelium Isospora spp. isosporiasis Intestinal epithelium microsporidia microsporidiosis Blastocystis hominus blastocystosis Intestinal epithelium Brain, liver, kidney… intestine Pneumocystis jeroveci (Pneumocystis carinii) Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) lung Toxoplasma gondii (toxoplasmosis) Introduction • Toxoplasma gondii has very low host specificity, and it will probably infect almost any mammal. It invades all kinds of cells except RBC • Cats (both domestic and wild) are the only definitive hosts and can also be the intermediate hosts • The disease that Toxoplasma gondii caused (toxoplasmosis) has been found in virtually every country of the world • Toxoplasmosis is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in AIDS patients and congenitally infected infants -- opportunistic infection for human Morphology • Trophozoite – The intracellular parasites (tachyzoite速殖子) are 3x6µm, crescent shaped organisms that are enclosed in a cell membrane to form a pseudocyst (假包囊) measuring 10-100 µm in size Morphology • Pseudocyst -intracellular tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii Morphology • A cyst (包囊)of Toxoplasma gondii filled with bradyzoites; cyst in cardiac muscle Cyst in brain Morphology • A sporulated oocyst (卵囊)of Toxoplasma gondii. • The oocyst contains two sporocysts(孢子囊), each of which contain four crescent-shaped sporozoites (子孢子) • Only cats produce and pass Toxoplasma oocysts; approximate diameter = 10 µm Life Cycle Life Cycle • Two host pattern with alternation of generations----mammal mammal • Toxoplasma gondii is a serious zoonotic parasite that has almost all the warm blooded animals as the reservior hosts (intermediate hosts) • Life cycle includes two phases called the intestinal (or enteroepithelial) and extraintestinal phases Life Cycle • The intestinal phase occurs in cats only and produces "oocysts" (___ hosts) – Schizogony – schizont merozoite asexual reproduction – Gametogony – male & female gamete fertilize oocyst sexual reproduction – Sporogony – sporocyst sporozoites asexual reproduction • The extraintestinal phase occurs in all infected animals (including cats) and produces trophozoites -- asexual reproduction (__ hosts) – Tachyzoites – pseudocysts – Bradyzoites -- cysts Life Cycle • Toxoplasmosis can be transmitted by ingestion of oocysts (in cat feces) or “pseudocysts" or “cysts"(in raw or undercooked meat) • Shedding of oocysts in faeces is most common in kittens, but can occur in any age of cat • Oocysts can remain infectious for several months and are quite resistant to disinfectants, drying and freezing. Tissue cysts are less resistant, and are destroyed by proper cooking of food Pathogenesis In general, most of the human population infected with Toxoplasma are asymptomatic carriers There are a number of factors which determine whether an infected host will express disease symptoms –The strain of the pathogen (RH strain) –The susceptibility of the host -- immunocompromised –Age of the host – new born infants –Degree of acquired immunity Pathogenesis The tachyzoites directly destroy host cells Clinical features • Although Toxoplasma infection is common (~13% overall world prevalence), it rarely produces symptoms in normal individuals • Could be classified as – Congenital toxoplasmosis – Acquired toxoplasmosis Congenital Toxoplasmosis • Two types: – Asymptomatic Congenital Toxo • 60% of infected • may suffer from Long Term Sequela – Symptomatic Congenital Toxo • 40% of infected • more likely if mother infected in 1st/2nd Trimester • Severe damage to fetus = stillbirth or abortion • or may be severely affected Asymptomatic Congenital Toxo • Diagnosis: – + IgM titer in serum of newborn (TORCH +) – no overt clinical disease at birth • Long Term Sequela: – within 7 years of birth - children born to women with high levels of Toxo antibody had • 2x > frequency of deafness • 60% more microcephaly (small head) • 30% more Low IQ babies Symptomatic Congenital Toxo • Spontaneous abortion or stillbirths • Bilateral retinochoroiditis (双侧视网膜脉络膜炎) • Microcephalus(小头畸形)or hydrocephalus(脑积 水) • Intracerebral calcification(大脑钙化灶) • Neurological Damage • Learning Difficulties • Jaundice(黄疸) and hepatosplenomegaly Acquired Toxoplasmosis • usually asymptomatic – majority of population was infected • IgG titer is demonstrable for 10 yr. post-infection • Symptoms – flu-like – swollen neck (cervical lymphadenopathy) – fever, malaise(不舒服) – enlarged liver/spleen (hepatosplenomegaly) – mimics infectious mononucleosis(单核细胞增 多症) Toxoplasmosis in AIDS patients • A significant OI (opportunistic Infection in AIDS) – Toxo lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph glands) – Toxo encephalitis (TE) & CNS Toxo death – pulmonary Toxo & Toxo pneumonia – UTIs - Toxo urinary tract infections – disseminated Toxo • Peritonitis(腹膜炎), chorioretinitis(脉络视网膜炎), etc. Immunology • Both humoral and cell mediated immune responses are stimulated in normal individuals • CMI is protective – Th1 cytokines such as IFN-gamma, IL-12 • Humoral response is of diagnostic value Diagnosis • Microscopic Examination -Smears and Sections – Specimens -Blood, Sputum, CSF, bone marrow -Tissue Biopsy • Animal Inoculation • Serological tests – IHA, IFA, ELISA (IgM/IgG) • PCR & DNA probes Positive result of IFA Epidemiology and control • Worldwide cases of congenital toxoplasmosis are estimated at between 140,900 and 1,127,200, based on an estimated rate of 0.1 to 0.8% of 140.9 million live births in 1992 • Some countries have instituted screening programs of pregnant women • About 5-10% of AIDS patients complicated with toxoplasmosis Reasons of epidemic • Source of oocysts ... – domestic and wild cats, passes tons of oocysts • Persist in environment if moist – reservoir of infective oocysts • Many intermediate hosts with infective stage – reservoir of infective tissue cysts Epidemiology and control • Transmission route for humans – Infected • by ingesting infective oocysts (in >4 day old cat feces) • by ingesting tachyzoites or bradyzoites in rare meat • by receiving blood or tissues with “-zoites” • CONGENITALLY by transplacental tachyzoites Epidemiology and control • Avoid contact with cat feces • Change cat litter daily to prevent infective oocyst formation • Pregnant women should avoid all contact with cats • Instituted screening programmes of pregnant women • Avoid raw or undercooked meat • Handle uncooked meat carefully • Wash your hands Treatment • Combination Therapy – Pyrimethamine(乙胺嘧啶) plus either – Sulfadiazine(磺胺嘧啶) or – Trisulfapyrimidines(三重磺胺嘧啶) • During pregnancy, – spiramycin(螺旋霉素) until delivery Summary • Toxoplasma gondii: pathogenesis, clinical features, control – Opportunistic infection – What are the infective stages of toxoplasma gondii? – Please describe the possible consequences of toxoplasma infection in a young lady. • What parasitic diseases can be transmitted by blood transfusion? Cryptosporidium spp. Introduction Cryptosporidium is a protozoan parasite in water environment Have a low infectious dose necessary to infect human as less than 10 organisms Potentially lethal for immunosuppressed individuals A threat to the quality of surface water and the environment...! Introduction • Cryptosporidiosis:an emerging infectious disease – 1907 ---Tyzzer identifies the oocysts of C. muris in mice – 1910 --- Infection is transmitted by oocysts – 1912 --- Description of C. parvum – 1952 --- C. parvum causes morbidity and mortality – 1971 --- Diarrhea in cattle is associated with C. parvum – 1976 --- Human cryptosporidiosis – 1982 --- First case in AIDS patients – 1987 --- first report in Nanjing, China Introduction • A complex life cycle, with multiple asexual and sexual developmental stages • Causal agent of acute diarrheal disease in human (third major cause of diarrheal disease worldwide) and animals -- zoonosis • Cryptosporidium parvum has emerged as a very important pathogen worldwide due to its morbidity in AIDS patients • Despite its significance, little is known about this parasite biology and specific chemo- or immunotherapies to treat cryptosporidiosis are yet to be developed Morphology • Oocysts are spherical to subspherical, measuring from 4-6 m • Acid-fast method:against a blue-green background, the oocysts stand out in a bright red stain • Four banana-shaped red sporozoites and one dark residual body Life cycle Life cycle Clinical features • Latent duration: 1wk -- cryptosporidiosis • immunocompetent patients – acute, self-limiting diarrheal illness (1-2 week duration), and symptoms include • • • • • Frequent, watery diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Abdominal cramps Low-grade fever Clinical features • immunocompromised persons – – – – – – – Debilitating, cholera-like diarrhea (up to 20 liters/day) Severe abdominal cramps Malaise(不适) Low-grade fever Weight loss Anorexia (厌食) C. parvum infection has also been identified in the biliary tract (causing thickening of the gallbladder wall) and the respiratory system Diagnosis • Stool examiniation for oocysts • Biopsy of the intestine epithelium • !!Multiple stool samples (at least 3) should be tested before a negative diagnostic interpretation is reported Diagnosis • Direct fluorescent antibody (FA) assay • ELISA: controls are necessary to determine whether the kit is performing or not • Molecular diagnosis Epidemiology and control • Transmission is usually fecal-oral, including water-borne and food-borne means • The highly environmentally resistant cyst of C. parvum allows the pathogen to survive various drinking water filtrations and chemical treatments such as chlorination Epidemiology and control • Swimming pools and water park wave pools have also been associated with outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis • Food can also be a source of transmission, when either an infected person or an asymptomatic carrier contaminates a food supply Epidemiology and control • Special cautions must be taken by immunocompromised persons : – – – – With HIV/AIDS Patients receiving treatment for cancer Recipients of organ or bone marrow transplants Congenital immunodeficiencies • Avoid: – sexual practicing involving fecal exposure – contacting with infected adults or infected children who wear diapers – contacting with infected animals – drinking or eating contaminated water or food, and exposure to contaminated recreational water • Drink : boiled water; filtered (1um) water or bottled water Treatment • No safe and effective therapy for cryptosporidial enteritis has been successfully developed • The urgent need of chemotherapy for persons with AIDs has led to administration of a variety of drugs: – Spiramycin (螺旋霉素),Paromomycin (巴龙霉素) – Berberine to contorl diarrhea • All these drugs have met with different levels of success