* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science: Directed Reading Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
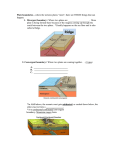
Science: Directed Reading Study Guide Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Lesson 2: Plate Boundaries Section1: Types of Boundaries (pages 202-203) 1. A ____________________ is a place where tectonic plates touch and interact with one another. These are typically areas with intense geologic activity such as frequent and sometimes violent earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building. 2. Along boundaries, plates can _______________, __________________, or ____________ _____________ each other. Earthquakes result in all three of these cases. The ________________ of boundary depends on how the plates ________________ relative to each other. 3. When two plates collide, a ______________________ boundary is formed. What happens geologically at this type of boundary depends on the type of _________________ at the leading edge of each tectonic plate. 4. When two tectonic plates carrying ______________________ crust at the boundary collide, they _______________ and ________________, which pushes the continental crust ________________. This type of convergent boundary is called a “collision zone”. 5. When a plate with continental crust collides with a plate with ocean crust, the denser __________________ crust sinks back into the aesthenosphere. This type of convergent boundary is called a ______________________ ________________. This also occurs where two plates both carrying ____________ crust collide. 6. When two tectonic plates separate, the boundary between them is called a ____________________ boundary. New __________ ________________ forms at these types of boundaries. ______________ _______________ are the most common type of this boundary. 7. When two tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally, a _____________________ boundary is formed. The ____________ _______________ fault in California is a good example of this type of boundary. Here, the _________________ ____________________ and _________________ plates are sliding past each other. Section 2: Features of Plate Boundaries (Tectonic Plate Boundaries supplement) 1. In the area of a “subduction zone” boundary, a deep V-shaped ________________ forms where the plates meet. This is usually forms offshore of a continent or island. 2. _____________________ are a common occurrence near any type of plate boundary. This is because rocks stick, bend, and break along the boundary as plates move past each other. 3. In the area of a “subduction zone” boundary, mountains are a common feature. Many of these mountains are ______________________ due to the melting of the subducting oceanic plate. 4. If a convergent boundary forms out at sea, the volcanoes form on the sea floor of the non-subducted plate (it is usually the older of the oceanic plates that is denser and subducts). These often build a ____________________ __________________ __________________, a chain of volcanic islands such as Japan. 5. In the case of a “collision zone” boundary, huge _______________________ form from the folding and buckling of the crust. Unlike the “subduction zone” convergent boundary, there are no _________________ or _____________________ found here, but plenty of violent _______________________. 6. Along divergent boundaries, a section of the lithosphere typically separates along parallel faults and drops down into the aesthenosphere, forming a _________________ _______________________. The cracks (rifts) are filled with _______________________ from the mantle to form new crust. 7. __________________________ occur along the faults and _______________________ form where magma reaches the surface. 8. Most divergent boundaries are formed on the sea-floor and their location is marked by a ________________________ ____________________ that rises about a kilometer about the surrounding sea floor. 9. _________________________ boundaries lack the large mountains and volcanoes found near other types of boundaries. Rather, they feature a ______________________ ______________________. These are also known as __________________________ faults. These appear as a large crack in the crust at the surface surrounded by very small mountains on its sides. 10. The most famous transform boundary in the world is the _______________ _____________________ fault, which runs through part of California. The sliding motion along the fault causes frequent and sometimes severe _______________________. NOTE: The Tectonic Plate Boundaries supplement can be found on the “science assignments” page of team8a.com.