* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interactions in Ecosystems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
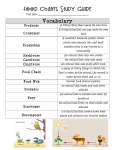
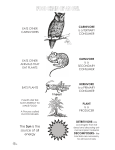
Lesson 3 – Interactions in Ecosystems Ecological Niche • An ecological niche is the function a species serves in its ecosystem, including where it lives, what it eats, what eats it, and how it behaves • Consider a black bear: – They eat plant parts (nuts and insects, other small – Few predators other than humans – Biting insects and parasites feed them – Hibernate in winter animals berries), on Types of Consumers • What each species eats has an important impact on an ecosystem • Consumers fit into the following types based on what they eat and how they behave – – – – Herbivore – eats only plants or other producers Carnivore – eats only other consumers Omnivore – eats both producers and consumers Scavenger and decomposer – feed on the remains of other, dead or decaying, organisms Food Chains • Food chains show the feeding relationships among species in an ecosystem • Food chains illustrate what each species uses for food – Seeds of a pine tree (producer) are eaten by a red squirrel (herbivore) – Red squirrel is eaten by a weasel (carnivore) – Weasel is eaten by a goshawk (carnivore) Food Chains • Carnivores linked in a food chain have a predator-prey relationship • The animal being eaten is the prey (the fish), the animal eating is the predator (the osprey) Energy in the Food Chain • Chemical energy stored in pine seeds is passed to the red squirrel • Some energy passes to the weasel, and some of that to the goshawk • Food chains show how energy passes through an ecosystem Energy in the Food Chain • The arrows show the direction of energy flow (always point at the organism that is eating) Feeding Levels • The trophic level describes the position of an organism in a food chain • The first trophic level contains producers • The second contains herbivores or primary consumers • The third contains carnivores or secondary consumers • The fourth contains carnivores and are called tertiary consumers Feeding Levels Feeding Levels • Organisms use energy to live and release thermal energy • Typically, only about 10 % of the energy taken in by organisms is passed on to the organism that consumes it Food Webs • Food chains show simple feeding relationships • A more complete model can be seen in a food web • Food webs show a series of interconnecting food chains • A consumer that feeds on many species is less affected if one of those populations decreases or becomes scarce • A newly introduced species can disrupt a food chain Food Webs Food Webs • The rusty crayfish invades this ecosystem and competes with native species for the same food