* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protection and control HV/MV substation Sepam
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Protective relay wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Residual-current device wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
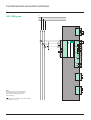
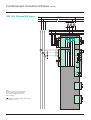
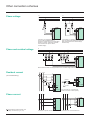
Protection and control HV/MV substation Sepam 2000 Substation Presentation Contents HV MV The protection and control of primary substations consists of performing the metering, protection, control and monitoring functions required for operation. Sepam 2000 provides all these functions globally. All the equipment and mechanisms that are generally found in a MV cubicle control cabinet are replaced by a single device which performs: c protection, c metering, c control and monitoring implementing protections and logic inputs to activate tripping and closing outputs and the display of annunciation. page presentation selection table metering protection control and monitoring functional and connection schemes other connection schemes connection of logic inputs/outputs communication characteristics installation ordering information 2 3 4 6 8 11 13 14 16 17 18 20 Advantages c Indication of phase and earth fault values at the time of breaking provides the operator with useful assistance in determining the causes and seriousness of faults. c The high level of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) makes it possible to use advanced digital technology-based functions in electrical substations, without the need for any particular precautions. c Sepam 2000’s continuous self-testing sets the device in a predetermined fail-safe position whenever a failure occurs, thereby preventing random operation. c Terminals that are individually disconnectable while energized allow easy maintenance. c The communication function option can be used for remote setting, remote metering, remote annunciation and remote control via a two-wire link with a central computer for centralized control. c Setting and testing are extremely simple: direct readout of primary current and voltage and simple testing of the metering function by injection guarantee the coherency of all settings. c Each Sepam is designed to meet all the application needs and includes all the necessary functions ready for use (protection, metering, program logic and annunciation). The program logic can be adapted for the usual schemes by simple parameter setting at the time of commissioning. This allows optimization of cables and more dependable operation (the schemes have been qualified and specified to take into account the most frequent needs). The extended setting ranges provide for the widest variety of cases. c The disturbance recording function allows up to 12 analog signal and 32 logical signals to be recorded. Sepam 2000 standard S36. Installation in the switchboard is simplified: c just one device to install, the Sepam 2000 S36 (standard), c cabling is limited to: v standard 1 A or 5 A current transformers or linear CSP sensors (Rogowski coil), v voltage transformers, v control and annunciation units (open/close push-button...), v actuators (tripping and closing coils). Customization Standard control and monitoring carried out in Sepam’s internal PLC can be customized. 2 Substation Selection table functions protection breaker failure phase overcurrent earth fault undervoltage overvoltage neutral voltage displacement directional overcurrent directional earth fault metering phase current (I1, I2, I3) max. demand phase current (I1, I2, I3) voltage (U21, U32, U13) real / reactive power (P, Q) peak demand real / reactive power power factor frequency real / reactive energy (±Wh, ±VArh) tripping currents (I1, I2, I3, Io) true rms current disturbance recording residual current residual voltage cumulative breaking current and number of breaks control and monitoring open / close lockout relay inhibit closing annunciation CB control monitoring upstream & coupling breaker tripping external protection tripping external disturbance recorder triggering disturbance recording triggering power supply monitoring detection of plugged connectors fault counter logic discrimination cycle counter Sepam models standard S36 number of standard ESTOR boards ANSI code 50BF/62 50/51 50N/51N 27 59 59N 67 67N types of Sepam S61 S62 4 4 S64 S65 S66 4 4 1 1 4 4 1 1 4 4 1 4 4 1 4 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c YR 2 XR 2 c c c c c 86 69 30 74 S63 c c c c c 1 1 c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c c XR 2 XR 2 YR 2 XR 2 c The figures in the columns represent the number of similar protection devices. Examples: for phase overcurrent protection, “4” means 4 separate 3-phase protection devices. Substation 3 Metering Sepam 2000 is a precision instrumentation device. It gives a direct readout of values, together with the related units, A, V, W... All the values needed for operation and used for commissioning are available locally and in the control room. Measurements needed for operation Currents Measurement of the current for each of the 3-phases of the circuit. Peak demand current Measurement of the greatest average current value in the 3 phases, used to find the current demand during peak load periods. The average current measurement is reset to zero periodically (adjustable period: 5, 10, 15, 30 or 60 minutes). The “clear” button is pressed for zero reset. Voltage Measurement of the 3 phase-to-phase voltages of the circuit. Real / reactive power Measurement of the real and reactive power, with the sign, in balanced and unbalanced 3-phase networks. Peak demand real / reactive power Measurement of the greatest average real power (and reactive power) value, to find the power absorbed during peak load periods. The average value is reset to zero periodically periodically (adjustable period: 5, 10, 15, 30 or 60 minutes). The “clear” button is pressed for zero reset. Power factor (p.f.) Measurement of the p.f. with the sign and type (capacitive or inductive) of the power conveyed. Measurements available on the Sepam display unit and on the TSM 2001 pocket terminal. Frequency Measurement of frequency (based on the U21 voltage input). Real and reactive energy The alphanumeric display unit shows the 4 accumulated energy values: c real energy consumed, c reverse real energy, c reactive energy consumed, c reverse reactive energy. The accumulated energy values are saved in the event of a power failure. Tripping currents Measurement of the 3-phase currents and earth current that were stored at the time that Sepam gave the tripping order. Used to find the fault current (fault analysis) and assess the level of wear of the breaker (maintenance assistance). The “clear” button is pressed for zero reset. Measurements available on the Sepam display unit and a PC via SFT 2801 software. True rms current Measurement of the rms value of phase 1 current up to 4XIn, taking into account: c fundamental, c harmonics up to rank 21st. Disturbance recording Recording of electrical signals and logical information before and after a fault recorder triggering order is given. 4 Substation Measurements used for commissioning and maintenance Characteristics functions ammeter (1) peak demand current Residual current / residual voltage Used to check the current and voltage sensor connections by giving the measurement of: c the residual current used for the earth fault protection function, c the voltage used for the neutral voltage displacement and directional earth fault protections. voltmeter Cumulative breaking current and number of breaks Used for breaking device maintenance. frequency meter wattmeter varmeter (1) (1) (1) (1) peak demand real power (1) peak demand reactive power power factor real energy (1) (1) (3) (1) (1) reactive energy accuracy 0 to 24 In ±0.5% 0 to 24 In ±0.5% 0 to 375 kV ±0.5% 0 to 999 MW ±1% 0 to 999 MVAr ±1% 0 to 999 MW ±1% 0 to 999 MVAr ±1% -1 to +1 0.01 45 to 65 Hz ±0.02 Hz 0 to 280.106 MWh ±1% 0 to 280.10 MVArh ±1% phase 0 to 24 In ±5% earth 0 to 10 Ino ±5% 0 to 4 In ±1% (1) tripping currents ranges 6 (1) true rms current up to harmonic 21 (2) disturbance recording (5) 12 samples per period residual current (2) 0 to 10 Ino ±5% residual voltage (2) 0 to 1.5 Un ±5% 0 to 9999 (kA)2 ±10% cumulative breaking current (2) number of breakers (2) (4) 0 to 99999 (1) indication available on the Sepam display unit or the pocket terminal. indication available on the pocket terminal only. (3) capacitive or inductive. (4) typical accuracy with nominal values according to IEC 60255-6. (5) transfer of records with SFT 2801 software. Use of records with SFT 2826 software. (2) Reminder: The rated current In, rated voltage Un and residual current Ino are general parameters that are set at the time of Sepam commissioning. In is the current sensor rated current (CT rating). Ino is the residual current sensor rated current. Un is the rated phase-to-phase voltage of the voltage sensor primary windings. Substation 5 Protection Breaker failure (ANSI 50BF-62) F981* Back up protection in the event that the incoming breaker fails to operate when a retripping order is given by the opposite and coupling breakers. Phase overcurrent (ANSI 50/51) F011 to F014* Three-phase protection against phase-to-phase faults. The following types of time delay settings are available: definite, standard inverse, very inverse and extremely inverse. Overvoltage (ANSI 59) F301* Protection against abnormally high voltage. The protection checks phase-to-phase voltage U21. Neutral voltage displacement (ANSI 59N) F391* Used with a sufficient time delay, detection of residual voltage is characteristic of voltage transformer fuse melting. Directional overcurrent (ANSI 67) F521* Quick, selective detection of upstream faults when several transformer incoming feeders are used in parallel. Earth fault (ANSI 50N/51N) F081 to F084* Earth fault protection. The following types of time delay settings are available: definite, standard inverse, very inverse and extremely inverse. Earth fault current may be detected by: c three phase current transformers, c a current transformer (1 A, 5 A) combined with a CSH30 interposing ring CT. Directional earth fault (ANSI 67N) F501* This function has several uses: c highly sensitive earth fault protection for in coming feeders supplied with power by a long cable (high capacitive current), c highly sensitive earth fault protection for long incomers characterized by high capacitive current. Undervoltage (ANSI 27) F321, F341, F361* This function checks for undervoltage in each of the phase-to-phase voltages measured. Current sensor sizing *Fxxx function identification for protection setting using the pocket terminal. 6 The current sensors should be such that they will not be saturated by the current values which they are required to measure (at least 5 In): c for definite time functions (DT): 1.5 times the setting current, c for IDMT functions (SIT, VIT, EIT and UIT): 1.5 times the greatest working value in the curve. Substation Setting ranges functions Fxxx (1) breaker failure F981 phase overcurrent F011-F012-F013-F014 definite time IDMT (2) earth fault settings time delays 0.2 to 2 In t : 0.05 to 65.5 s 0.3 to 24 In t : 0.05 to 655 s 0.3 to 2.4 In F081-F082-F083-F084 t : 0.1 to 12.5 s at 10 Is type of sensor definite time 0.05 to 10 In 0.1 to 20 A 1.5 to 300 A 0.05 to 10 Ino ∑3 Iph CSH cal. 2 A CSH cal. 30 A TC 1 A or 5 A t : 0.05 to 655 s IDMT (2) 0.05 to 1 In 0.1 to 2 A 1.5 to 30 A 0.05 to 1 Ino ∑3 Iph CSH cal. 2 A CSH cal. 30 A TC 1 A or 5 A t : 0.1 to 12.5 s at 10 Iso undervoltage F321-F341-F361 overvoltage F301 neutral voltage displacement F391 directional overcurrent F521 5% to 100% of Un t : 0.05 to 655 s 50% to 150% of Un t : 0.05 to 655 s 2% to 80% of Un if TP : Un/e/100/e 5% to 80% of Un if TP : Un/e/100/3 t : 0.05 to 655 s characteristic angle 30°, 45°, 60° definite time 0.3 to 24 In t : 0.05 to 655 s IDMT 0.3 to 2.4 In t : 0.1 to 12.5 s at 10 Is directional earth fault IDMT F501 characteristic angle 0°, 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90° and -45° 0.05 to 10 In 0.1 to 20 A 1.5 to 300 A 0.05 to 1 Ino ∑3 Iph CSH cal. 2 A CSH cal. 30 A TC 1 A or 5 A t : 0.05 to 655 s Reminder: the rated current In, rated voltage Un and residual current Ino are general parameters that are set at the time of Sepam commissioning. In is the current sensor rated current (CT rating). Un is the rated phase-to-phase voltage of the voltage sensor primary windings. Ino is the residual current sensor rated current. (1) function identification for protection setting using the pocket terminal. (2) IDMT curves: - inverse: SI - very inverse: VI, - extremely inverse: EI, - ultra inverse: UI, - long time inverse: LTI. Substation 7 Control and monitoring Open / close control Used to control breaking of devices equipped with different types of opening and closing coils: c circuit breaker with shunt-trip or undervoltage release coil. c parameter setting via the TSM 2001 pocket terminal allows the logic to be adapted to suit the equipment being used (by default, the logic is adapted for control of a circuit breaker with a shunt-trip coil). The opening order (via input I13) differs according to the programmed type of control : c normally open contact for shunt trip coil (circuit breaker or contactor with latched order control), c normally closed contact for undervoltage release coil (circuit breaker). Lockout relay (ANSI 86) Stores tripping orders (lockout) and requires user action to be put back into operation (reset). Inhibit closing (ANSI 69) Inhibits the closing of the circuit breaker or the contactor according to operating conditions. Annunciation (ANSI 30) Keeps the user informed by the display of messages. CB control monitoring: trip circuit, discrepancy (ANSI 74) Detects trip circuit faults (shunt-trip coil). The function can only be used if the Sepam and trip circuit auxiliary power sources have the same voltage rating. If the equipment contains an undervoltage release coil only, the trip circuit is not supervised since it is fail-safe. This function can also detect position information discrepancies (neither open nor closed or simultaneously open and closed) in the different control schemes. This function can also detect all control open and closed not executed. The connection scheme of inputs I1, I2 and trip output O1 on the ESB board must be complied with (see logic input (output connection schemes). 8 Tripping of upstream (HV) and couling breakers In the event of the failure of an incomer breaker to trip, it trips the upstream (HV) and coupling breakers. May also be used to trip the upstream (HV) breaker in the event of directional protection tripping. External protection tripping Allows the breaker to be tripped by a protection outside the Sepam. External disturbance recording triggering Used to start up external disturbance recording whenever an overcurrent or earth fault is detected. Sepam disturbance recording triggering Triggers recording of electrical signals and logical states by: c voluntary local or remote action, c instantaneous overcurrent and earth fault and directional protections, c protection tripping order. Power supply monitoring Detects all losses of auxiliary power supply or Sepam failures (watchdog). Detection of plugged connectors (DPC) (ANSI 74) Indication on the display unit that one or more connectors are not plugged in (the DPC connections must be made: see connection schemes). Phase and earth fault trip counter (1) Counts the number of operation for which breaking performances are required, in order to facilitate equipment maintenance. Logic discrimination (SSL) (ANSI 68) Enables quick and selective tripping of the phase overcurrent and earth fault protection relays, whether definite time (DT) or IDMT (standard inverse SIT, very inverse VIT, extremely inverse EIT, ultra inverse UIT). The function triggers the transmission of a blocking input (BI) signal whenever one of the protection settings is exceeded. The transmission of a blocking input may be used by the Sepam Logic Discrimination function for substation, overhead, underground or busbar coupling applications. Operation counter (1) Counts the number of closing operations performed by the breaking device, in order to facilitate equipment maintenance. (1) the counters are read on the pocket terminal. Substation Operation functions trip inhibit closing lock out O1 O11 fault trip O12 trans. BI O14 ext. dist. rec. trig. O23 messages c c c OVERCURRENT c c O13 phase overcurrent c c c earth fault c c c c EARTH FAULT directional overcurrent c c c c (1) c c DIR. O/C directional earth fault c c c c (1) c c DIR. E/F c c (2) neutral voltage displacement c c pole pressure c c c PRESSURE CB control c c c ?CONTROL? external tripping functions c N VOLT DISP EXT. TRIP inhibit closing lock out O11 c c c overvoltage (1) (2) O22 O24 c undervoltage HV upstream and coupling breaker tripping O21 messages UNDERVOLTAGE c CB FAULT c OVERVOLTAGE HV tripping by directional phase overcurrent and earth fault protections S62, S63, S66 application. S64 application. Substation 9 Control and monitoring (cont’d) Set up function open / close control circuit breaker with shunt-trip coil circuit breaker with undervoltage release coil display of parameterized control breaker failure protection breaker fault in service protection breaker fault out off service enable current monitoring by-pass disable current monitoring by-pass HV tripping by normally open contact by normally closed contact HV up stream breaker tripping by normally open contact by normally closed contact coupling breaker tripping by normally open contact by normally closed contact directional phase overcurrent tripping if at least one of the three phases is above the set point tripping if at least two of the three phases are above the set point receipt of blocking input normal fail-safe transmit of blocking input normal fail-safe pilot wire test external protection tripping by normally open contact by normally closed contact remote setting remote setting enable remote setting disable event counter resetting of fault counter resetting of operation counter disturbance recording storage automatic triggering manual triggering 10 parameters KP1 = 0 KP1 = 1 KP17 = 1 KP2 = 0 KP2 = 1 KP3 = 0 KP3 = 1 KP5 = 0 KP5 = 1 KP6 = 0 KP6 = 1 KP7 = 0 KP7 = 1 KP33 = 0 KP33 = 1 KP9 = 0 KP9 = 1 KP10 = 0 KP10 = 1 KP18 = 1 KP4 = 0 KP4 = 1 KP38 = 0 KP38 = 1 KP49 = 1 KP53 = 1 KP50 = 1 KP51 = 1 KP52 = 1 Substation Functional and connection schemes S61, S65 types L1 L2 L3 CE40 1B 1 2 3 1A 4 P1 S1 4 1 P2 S2 5 2 2B ECM 6 3 6 5 4 3 2 1 50 51 50N 51N 50BF L65 ESB 5A 21 DPC 20 CDG 2A DPC O2 O1 l2 l1 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ESTOR1 6A 21 1 ESTOR2 7A 21 N.B. Refer to the «other connection schemes» section regarding other arrangements. DPC: detection of plugged connectors CDG: watchdog 1 ■ Correspondence between primary and secondary connections (e.g. P1, S1). Standard S36YR Sepam 2000. Substation 11 Functional and connection schemes (cont’d) S62, S63, S64 and S66 types L1 L2 L3 N L1 L2 L3 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 4 1 4A 3U/Vo DPC 2B ECM 5 2 59N 27 L64 59 L62 L63 L66 67N 67 L62 L63 L63 L66 L66 CE40 1 2 3 1A 4 50 50BF 51 S66 50N 51N ESB 5A 21 DPC 20 6 3 6 5 4 3 2 1 1B CDG 2A DPC O2 O1 l2 l1 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ESTOR1 6A 21 1 N.B. Refer to the «other connection schemes» section regarding other arrangements. DPC: detection of plugged connectors CDG: watchdog. ESTOR2 7A 21 ■ Correspondence between primary and secondary connections (e.g. P1, S1) 1 Standard S36XR Sepam 2000. 12 Substation Other connection schemes Phase voltage L1 L1 L2 L2 L3 L3 3U/Vo A 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Connection of a voltage transformer (does not allow implementation of protections: positive sequence undervoltage, direction of rotation, directional earth fault and measurements: phase rotation, residual voltage). Phase and residual voltage 3U/Vo A 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DPC DPC V-connection of 2 voltage transformers (does not allow implementation of directional earth fault protection and residual voltage measurement). L1 L2 L3 3U/Vo A 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DPC Broken delta connection of voltage transformers for residual voltage measurement. Residual current L1 L2 L3 4 1 (recommended wiring) 2B ECM 5 2 CSH30 P1 S2 6 3 6 5 4 3 2 1 CSH30 Phase current P2 2A DPC 30 A 2A TC+CSH30 L1 L2 L3 1 S1 ECM A 6 5 4 3 2 1 DPC 30 A 2A TC + CSH30 5 turns For connection of 1 A transformers, make 5 turns at the CSH30 primary. L1 L2 L3 CCA 601 cable L1 2L1 2L2 2L3 L2 L3 ECA 4 1 B ECM 5 2 6 3 A c Correspondence between primary and secondary connections (e.g. P1, S1). Substation Connection of specific sensors CSP. Connection of 2 current transformers. 13 Other connection schemes (cont’d) Connection of logic inputs / outputs ESB board ESB DPC CDG O2 O1 l2 l1 A 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ESB DPC CDG O2 closing coil open Tripping by shunt-trip coil. O1 tripping coil l2 l1 A 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 closing coil open tripping coil Tripping by undervoltage release coil. N.B. The inputs are potential-free and require an external power supply source. 14 Substation ESTOR1 board ESTOR A DPC l28 l27 l26 l25 l24 l23 O24 O23 O22 O21 l22 l21 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 terminals 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 data connected to ESTOR1 board I18 enable remote control: allows closing and acknowledgment orders to be sent via the serial link: contact closed for enable I17 “disconnected” position: contact closed for disconnected I16 pole pressure: contact closed for breaking pole fault I15 external protection tripping: normally open or normally closed contact according to parameter setting I14 close: normally open contact I13 open: normally open contact for shunt-trip coil, normally closed contact for undervoltage release coil (1) common O14 transmit BI (blocking input) O13 breaker failure (pressure fault or control fault) O12 fault tripping O11 neutral voltage displacement (2) HV tripping up stream breaker receipt of BI (blocking input) from the busbar adjacent to incomer (3) receipt of BI (blocking input) from the busbar adjacent to the coupling I12 I11 (3) (1) if open control via input I13 is not used: c for shunt-trip coil, I13=0 continuously. c for undervoltage release coil, I13=1 continuously. ESTOR2 board ESTOR DPC l38 l37 l36 l35 l34 l33 O34 O33 O32 O31 l32 l31 A 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 terminals 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 (2) data connected to ESTOR2 board I28 reserved I27 reserved I26 3-phase tripping by external protection information I25 position of the coupling circuit breaker: contact closed for closed and racked in I24 HV tripping I23 earthing switch: contact open for earthing switch open common O24 overvoltage O23 external disturbance recorder triggering O22 coupling circuit breaker tripping O21 undervoltage I22 fault acknowledgment I11 reserved for external communication synchronization application S64. (3) incomer coupling Bus incomer adjacent other Bus coupling adjacent N.B. The inputs are potential-free and require an external power supply source. Substation 15 Communication Introduction The communication option can be used to connect Sepam 2000 to a remote monitoring and control system equipped with a communication channel. c Jbus/Modbus (Modbus sub-group), master-slave protocol with a physical link of the RS485 type in 2-wire mode (rate of 300 to 38400 bauds). MERLIN GERIN Communication table remote indications addresses logic inputs status logic outputs status operation counter C1 phase fault trip counter C2 addresses open KTC33 close KTC34 fault acknowledgment (RESET) KTC35 max. demand phase current reset (CLEAR) KTC36 earth fault trip counter C3 KTS1 peak demand W and VAR reset (CLEAR) KTC37 control fault: trip or discrepency instantaneous phase overcurrent KTS2 tripping current reset (CLEAR) KTC38 KTS3 disable disturbance recording KTC50 KTS4 re-enable disturbance recording KTC51 time-delayed earth fault KTS5 start up disturbance recording KTC52 instantaneous directional phase overcurrent KTS6 remote measurements time-delayed directional phase overcurrent KTS7 instantaneous directional earth fault KTS8 time-delayed directional earth fault KTS9 system overvoltage KTS10 external protection tripping KTS11 upstream and coupling breaker tripping KTS13 remote control fault disable KTS15 position/remote control discrepancy KTS16 Sepam not reset KTS17 HV tripping KTS19 breaking pole fault KTS20 logic discrimination (SSL) fault KTS22 time-delayed phase overcurrent instantaneous earth fault 16 remote control orders frequency real power reactive power neutral voltage displacement KTS28 undervoltage KTS30 transmit blocking input KTS32 disturbance recording storage KTS50 remote setting inactive KTS51 peak demand real power peak demand reactive power power factor (p.f.) inductive or capacitive network real energy reactive energy tripping current remote reading - remote setting protection function curves, set points, time delays, angles... program logic time delays Substation Characteristics Electrical characteristics analog inputs current transformer 10 A to 6250 A ratings 1 A CT 5 A CT < 0.001 VA < 0.025 VA voltage transformer 220 V to 250 kV ratings 100 to 120 V > 100 kW voltage 24/30 Vdc 28/127 Vdc 220/250 Vdc consumption 10 mA 10 mA 4 mA voltage 24/48 Vdc 127 Vdc 220 Vdc rated current 8A 8A 8A DC resistive load 4A 0.7 A 0.3 A AC resistive load 8A 8A 8A logic inputs logic outputs (relays) breaking capacity: auxiliary power supply DC voltage 24/30 Vdc 48/127 Vdc 220/250 Vdc consumption when de-activated 18 W 19.5 W 21 W Environmental characteristics dielectric power frequency IEC 60255-5 2 kV - 1 mn IEC 60068-2 - 5 °C to 55 °C climatic operation storage IEC 60068-2 - 25 °C to 70 °C damp heat IEC 60068-2 95% at 40 °C effect of corrosion IEC 60654-4 class I degree of protection IEC 60529 IP 51 vibrations IEC 60255-21-1 class I shocks IEC 60255-21-2 class I fire IEC 60695-2-1 mechanical on front panel glow wire electromagnetic radiation IEC 60255-22-3 class X electrostatic discharge IEC 60255-22-2 class III 30 V/m electrical 1.2/50 µs impulse wave IEC 60255-5 1 MHz damped oscillating wave IEC 60255-22-1 class III 5 ns fast transients IEC 60255-22-4 class IV “ Substation 5 kV ” marking on our products guarantees their compliance with European directives. 17 Installation Dimensions and weights mounting latches (x2) 222 201 e = 3 mm max 20 300 Standard Sepam (S36) Cut-out 222 202 338 352 weight: 9 kg Connections Sepam (S36) rear face with standard connectors. type wiring accessories reference type current transformers screw for Ø 4 eye lug i 6 mm2 CCA 660 (1) connector CSH sensors screw i 2.5 mm2 CCA 606 (1) connector voltage transformers screw i 2.5 mm 2 CCA 608 (1) connector temperature probes screw i 2.5 mm2 CCA 621 (1) connector logic inputs / outputs screw i 2.5 mm2 CCA 621 (1) connector power supply screw i 2.5 mm2 CCA 604 (1) connector CCA 602 cable (length: 3 m) with 2 9-pin sub-D connectors CCA 619 9-pin sub-D connector box Jbus / Modbus communication 9-pin sub-D connector (1) 18 accessories supplied with Sepam. Substation Notes Substation 19 Ordering information Sepam 2000 Sepam type (1) ............................................................................................. Standard S36 ........................................................................................................... Quantity ....................................................................................................... (1) example : S61 Options Communication ......................................................... without ............................... ..................................................................................... Jbus/Modbus ..................... Working language ..................................................... French ............................... ..................................................................................... English .............................. ..................................................................................... Spanish ............................. ..................................................................................... Italian ................................ Current sensors ......................................................... 1 A/5 A CT ......................... ..................................................................................... CSP ................................... Auxiliary power supply ............................................. 24/30 Vdc .......................... ..................................................................................... 48/127 Vdc ........................ ..................................................................................... 220/250 Vdc ...................... Accessories quantity Pocket terminal ............................................................ TSM 2001 ............. Setting software with PC connection kit ..................... SFT 2801 .............. Disturbance recording record processing software .................................................... SFT 2826 .............. Core balance CT ......................................................... CSH 120 ................ ..................................................................................... CSH 200 ................ Interposing ring CT for residual current input ............................................................................. CSH 30 .................. Jbus/Modbus communication c 9-pin sub-D connector box ....................................... CCA 619 ................ c Jbus/Modbus network connection box .................... CCA 609 ................ c cable (length: 3 m) with two 9-pin sub-D connectors ................................. CCA 602 ................ c RS485/RS232 interface box .................................... ACE 909 ................ Schneider Electric SA Postal address F-38050 Grenoble cedex 9 Tel: 33 (0)4 76 57 60 60 Telex: merge 320842 F http://www.schneider-electric.com Rcs Nanterre B 954 503 439 PCRED397087EN 20 ART.086642 As standards, specifications and designs change from time to time, please ask for confirmation of the information given in this publication. This document has been printed on ecological paper. Publishing: Schneider Electric SA Design, production: Idra Printing: Substation 07 / 1998