* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Note Packet
Ore genesis wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
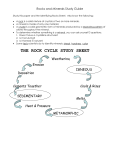
UNIT 7: ROCKS & MINERALS PACKET 8: IGNEOUS, METAMORPHIC & SEDIMENTARY ROCKS AND MINERALS This sandstone love sandstone, isIso cool, gritty I love rocks!!! … and cemented… I’m Lizzy Ps. P.S. I’m Lizzy EARTH SCIENCE MS. GILL NOTE PACKET #8 NAME:___________________CLASS:____ DATE: ________ Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 Vocabulary: Igneous Rocks Minerals Solidification Crystallization Lava Volcano Intergrown crystals Texture Composition Crystals Glassy Vesicular Extrusion Intrusion Magma Felsic Mafic Granitic Balsaltic Continental Crust Oceanic Crust Rock Cycle Metamorphic Re-crystallization Melting Weathering Banded Foliated Regional Metamorphism Contact Metamorphism Sediments Conservation Lithosphere Elements Luster Hardness Moh’s Scale of Hardness Cleavage Fracture Streak Specific gravity Clastic Bioclastic Crystalline Fragmental Cemented Evaporites Precipitates Monomineralic Fossils Road cut 2 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 Rocks are classified according to the environment in which they _________________ Types of Rocks: ________________________ _________________________ OR ______________________ 1. FORMATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS: A. Igneous rocks form directly from the ______________________________ and ______________________ of ________________ molten rock to form _________________ rock. B. ______________________________ _ is the process when a liquid rock cools, and it changes to a solid made of _______________________________ You must know how to read this chart on page 6 of your ESRT! 2. CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS: A. 2 characteristics that are used to classify igneous rocks 1. ___________________________ 2. _____________________________ B. Texture of an igneous rock describes the size shape and ____________________ of the mineral crystals it was made from. C. The _________ of the crystals depends on the ______________________________. Slow cooling = ______________________________ (Inside earth, Intrusive) Fast cooling = ______________________________ ( Lava, Extrusive) 3 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill 3. EXTRUSIVE IGNEOUS ROCKS: A. _____________________ occurs when molten (liquid) rock flows out of the earth as ___________ and cools ________________ to form fine or no ________________ 4. Note Packet #8 INTRUSIVE IGNEOUS ROCKS: A. ________________ occurs when molten rock beneath the surface ________________ and cools _________________ to form __________________________ B. To form magma _____________________ must be melted. C. Minerals melt at different pressures and temperatures. D. Igneous rocks of different _____________, can form from the same body of ________ E. LAVA = fine grained 5. FELSIC: A. Igneous rocks of the continental crust are rich in ____________ density , _______________ colored minerals. ( ________________ ) 6. A. MAFIC: Igneous rocks of the ocean floor are rich in ________________ density, ________________ colored minerals. (______________ ) 4 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 Continental Crust 1. _________________________ Oceanic Crust 1. ___________________________ 2. __________________________ 2. ___________________________ 3. _________________________ 3. ___________________________ 4. __________________________ 4. ___________________________ 5. __________________________ 5. ___________________________ Use this diagram in your ESRT to answer the following: What is the temperature for the interface between the following… inner core and outer core? _________________ Outer core and stiffer mantle? __________ Stiffer mantle and athenosphere? ________ Asthenosphere and lithosphere? ______ What is the depth of the interface between the stiffer mantle and the outer core? _______________________________ State the relationship between depth and pressure :_________________________________ ___________________________ State the relationship between depth and temperature: __________________________________ __________________________________ 5 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 FORMATION OF METAMORPHIC ROCKS A Metamorphic rock is one whose original form has been ________________ by _____________ and ______________. This alteration is called ________________________. These changes are NOT caused by MELTING. If the rock melted and cooled it would be an IGNEOUS ROCK. 1. Changes are caused by ______________________. May include the creation and growth of __________________________. 2. Rocks which are intensely __________________can also become ______________________ rock, making it more DENSE and RESISTANT. The growth of new minerals may cause the rock to appear ___________________ or _______________ (stripes of light and dark minerals). It can also _________________ (bend) or __________________ original structure. 3. There are two types of Metamorphism: a. ____________________ b. ____________________ Regional Metamorphism: Occurs over large areas with extreme pressures and temperatures. The extreme heat and pressure is what builds _____________________. Contact Metamorphic: Is the zone of contact where an igneous intrusion meets the existing rock but does not melt it. Contact metamorphism occurs only at the place where the magma ________________________ rock and transfers heat via conduction. 6 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 Any kind of rock: IGNEOUS, SEDIMENTARY, and METAMORPHIC can undergo __________________________ to form metamorphic rock. ____________________ Rock: Is rock from which metamorphic rock is formed. LIMESTONE metamorphoses to become ____________________. SANDSTONE metamorphoses to become ____________________. SHALE metamorphoses to become _________________. We will NOT find fossils in Metamorphic rock because __________________ ___________________________________________________________. 7 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 FORMATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Sedimentary rocks originate from: _______________________ because this is where deposition occurs. Sedimentary rock forms a thin ____________on top of existing rock. 1. Clastic:_________________________________________________________ 2. Bioclastic: _________________________________________________________ 3. Crystalline: _______________________________________________________ 1. Clastic Sedimentary Rock: contain layers of _________________________ formed from the breakdown of other rocks. ( ) Characteristics of Clastic Sedimentary Rock ( ____________________ ) A. Varied particle size B. Horizontal layers C. Formed in water Sedimentary rocks are UNLIKE loose sediments because sediments have been ___________________________ and __________________________ together. Two examples of natural cement are: _________________ & __________________ Classification of Sedimentary rocks is based on ______________________________or ____________________________. 8 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 2. Bioclastic Sedimentary Rock: are formed by the ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ * Limestone is the accumulation of _______________ and __________________ * Coal is the remains of _____________ that accumulate in layers and become buried and compressed for millions of years!! 3. Crystalline Sedimentary Rocks: Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed from minerals that were _________________ in water. Minerals that were once dissolved are called __________________________ and ___________________________ Crystalline sedimentary rocks are made of only one _____________________ and are called ___________________________________ Examples include: ______________________ and ______________________ A fossil is evidence that a rock is ________________________________________. Fossils are rare in ____________________ and ________________________ rocks. 9 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 Use your Reference Table to answer the following questions: 1. Name 2 clastic sedimentary rocks: ________________ and __________________ 2. Name 2 crystalline sedimentary rocks: ___________________________________ 3. Name 2 bioclastic rocks: _____________________________________________ 4. What mineral is limestone made from? ___________________________________ 5. What mineral is coal made from? _______________________________________ 6. What mineral is rock salt made from? ___________________________________ 7. Another word for clastic is ___________________________ (see reference table) 8. Which clastic rock is made from clay sized particles? ________________________ 9. Which clastic rock is made from many different particle sizes? _________________ 10. Which bioclastic rock is made from carbon? ______________________________ 11. Which rocks were formed from minerals, which were once dissolved in water? ________________________________________________________________ 10 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 MINERALS 1. Lithosphere is composed of _____________________________ 2. Rocks are composed of _________________________________ 3. Minerals are composed of _______________________________ The most abundant elements are _____________________ & ___________________ Minerals containing these elements are known as _______________________________ Minerals are ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ Review Questions: Use the back page of your reference tables 1. What properties are most important in identifying a mineral? 2. What property causes a mineral to break in a particular pattern? 3. Which mineral would best be used in the manufacture of glass, jewelry and electronics? 4. Which mineral would best be used in the manufacture of cement and polarizing prisms? 5. Which mineral would best be used as a food additive and to melt ice? 6. Describe 3 tests you can use to distinguish colorless halite from colorless calcite: (use your reference table) 11 Unit 7: Rocks & Minerals Earth Science- Ms. Gill Note Packet #8 MINERAL CHARACTERISTICS: LUSTER: Appearance of ___________________ reflected from a minerals surface Metallic: “shiny like a coin” Non-metallic (glassy, waxy, greasy, pearly, earthy, dull) HARDNESS: Resistance to being ______________________ Moh’s scale of hardness: The scale is from _________ to __________ ( _________________ is the hardest mineral) Larger values will scratch mineral of lower or equal value! Hardness is due to the ______________________________________________________ CLEAVAGE: Some minerals tend to break along one or more smooth surfaces. Cleavage is also due to ______________________________________________________ FRACTURE: When a mineral has no well defined cleavage plane. Breaks in ____________________ jagged surfaces. COLOR: May be used to identify ____________________ minerals. Many minerals have the ____________________ color. Some minerals come in ____________________ colors. STREAK: Color of the _____________________ of a mineral when crushed or scratched across a porcelain streak plate. CRYSTAL: The appearance that results from the internal atomic ____________________________. SPECIFIC GRAVITY: Equal to it’s _________________________ SPECIAL PROPERTIES: * _____________________________ * _____________________________ * _____________________________ *_____________________________ * ____________________________ * ____________________________ A mineral containing _______________ will “fizz” when in contact with ____________ 12