* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9, Intro – Part I (p
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Muslim conquest of the Maghreb wikipedia , lookup
Early Muslim conquests wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 13th century wikipedia , lookup
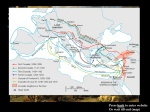
Chapter 9, Intro – Part I (p.324-328) The Crusades, Military Orders, and the Inquisition - By 1071, Muslims had conquered 2/3 of the Christian world. o Christian Europe was on the brink of annihilation. - Church unity was being threatened by growing heretical groups. I. Post-Carolingian Europe A. Social structure 1. Empire broke into thousands of principalities, counties, and fiefs (landed estates) a. Feudalism arose – economic system that created three class distinctions i. ii. iii. b. every member of society was obligated to someone else i. ii. iii. B. Feudalism 1. very effective for prosperity at first a. as populations grew, class distinctions became more definite. What happened? i. ii. 2. Feudal wars of 10th and 11th centuries a. characterized by ferocity, cruelty, injustice C. Rise of the Seljuk Turks 1. resumed expansion of Islamic forces in the east a. with the defeat of the Byzantine army it was clear that the Turks could force expansion of Islam into the remainder of the Christian world. D. Medieval mindset 1. How was heresy viewed in the Middle Ages? 2. some atrocities committed by Christians in the name of Christ that correspond to an 11th century worldview that is very different from that of today. II. The Crusades A. In the Middle Ages, “crusade” referred specifically to a series of eight military expeditions that Christians undertook between 1096 and 1270 1. Defensive action in the Holy Land against Muslim expansion a. Efforts directed against: i. ii. iii. B. Crusaders were united under the Pope 1. Swore a solemn vow 2. Received a cross from the pope or his legate C. Crusades created a situation in which some infighting among European rulers could be avoided 1. United under a common cause 2. Rulers were not allowed to invade the lands of a ruler on Crusade III. Fall of the Holy Land A. Islam 1. Within 100 years of Muhammad’s death, Islam spread throughout much of the Christian world a. as much to do with the success of Muslim military expansion as it did with authentic religious conversion. b. Islamic forces seized: i. ii. iii. iv. 2. Muslim expansion into Europe was halted by Charles Martel’s defense of Western Europe and the Byzantine Empire’s defense of the East a. borders remained more or less stable between Muslim and Christian lands B. Renewed persecutions 1. Rise of the Fatimite Muslims in Egypt during early part of 11th century led to renewed Christian persecutions. 2. 2nd half of 11th century – new militant Islamic nation of Seljuk Turks persecuted Christians and expanded westwards into lands that had been protected by Byzantium. a. 1071 – Turks annihilated Byzantine army and were on the verge of taking Constantinople. i. 2/3 of the Christian world had been taken by Muslim forces ii. Eastern Emperor looked west for assistance C. Western help for the Eastern Empire 1. Many – including Pope Bl. Urban II and the Eastern Emperor – hoped the Schism of 1054 could be healed. 2.1095 – Pope Bl. St. Urban II called a council in Clermont in central France to gain Western support to aid Eastern Christians D. Beginning of the Crusades 1. Pope Bl. Urban II began the Crusades by proclaiming an organized assault in defense of Christian Europe. a. Not a Christian offensive b. Crusades were a desperate attempt to hold off Islamic expansion i. Islam was the strongest power of the Medieval world 1. Threatened to take over the entire west 2. Christianity had to defend itself or be lost 2. Muslim perceptions of the world a. Islam was born in war b. Muslim thought divided the world into two spheres: i. ii. 1. Christianity – or any other non-Muslim religion - has no abode. a. What were the Crusades meant to prevent? 3. Plight of Pilgrims in the Holy Land a. Pilgrims were often robbed, beaten, or killed b. Pope St. Gregory VII had been ready to invade the Holy Land two decades earlier but was prevented by the lay investiture controversy 4. Objectives of Crusaders a. b. i. both objectives had as an end the avoidance of further killing of Christians.