* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War Notes`12
Ex parte Merryman wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Photographers of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
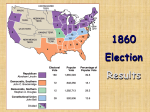
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
The Civil War (1861 – 1865) The immediate or primary cause was the firing on Fort Sumter an island fortress in the harbor of Charlestown, South Carolina that was held by U.S. forces. The South wanted the fort to be surrendered to the South. Lincoln refused and the war began. A. Advantages North (Union) their advantages South (Confederacy) 1. Population (2x’s the South’s) 1. Strategic Position –So. held defensive 22 mil 1860 to 9mil (6mil free, 3 mil slaves) positions. No. was forced to attack. 2. Economic Resources Industrialized = war materials So.=agric----cotton, no food. 2. Preparation for War So. well trained in warfare. No need for Training. 3. Political Leadership Lincoln better able than Jefferson Davis 3. Military Leadership Superior Generals like Robert E. Lee and Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson 4. Foreign Relations US already recognized So. struggled for recognition 4. Morale - fighting to protect their homeland made a better fighting spirit. 5. Naval Superiority So. had few ships No set up blockade B. Turning Points 1861-1862 battles went to the South, but by 1863 the tide had changed 3 particular battles 1. Battle of the Ironclads – iron plates put on sides of ships. The South captured the Merrimac, which was iron reinforced and renamed the Virginia. Was able to break the blockades. The North’s ironclad = the Monitor challenged the Va. And resulted in a draw. This strengthened future blockades. No more wooden ships. 2. Battle of Gettysburg (1863) July 1 to 3 General Robert E. Lee tries to route North’s troops @ Gettysburg Pa. This offensive turned bad for the South---7,000 deaths. North begins a draft to replace lost soldiers. 3. Siege at Vicksburg (1863) July 4th (One day later) Gen. Ulysses S. Grant takes control of the South’s river fortress and now controls the Mississippi River dividing the Confederacy in two. C. Final Campaigns 1. Sherman’s March to the Seas - North’s General William T. Sherman marched eastward and deliberately burned the homes of civilians as an act of policy, “war is hell,” he said. Forced Lee to surrender to protect civilians. 2. Surrender @ Appomattox April 2, 1865 Lee surrenders in a Va. Court house D. Lincolns Leadership Apr 1865 he started his second term but was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth, actor + Southern sympathizer. Booth was hope to reignite the war. Lincoln’s Strengths 1. His firm political purpose - preserving the Union was paramount. He made all his decisions with this in mind. 2. His Political Shrewdness and Courage- used his political shrewdness to his advantage---chose an excellent General (U. Grant) 3. His Decision to Emancipate Slaves “Emancipation Proclamation (1862 following Battle at Antietam. Issued 1/1/1863) 4. As a great Orator -his speeches such as the Gettysburg Address, spoke eloquently of democratic ideals. 5. His executive decisions – because Congress was not in session. Lincoln did the following: a. Suspended the Writ of Habeas Corpus in order to keep the insurrections of the pro-slavery people down in the border states. Ex Parte Milligan (1866) treasonists must be tried in civilian courts. b. Imposed a Draft (1863) to replenish the heavy losses at Gettysburg 6. As Commander and Chief a. Fort Sumter (1861) the South held control of all federal forts except for 3, Sumter being one. Lincoln sent “provisions” instead of “reinforcement”, but still caused South Caroline to be the aggressor, keeping the border states with Union. b. Increased the size of the army by appropriating $2million. c. Naval Blockade which kept the British at bay, suffocated the South, kept the border states loyal to the Union. 7. His economic policies – a shift from agriculture to industrialization helped the North win this “war of attrition”. a. Morrill Tariff Act (1863) – high protective tariff that raised revenue to pay for war costs. b. National Banking System (1863) later becomes the Federal Reserve (1913) establishes a single national currency, “Greenbacks” c. 1862 began to build the trans-continental railroad. Completed in 1869. E. Results of the War 1. Union remained intact. 2. Slavery was abolished (13th Amendment) 3. Freedmen gained citizenship and voting rights (14th and 15th Amendments) 4. The first Civil Rights laws were passed. 5. 620,000 deaths (360,000 Union / 260,000 Confederacy) In 1861 = 2% of the population, (Todays population would be 6 million deaths). F. African- Americans Women Not allowed to enlist until late in the war. Replaced men in industrial jobs Post 1863 – segregated units 180,000 join Battlefield nurses 38,000 die / 22 win the Medal of Honor Made nursing a respectable job Increased: black respect, literacy, +leadership Clara Barton / Dorothea Dix Later the Red Cross 1877