* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Soil Exploration
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
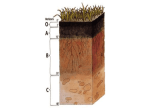
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Soil Exploration Purpose: To compare and contrast different kinds of soil. To measure the rate at which water drains through the soil and to classify different soil samples. Materials List: Samples of soil Glass Funnel Graduated cylinder Clock dissecting microscope paper towels beaker with graduations filter paper Procedure: 1. Examine each of the three soil samples using your unaided vision and the dissecting microscope. Sketch a drawing of each type of soil in your data book using the microscope view and describe it in detail using the appropriate vocabulary. 2. Moisten a small amount of soil and note whether the moist soil feels grainy or sticky. Note how well the soil molds (friability). Record this information. 3. Fold a piece of filter paper and place it into the glass funnel. Place 30 grams of soil onto the filter paper and carefully place the funnel into the beaker as demonstrated by the teacher. 4. Measure 50 ml of water into the graduated cylinder. 5. Gently pour the water from the graduated cylinder over the soil in the funnel. Record the amount of time it takes for the first drop of water to come through the hole in the bottom of the funnel. Record the volume of water collected in the beaker after 2 minutes and after five minutes. 6. Repeat for each different soil sample. Record your data in the table. Data: Soil Sample Feel when moistened Ease of molding Time for first drop Water volume after 2 minutes Water volume after 5 minutes 1 2 3 Results/Calculations: Diagram and color your soil samples using the dissecting and compound microscopes. Classify the samples using the soil triangle. Questions: 1. Which type of soil drained the fastest? Which drained the slowest? What factors in the soil do you think resulted in the speed of percolation? 2. Which types of soils contained organic material? How do you know? How would that affect the number and type of organisms that live in and around the soil? 3. Which of the soil samples would be best for your garden? Explain your answer. 4. Which of the soil samples had the greatest friability? What factors contribute to this characteristic? 5. Explain why a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay results in the best suited soil for growing plants. Discussion of Error: List three possible errors that may have occurred while you were testing. Conclusion: Summarize how the different soils are constructed including a description of the size of the particles included in each sample. Explain where your soil samples belong in the soil triangle and why.