* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of Cellular Organization
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
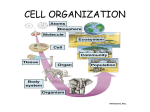
Levels of Cellular Organization BY MS. ETHRIDGE, MS. MILSTEAD, MS. MYERS, MS. PALERMO Objectives Define cell organization. Illustrate levels of cell organization. Differentiate types of cell organization within the body. Key Terms Cell: The smallest organized unit of a living organism. Organelle: A structure inside the cell that helps it survive. Protoplasm: All the living material found in a cell capable of carrying on all the life processes. Why is Cellular Organization Important? Living organisms need to do things in order to survive. Different parts of the body take care of chores to keep itself running. All parts work together in harmony to keep the animal alive. Atom The most basic unit of matter. Essentially the building blocks of everything in the universe. Can be neutral, negative, or positively charged A group of atoms is called a molecule Molecule A group of two or more atoms held together with a neutrally charged covalent bond. May consist of like atoms (O2) or several different atoms (H2O) Too small to be seen with the naked eye Cell Basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. Smallest classified living thing. “The Building Block of Life” Can be single celled or multicellular Two types: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Prokaryotic are usually independent Eukaryotic are inside multicellular organisms Tissue A group of cells (not necessarily identical) that perform the same function. Four types of animal tissue: Connective, Muscle, Nervous, and Epithelial Connective Tissue Fibrous, nonliving material Gives shape to organs and holds them in place. Examples: Blood and Bone Muscle Tissue Most active tissue Contractile: has the ability to contract and expand Produces force and movement Separated into three different categories: Visceral/Smooth: inner lining of organs Skeletal: Attaches to bones to create movement Cardiac: Found in the heart used to pump blood throughout the body Nervous Tissue Transmits communication throughout the body. Two Types: Central Nervous System: Forms the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System: Cranial Nerves and Spinal Nerves as well as the motor neurons Epithelial Tissue Covers organ surfaces Provides barrier between exterior and interior of organism Can specialize in secretion and absorption Protection from microorganisms, injury, and fluid loss Organ A group of tissues joined together to serve a common function. Classified into two types: Parenchyma: Main tissue, unique for the specific organ Ex. Myocardium in the heart Sporadic: Stroma, Include nerves, blood, and connective tissues Organ System Also called a biological system or body system Two or more organs working together to perform a specific task Ex. Muscle and Skeletal create Musculoskeletal System Eleven major organ systems in animals: Circulatory, Digestive, Endocrine, Excretory, Immune, Integumentary, Muscular, Muscular, Nervous, Reproductive, Respiratory, Skeletal Organism A contiguous living system such as an animal or plant. It is a complex system that has the ability to reproduce and sustain life. Review Define cell organization. Illustrate levels of cell organization. Differentiate types of cell organization within the body.