* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 272 First review
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian physics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
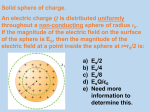
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
1. A charged conductor is brought near an uncharged insulator. Then (a) both objects will repel each other (b) both objects will attract each other (c) neither object exerts an electrical force on the other (d) the objects will repel each other only if the conductor has a negative charge (e) the objects will attract each other only if the conductor has a negative charge 2. Consider three identical metal spheres. Sphere A carries a charge of -2.0 µC; sphere B carries a charge of -6.0 µC; and sphere C carries a charge of + 5.0 µC. Spheres A and B are touched together and then separated. Spheres B and B are the touched and separated. Does sphere C end up with an excess or a deficiency of electrons and how many electrons is it? (a) deficiency, 6 x 1013 (b) excess, 3 x 1013 (c) excess, 2 x 1013 12 12 (d) deficiency, 3 x 10 (e) deficiency, 1 x 10 3. Two positive point charges Q and 2Q are separated y a distance R. If the charge Q experiences a force of magnitude F when the separation is R, then the magnitude of the force on the charge 2Q when the separation is 2R is (a) F/4 (b) F/2 (c) F (d) 2F (e) 4F 4. Two identical conducting spheres A and B carry equal charge. They are separated by a distance much larger than their diameters. A third identical conducting sphere is uncharged. Sphere C is first touched to A and then to B, and finally removed. As a result, the electrostatic force between A and B, which was originally F, becomes: (a) F/2 (b) F/4 (c) 3F/8 (d) F/16 (e) F/8 5. Two spheres, one with radius R and the other with radius 2R, surround an isolated point charge. The ratio of the number of field lines through the larger sphere to the number through the smaller is (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) ½ (e) 1/4 6. An electron traveling east enters a region where a uniform electric field is directed north. Then the electron is (a) slows down (b) speeds up (c) veers north (d) veers south (e) continues with the same speed in the same direction 7. Which of the following statements is true concerning the electrostatic charge on a conductor? (a) It is uniformly distributed throughout the volume. (b) It is confined to the surface and is uniformly distributed. (c) Most of the charge is on the surface, but it is not uniformly distributed. (d) It is entirely on the surface and it is distributed according to the shape of the object. (e) It is dispersed throughout the volume of the object and distribute according to the object’s shape. 8. The torque exerted by the electric field on a dipole is (a) parallel to the field and perpendicular to the dipole moment (b) parallel to both the field and the dipole moment (c) perpendicular to both the field and the dipole moment (d) parallel to the dipole moment and perpendicular to the field (e) not related to the directions of the field and dipole moment 9. A point charge is placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface. The electric flux is changed if (a) the sphere is replaced by a cube of the same volume (b) the sphere is replaced by a cube of 1/10 the volume (c) the point charge is moved off center (but still inside the original sphere) (d) the point charge is moved to just outside the sphere (e) a second point charge is placed just outside the sphere 10. A spherical conducting shell has charge Q. A point charge q is placed at the center of the cavity. The charge on the inner surface of the shell and the charge on the outer surface of the shell, respectively, are: (a) 0, Q (b) q, Q – q (c) Q, 0 (d) – q, Q + q (e) - q, 0 11. Two point charges, separated by 1.5 cm, have charge values of + 2 C and – 4 C, respectively. Suppose that it is determined that 10 field lines radiate from the + 2 C charge, then for the – 4 C charge (a) 20 field lines will radiate in (b) 10 field lines will radiate in (c) 20 field lines will radiate out (d) 5 field lines will radiate out (e) 5 field lines will radiate in 12. A certain physics textbook shows a region of space in which two electric field lines cross each other. We conclude that (a) at least two point charges are present (b) an electrical conductor is present (c) an insulator is present (d) the field points in two directions at the same time (e) the author made a mistake 13. Two particles have charges Q and -Q. For a net force of zero to be exerted on a third charge it must be placed (a) midway between Q and -Q (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining Q and -Q (c) on the line joining Q and -Q, to the side of Q opposite -Q (d) on the line joining Q and -Q, to the side of -Q opposite Q (e) there is no place