* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kinetics PPT
Equilibrium chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Industrial catalysts wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme catalysis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Reaction progress kinetic analysis wikipedia , lookup
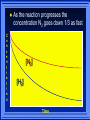
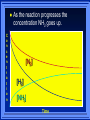
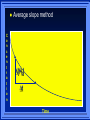
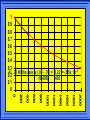
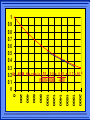
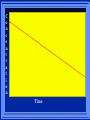
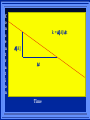
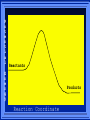
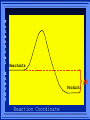
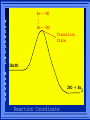
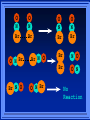
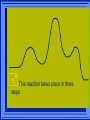
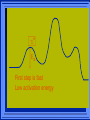
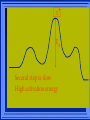
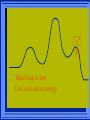
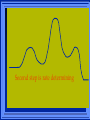
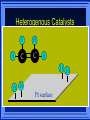
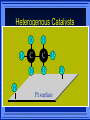
Kinetics The study of reaction rates. Spontaneous reactions are reactions that will happen - but we can’t tell how fast. Diamond will spontaneously turn to graphite – eventually. Reaction mechanism- the steps by which a reaction takes place. Reaction Rate Rate = Conc. of A at t2 -Conc. of A at t1 t2- t1 Rate = D[A] Dt Change in concentration per unit time For this reaction N2 + 3H2 2NH3 C o n c e n t r a t i o n As the reaction progresses the concentration H2 goes down [H2] Time C o n c e n t r a t i o n As the reaction progresses the concentration N2 goes down 1/3 as fast [N2] [H2] Time C o n c e n t r a t i o n As the reaction progresses the concentration NH3 goes up. [N2] [H2] [NH3] Time Calculating Rates Average rates are taken over long intervals Instantaneous rates are determined by finding the slope of a line tangent to the curve at any given point because the rate can change over time Derivative. C o n c e n t r a t i o n Average slope method D[H2] Dt Time C o n c e n t r a t i o n Instantaneous slope method. D[H2] Dt Time Defining Rate We can define rate in terms of the disappearance of the reactant or in terms of the rate of appearance of the product. In our example N2 + 3H2 2NH3 -D[N2] = -D[H2] = D[NH3] Dt 3Dt 2Dt Rate Laws Reactions are reversible. As products accumulate they can begin to turn back into reactants. Early on the rate will depend on only the amount of reactants present. We want to measure the reactants as soon as they are mixed. This is called the Initial rate method. Rate Laws Two key points The concentration of the products do not appear in the rate law because this is an initial rate. The order must be determined experimentally, can’t be obtained from the equation 2 NO2 2 NO + O2 You will find that the rate will only depend on the concentration of the reactants. Rate = k[NO2]n This is called a rate law expression. k is called the rate constant. n is the order of the reactant -usually a positive integer. Types of Rate Laws Differential Rate law - describes how rate depends on concentration. Integrated Rate Law - Describes how concentration depends on time. For each type of differential rate law there is an integrated rate law and vice versa. Rate laws can help us better understand reaction mechanisms. Determining Rate Laws The first step is to determine the form of the rate law (especially its order). Must be determined from experimental data. For this reaction 2 N2O5 (aq) 4NO2 (aq) + O2(g) The reverse reaction won’t play a role [N2O5] (mol/L) 1.00 0.88 0.78 0.69 Now graph 0.61 0.54 0.48 0.43 0.38 0.34 0.30 Time (s) 0 200 400 600 the data 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 To find rate we have to find the slope at two points We will use the tangent method. 0 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 At .90 M the rate is (.98 - .76) = 0.22 =- 5.5x 10 -4 0.2 (0-400) -400 0.1 0 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2At .40 M the rate is (.52 - .31) = 0.22 =- 2.7 x 10 -4 (1000-1800) -800 0.1 0 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Since the rate at twice the concentration is twice as fast the rate law must be.. Rate = -D[N2O5] = k[N2O5]1 = k[N2O5] Dt We say this reaction is first order in N2O5 The only way to determine order is to run the experiment. The method of Initial Rates This method requires that a reaction be run several times. The initial concentrations of the reactants are varied. The reaction rate is measured bust after the reactants are mixed. Eliminates the effect of the reverse reaction. An example For the reaction BrO3- + 5 Br- + 6H+ 3Br2 + 3 H2O The general form of the Rate Law is Rate = k[BrO3-]n[Br-]m[H+]p We use experimental data to determine the values of n,m,and p Initial concentrations (M) Rate (M/s) BrO30.10 0.20 0.20 0.10 Br0.10 0.10 0.20 0.10 H+ 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.20 8.0 x 10-4 1.6 x 10-3 3.2 x 10-3 3.2 x 10-3 Now we have to see how the rate changes with concentration Integrated Rate Law Expresses the reaction concentration as a function of time. Form of the equation depends on the order of the rate law (differential). Rate = D[A]n Dt We will only work with n=0, 1, and 2 Changes First Order For the reaction 2N2O5 4NO2 + O2 We found the Rate = k[N2O5]1 If concentration doubles rate doubles. If we integrate this equation with respect to time we get the Integrated Rate Law ln[N2O5] = - kt + ln[N2O5]0 ln is the natural log [N2O5]0 is the initial concentration. First Order General form Rate = D[A] / Dt = k[A] ln[A] = - kt + ln[A]0 In the form y = mx + b y = ln[A] m = -k x=t b = ln[A]0 A graph of ln[A] vs time is a straight line. First Order By getting the straight line you can prove it is first order Often expressed in a ratio First Order By getting the straight line you can prove it is first order Often expressed in a ratio A 0 ln = kt A Half Life The time required to reach half the original concentration. If the reaction is first order [A] = [A]0/2 when t = t1/2 Half Life • The time required to reach half the original concentration. • If the reaction is first order • [A] = [A]0/2 when t = t1/2 A 0 ln 0 A 2 ln(2) = kt1/2 = kt 12 Half Life t1/2 = 0.693/k The time to reach half the original concentration does not depend on the starting concentration. An easy way to find k Second Order Rate = -D[A] / Dt = k[A]2 integrated rate law 1/[A] = kt + 1/[A]0 y= 1/[A] m=k x= t b = 1/[A]0 A straight line if 1/[A] vs t is graphed Knowing k and [A]0 you can calculate [A] at any time t Second Order Half Life [A] = [A]0 /2 at t = t1/2 1 [ A ]0 2 1 = kt1 2 + [A] 0 2 1 = kt1 2 [ A] 0 [ A] 0 1 [A] 0 = kt1 2 t1 2 = 1 k[A] 0 Zero Order Rate Law Rate = k[A]0 = k Rate does not change with concentration. Integrated [A] = -kt + [A]0 When [A] = [A]0 /2 t = t1/2 t1/2 = [A]0 /2k Zero Order Rate Law Most often when reaction happens on a surface because the surface area stays constant. Also applies to enzyme chemistry. C o n c e n t r a t i o n Time C o n c e n t r a t i o n k = DA]/Dt DA] Dt Time Summary of Rate Laws Reaction Mechanisms The series of steps that actually occur in a chemical reaction. Kinetics can tell us something about the mechanism A balanced equation does not tell us how the reactants become products. Reaction Mechanisms 2NO2 + F2 2NO2F Rate = k[NO2][F2] The proposed mechanism is NO2 + F2 NO2F + F (slow) F + NO2 NO2F (fast) F is called an intermediate It is formed then consumed in the reaction Reaction Mechanisms Each of the two reactions is called an elementary step . The rate for a reaction can be written from its molecularity . Molecularity is the number of pieces that must come together. Unimolecular step involves one molecule - Rate is rirst order. Bimolecular step - requires two molecules - Rate is second order Termolecular step- requires three molecules - Rate is third order Termolecular steps are almost never heard of because the chances of three molecules coming into contact at the same time are miniscule. A A+A 2A A+B A+A+B 2A+B A+B+C products products products products Products Products Products Rate = k[A] Rate= k[A]2 Rate= k[A]2 Rate= k[A][B] Rate= k[A]2[B] Rate= k[A]2[B] Rate= k[A][B][C] How to get rid of intermediates Use the reactions that form them If the reactions are fast and irreversible - the concentration of the intermediate is based on stoichiometry. If it is formed by a reversible reaction set the rates equal to each other. Formed in reversible reactions 2 NO + O2 2 NO2 Mechanism 2 NO N 2O 2 (fast) N 2O 2 + O 2 2 NO2 (slow) rate = k2[N2O2][O2] k1[NO]2 = k-1[N2O2] rate = k2 (k1/ k-1)[NO]2[O2]=k[NO]2[O2] Formed in fast reactions 2 IBr I2+ Br2 Mechanism IBr I + Br IBr + Br I + Br2 I+I I2 Rate = k[IBr][Br] but [Br]= [IBr] Rate = k[IBr][IBr] = k[IBr]2 (fast) (slow) (fast) Collision theory Molecules must collide to react. Concentration affects rates because collisions are more likely. Must collide hard enough. Temperature and rate are related. Only a small number of collisions produce reactions. P o t e n t i a l Reactants E n e r g y Products Reaction Coordinate P o t e n t i a l Activation Energy Ea Reactants E n e r g y Products Reaction Coordinate P o t e n t i a l Activated complex Reactants E n e r g y Products Reaction Coordinate P o t e n t i a l Reactants E n e r g y } Products Reaction Coordinate DE Br---NO P o t e n t i a l Br---NO Transition State 2BrNO E n e r g y 2NO + Br2 Reaction Coordinate Terms Activation energy - the minimum energy needed to make a reaction happen. Activated Complex or Transition State The arrangement of atoms at the top of the energy barrier. Arrhenius Said the at reaction rate should increase with temperature. At high temperature more molecules have the energy required to get over the barrier. The number of collisions with the necessary energy increases exponentially. Arrhenius Number of collisions with the required energy = ze-Ea/RT z = total collisions e is Euler’s number (opposite of ln) Ea = activation energy R = ideal gas constant T is temperature in Kelvin Problems Observed rate is less than the number of collisions that have the minimum energy. Due to Molecular orientation written into equation as p the steric factor. O O O O N Br N Br N Br N Br Br N O Br O N O N Br Br N O Br N O O N Br No Reaction Arrhenius Equation k = zpe-Ea/RT = Ae-Ea/RT A is called the frequency factor = zp ln k = -(Ea/R)(1/T) + ln A Another line !!!! ln k vs t is a straight line Activation Energy and Rates The final saga Mechanisms and rates There is an activation energy for each elementary step. Activation energy determines k. (E /RT) k = Ae a k determines rate Slowest step (rate determining) must have the highest activation energy. This reaction takes place in three steps Ea First step is fast Low activation energy Ea Second step is slow High activation energy Ea Third step is fast Low activation energy Second step is rate determining Intermediates are present Activated Complexes or Transition States Catalysts Speed up a reaction without being used up in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts. Homogenous Catalysts are in the same phase as the reactants. Heterogeneous Catalysts are in a different phase as the reactants. How Catalysts Work Catalysts allow reactions to proceed by a different mechanism - a new pathway. New pathway has a lower activation energy. More molecules will have this activation energy. Do not change DE Heterogenous Catalysts H H Hydrogen bonds to surface of metal. Break H-H bonds H H H H Pt surface H H Heterogenous Catalysts H H H C C H H H H H Pt surface Heterogenous Catalysts The double bond breaks and bonds to the catalyst. H H H C H C H H Pt surface H H Heterogenous Catalysts The hydrogen atoms bond with the carbon H H H C H C H H Pt surface H H Heterogenous Catalysts H H H H C C H H H Pt surface H Homogenous Catalysts Chlorofluorocarbons catalyze the decomposition of ozone. Enzymes regulating the body processes. (Protein catalysts) Catalysts and rate Catalysts will speed up a reaction but only to a certain point. Past a certain point adding more reactants won’t change the rate. Zero Order Catalysts and rate. R a t e Rate increases until the active sites of catalyst are filled. Then rate is independent of concentration Concentration of reactants