* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
War Front: Turning Point wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
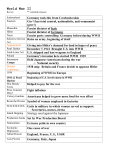
Study Guide World War II --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------You are responsible for the following terms: 1. atomic bomb: Type of bomb built 8. Battle of Stalingrad: unsuccessful during WWII that was the most powerful German attack on the city of yet. Stalingrad during World War II, from 1942 to 1943 that was the farthest 2. Battle of the Bulge: WWII battle in extent of German advance into the December 1944 between Germany and Soviet Union. Allied troops that was the last German 9. Lend-Lease: Policy that allowed offensive in the West. General George Britain to borrow military supplies S. Patton led the Allies to victory. from the United States during World War II. 3. fascism: form of government in which individual freedoms are denied and the government has complete power. 4. dictator: leader with complete control of a country’s government 5. Manhattan Project: code name given to the effort to build an atomic bomb in the United States. 6. World War II: War fought from 1939 to 1945 between the Allies and the Axis, involving most of the countries in the world. The United States joined the Allies in 1941, helping them to victory. 7. Battle of Midway: World War II naval battle between the United States an Japan in 1942 that weakened the Japanese threat in the Pacific 15. concentration camp: prison in which the Nazis enslaved and murdered Jews and other people during World War II. 10. Holocaust: murder of about 12 million people, including 6 million Jews, by Nazis during World War II. 11. rationing: government limiting of the amount of food each person in the United States could buy during World War II 12.Tuskegee Airmen: first African American fighter pilots. 13. D-Day: Normandy invasion 14. V-E Day: The day of the Allied Victory in Europe 16. V-J Day: Japan surrenders on T-Chart Allies 1. 2. 3. 4. Axis United States Great Britain France Soviet Union 1. Germany 2. Italy 3. Japan People 17. Franklin D. Roosevelt: President during World War II and he died before the war ended. 18. Adolf Hitler: German, Nazi dictator during WWII. 20. Douglas McArthur: General who commanded U.S forces in South Pacific during WWII. 21. Harry Truman: Became president when FDR died at the end of WWII. 19. Joseph Stalin: Dictator in Soviet 22. Dwight Eisenhower: Commander of Union during WWII-he was a communist. Allied forces during World War II and later becomes President of the U.S. 23. Why did Great Britain and France declare war on Germany? They declared war on Germany because they invaded Poland. 24. What event caused the United States to enter World War II? The bombing of Pearl Harbor? December 7, 1941. 25. What effect did WWII have on the U.S. economy? It helped bring us out of the Great Depression and created many new jobs for Americans. 26. Where did the first African American fighter pilots begin training? They were trained at the Tuskeegee Institute in Tuskeegee, Alabama 27. What did Executive Order #9066 state? It stated that all Japanese Americans that were seen as a threat would be moved into internment camps. 28. What was the Manhattan Project? The code name given to the project in which the atomic bomb was built. 29. After which battle did Japan’s navy become too weak to continue capturing islands in the Pacific? The Battle of Midway. 30. After which battle was Germany forced to retreat from the Soviet Union? Battle of Stalingrad. 31. Where did the largest sea invasion in world history take place? Normandy, France. 32. How did the use of atomic bombs impact the outcome of World War II? It helped the U.S. have victory of Japan. 33. Why were Japanese-Americans put in internment camps in WWII? Because our government did not trust them after the bombing of Pearl Harbor and they were seen as a possible threat. 34. Why could very few people in the world break the Navajo code? Because the Navajo language was known by very few people and was not a written language. 35. Why did the Great Depression end when the United States entered WWII? It ended then because factories were creating machines and products for war, which provided jobs for many Americans and improved the economy. 36. Why did the United States ration goods during WWII? Name two goods that were rationed. Goods were rationed because we wanted to make sure our soldiers could have goods…two things that were rationed are: Bread and Cheese. 37. Why did the United States drop the atomic bomb on Japan instead of invading by land? Japan is an island and easier to attack from the sea or from the sky.