* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning objectives
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
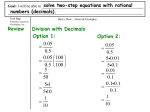
Unit 2 Higher Learning objectives Learning objectives Grade Prime factors find the least common multiple (LCM) of two simple numbers find the highest common factor (HCF) of two simple numbers write a number as a product of prime factors C find the least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers find the highest common factor (HCF) of two or more numbers. B Fractions find one quantity as a fraction of another solve problems involving fractions divide a quantity in a given ratio solve simple ratio and proportion problems, such as finding the ratio of teachers to students in a school add and subtract decimals multiply and divide decimals D add and subtract mixed numbers multiply and divide fractions find the reciprocal of a number solve more complex ratio and proportion problems such as sharing money in the ratio of people’s ages solve ratio and proportion problems using the unitary method round numbers to different degrees of accuracy, decimal places and significant figures recognise that recurring decimals are exact fractions and that some exact fractions are recurring decimals C understand the effect of multiplying and dividing by numbers between 0 and 1 convert recurring decimals to fractions. B Indices and standard index form use the terms square, positive square root, negative square root, cube and cube root recall integer squares from 2 x 2 to 15 x 15 and the corresponding square roots recall the cubes of 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 D use index notation and index laws for positive powers C use index notation and index laws for negative powers convert between ordinary and standard index form numbers use standard index form for calculations involving multiplication and/or division B 1 use index notation and index laws for fractional powers such as 16 2 and 16 0 .5 2 use index notation and index laws for fractional powers such as 8 3 and 8 2 3 A A* Surds rationalise the denominator of a surd simplify surds, such as write (3 - 5 )2 in the form a + b 5 A A* Sequences write the terms of a sequence or a series of diagrams given the nth term D write the nth term of a sequence or a series of diagrams. C Graphs of linear functions draw the graph of a line, such as y = 3x - 5, without being given a table of values solve problems such as finding where the line y = 3x - 5 crosses the line y = 4 D find the gradients of straight-line graphs find the midpoint of a line segment such as the line from A(1, 5) to B(3, 7) C find the gradient and equation of a line through two points such as (0, 3) and (5, 13) find the equation of a line parallel to another line, such as y = 3x - 5, passing through a given point, such as (1, 4). B Percentages increase or decrease by a given percentage express one quantity as a percentage of another D work out a percentage increase or decrease C understand how to use successive percentages work out reverse percentage problems. B Working with symbols expand brackets such as 4(x - 3) factorise an expression such as 6x + 8 D expand and simplify an expression such as 3(3x - 7) - 2(3x + 1) C expand and simplify two brackets such as (x - 3)(x + 5) expand and simplify two brackets such as (3x + 1)(2x - 3) B simplify fractions such as x x 2( x 1) 2 + and 3 5 x 1 Equations and inequalities solve an equation such as 3x + 2 = 6 – x or 4(2x – 1) = 20 represent and interpret inequalities on a number line solve an equation such as 4 x 5 3( x 4) or 2x 7 x x 9 or 1 2 8 4 D C solve an inequality such as 2x - 7 < 9 find the integer solutions of an inequality such as -8 < 2n ≤ 5 2x 1 x 3 5 6 3 2 solve an inequality such as 3x + 2 ≤ 4 - x represent linear inequalities in two variables, such as x + y < 7, as a region on a graph. solve an equation such as B Formulae substitute numbers into formulae such as ( A 1) C= 9 derive complex expressions and formulae distinguish between an expression, an equation, an identity and a formula D rearrange linear formulae such as XXX C rearrange formulae involving brackets, indices, fractions and square roots B rearrange formulae where the variable appears twice. A Real life graphs interpret real-life graphs find simple average speed from distance–time graphs recognise from a distance–time graph when the fastest average speed takes place D find the average speed in km/h from a distance–time graph with time in minutes C discuss and interpret graphs modelling real situations. B Quadratic graphs solve a problem using step by step deductions C factorise an expression such as x2 - 5x + 14 or x2 - 9 solve an equation such as x2 - 5x + 14 = 0 B factorise an expression such as 3x2 + 7x + 2 or 3x2 - 27 A x 3x 2 2 simplify an expression such as by factorising x2 1 solve an equation such as 3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0 by factorising derive a proof using reasoning and logic 3 4 2 x 2 x 1 solve an equation such as x2 - 8x + 11 = 0 by completing the square. solve an equation such as A* Simultaneous equations solve a pair of simultaneous equations such as x + 3y = 9 and 3x - 2y = 5 B solve a pair of simultaneous equations such as y = 4x + 5 and y = x2 A solve a pair of simultaneous equations such as x + 2y = 1 and x2 + y2 = 29 A*