* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of Structural Organization within the Human Body
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
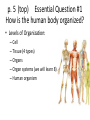
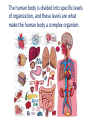
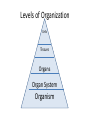
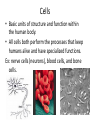
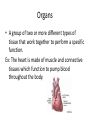
p. 5 (top) Essential Question #1 How is the human body organized? • Levels of Organization: – Cell – Tissue (4 types) – Organs – Organ systems (we will learn 8) – Human organism Levels of Structural Organization within the Human Body The human body is divided into specific levels of organization, and these levels are what make the human body a complex organism. Levels of Organization Cells Tissues Organs Organ System Organism Cells • Basic units of structure and function within the human body. • All cells both perform the processes that keep humans alive and have specialized functions. Ex: nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. Tissues • A group of specialized cells that work together to perform the same function. – Nerve tissue—carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body – Muscle tissue (3 types: cardiac, smooth, skeletal)— contracts and shortens, making body parts move – Epithelial tissue—covers the surfaces of the body, inside (as lining and/or covering of internal organs) and outside (as layer of skin) – Connective tissue—connects all parts of the body and provides support (for example tendons, ligaments, cartilage—blood, bone, and fat are also connective) Organs • A group of two or more different types of tissue that work together to perform a specific function. Ex: The heart is made of muscle and connective tissues which function to pump blood throughout the body. Body Systems • A group of two or more organs that work together to perform a specific function. • Each organ system has its own function but the systems work together and depend on one another. • Ex: circulatory, digestive, excretory (urinary), integumentary (skin), muscular, nervous, respiratory, and skeletal. Body Systems with Organ Examples 1. Integumentary: skin 2. Muscular: biceps, gluteus maximus, abdominals 3. Skeletal: skull, femur, humerus 4. Nervous: brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves 5. Circulatory: heart, arteries, veins, capillaries 6. Digestive: mouth, stomach, small and large intestines 7. Respiratory: mouth, nose, lungs 8. Excretory (urinary): urinary bladder, ureters, urethra Human Organism • Body systems interact with each other and with the environment outside the body to keep the whole person healthy.