* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
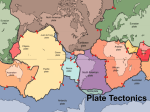
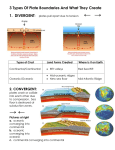
Formation of Planets • Accretion of dust in space due to GRAVITATIONAL FORCES – Dust – Asteroids – Planets 1. accretion of Heavy elements 2. attraction of Light gases to dense nucleus Origin Solar System Formation of Planets • Recent planets were HOT – Compressional Heating – Impact Heating – Radioactive Decay • The Earth is layered by Densities – Densest Core – Lightest Crust Earth’s Layers • Core (Fe, Ni) – – • Mantle (plastic) – – – • Inner Core (solid) Outer Core (liquid) very close to melting point Inner Mantle Asthenosphere Lithosphere (rigid) – – Upper Mantle (~100km) (Lithosphere) Crust • • Oceanic Continental Earth’s Core, Mantle and Crust Ocean Floor and Margins If the entire history of the earth were 1 year long: •Origin of Earth 4600 MY •Oceans first form 4000 MY •Oldest dated rocks 3800 MY •First life form 3600 MY •Ocean – Atmosphere equilibrium 1000•Multicelular MY complex organisms 700 MY •Beginning of well known Geology 600 MY •First FISH! •First510 LandMY Plants 430 MY * DECEMBER Dinosaurs evolve Dinosaurs extinct * December 31st • 9:15 pm Homo sapiens evolves • Historical Times = 1 minute 18 sec. • Columbus discovers America = 3 sec. till midnight • HMS Challenger Expedition = 0.9 sec. till midnight • You have been around for ~0.13 seconds Asthenosphere & Lithosphere Crust • Oceanic Crust – – – – – Density: ~2.9 g/m3 Mineral composition: Basalt (Fe, Mg, SiO2) Thickness: ~5-10 km Elevation: ~ 3800m below sea level Age: <200 MY • Continental Crust – – – – – Density: ~2.75 g/m3 Mineral Composition: Granite (Na, K, SiO2) Thickness: ~20-90 km Elevation: ~840m above sea level Age: <3800 MY Lithosphere Study of Earth’s Interior • Rock Sampling & Drilling • Meteorites • Seismic Studies Rock Drilling ODP (Ocean Drilling Program) Meteorites http://www.nmnh.si.edu/minsci/images/gallery/43.htm Seismic Studies http://pangea.stanford.edu/~sklemp/ http://www.oceanmarine.com/ Seismic Studies • Differential speed of seismic/sound waves due to density differences – Pressure Waves (p) • Parallel to direction of motion • Travel through liquids – Shear Waves (s) • Perpendicular to direction of motion • DO NOT travel through liquids Seismic waves refract & reflect at density boundaries Seismic Waves Seismic Waves Convection Processes Shallow and deep mantle convection cells Convection Processes Divergent Margins - Ridges • New oceanic crust formation • Spreading Convergent Margins - Trenches • Oceanic crust Destruction • Convergence & Subduction Lithosphere Plates Earthquakes Shallow (0-70 km) Medium (70-300 km) Deep (>300 km) 250 – 225 MY Spreading Cycles Hot Spot Hot Spot Loihi Volcano Evolution of Coral Reefs Fringe reefs Barrier reefs Atolls Hot Spot Map Convergent Margins • Continental Convergent Margins – Oceanic crust / Continental crust – Pacific Coast South America • Oceanic Convergent Margins – Oceanic crust / Oceanic crust – Aleutian Trench, Caribbean Arch • Continental Collision Margins – Continental crust / Continental crust – Himalaya mountains Continental Convergent Margins Oceanic Convergent Margins Continental Collision Margins Continental Convergent Margins Andes Mountains Oceanic Convergent Margins Caribbean Island Arch Convergent margin vulcanism St Helens Convergent margin vulcanism http://www.rsiphotos.com http://www.montserratreporter.org/ Soufriere - Montserrat Continental Collision Margin Himalaya Mountains Divergent Margins • Oceanic Divergent Margins – – – – Two spreading plates, upwelling magma Central Rift Valley and Oceanic Ridge Mid Atlantic Ridge (Slow 1-5 cm/year) East Pacific Rise (Fast 9-18 cm/year) • Continental Divergent Margins – Crustal upwarp, Rift Valley, Linear Ocean – East African Ridge, Red Sea Continental Divergent Margins African Rift Valley Mid Atlantic Ridge http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ Mid Atlantic Ridge http://faculty.washington.edu/lyn4/images/iceland.jpg Mid Atlantic Ridge httphttp://www.geomorph.org/gal/mslattery/IAG1.jpg East Pacific Rise http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ East Pacific Rise http://geologyindy.byu.edu/ East Pacific Rise Divergent margin vulcanism Divergent margin vulcanism Ocean Crust Age Convection Processes Shallow and deep mantle convection cells Passive Continental Margins Figure 2.28 Transform Faults • Two plates slide by each other • Numerous earthquakes along faults • Common in divergent and convergent margins Transform Fault Mid Atlantic Ridge http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ San Andreas Fault between Pacific & N. American plates •http://quake.wr.usgs.gov/kap/carrizo/ Plate Tectonics History • Alfred Wegener (1915) – Continental Drift Theory – Panagea (200-250 MY) Plate Tectonics History • Alfred Hess (1960) – Seafloor spreading theory – Geo-Poetry WHAT DATA PROVES PLATE TECTONICS? Figure 2.17 Magnetic Anomaly Reversal Earth’s Magnetic Polarity Sediment Thickness Ocean Sediment Drilling ODP (Ocean Drilling Program) Age Difference Ocean Crust: <200 MY Continental Crust: <3800 MY Earth Quake Distribution Earthquakes Shallow (<100km) Deep (>100km) Continent Fitting Paleomagnetism Direct Movement Measurements