* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sheep Heart Dissection
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
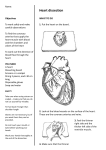
Name:___________________ KEY Per:____ Date:____________ Sheep Heart Dissection Learning Goal/Question: You will observe the outside and inside of a sheep heart to locate and label the parts of a heart, including blood vessels, chambers and valves. You will also study the direction of blood flow through the heart, including oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Collect Info: Your heart is a muscle that can push about five liters of liquid through your body each minute. You heart squeezes or contracts 70 to 100 times a minute and relaxes for only about half a second between contractions. When the heart contracts the right side sends deoxygenated blood (blood low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide) to your lungs. The left side of your heart sends oxygenated blood (blood high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide) to the body. The muscle on the left side of the heart is much thicker than the right side of the heart because it has to pump blood out of the heart with enough force to reach all the parts of your body. You heart has valves separating each atrium and ventricle. The function of these valves is to prevent backflow of blood in the heart. They keep blood flowing in one direction from the atrium to the ventricle. You have blood vessels that carry blood to and from the heart. The vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries. Most arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart and to the body. The vessels that carry blood toward the heart are called veins. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body cells toward the heart. Blood pressure is caused by the force in which your heart contracts and pushes blood against your artery walls. The big push of blood causes the arteries to push out and produce a pulse. When you measure your heart rate, you are feeling for and counting that surge of blood, or “pulse”, each time your heart contracts. Sheep have a four-chambered heart, just like humans. By studying the anatomy of a sheep's heart, you can learn about how your own heart pumps blood through your body and keeps you alive! Label the parts of the heart. This will help you during the heart dissection. superior vena cava right atrium from body aorta pulmonary artery pulmonary vein valves left atrium valves inferior vena cava from body right ventricle left ventricle Discussion: 1. As blood passes through the pulmonary artery, it is pumped to the lungs. If blood leaves the right side of the heart deoxygenated and returns to the left side oxygenated, what gas has been added to the blood? Oxygen a. Through what organ system must the blood pass through in order to change in this way? Respiratory system (lungs) 2. Red blood cells carry oxygenated blood to all the tissues/cells in your body. If a person has sickle cell anemia, red blood cells do not work properly. How would this affect a person’s body(tissues/cells)? Red blood cells carry oxygen, so if they are not working properly this will reduce/lower the amount of oxygen carried/distributed to your cells/tissues. This will affect your cells ability to release energy through cellular respiration. 3. When you exercise, your cells need more oxygen so they can do cellular respiration to release more energy. Why does your heart rate and breathing increase when you exercise? Your breathing will increase to take in more oxygen that your cells need for respiration. Your heart rate will increase to pump blood faster through the body to deliver the oxygen your cells need for respiration. 4. What are the two functions of the valves in the heart? Your valves prevent the backflow of blood in the heart (and veins). Your vavles keep blood flowing in one direction. a. If a person is diagnosed with a heart murmur, it could mean that one of the valves in the heart is not functioning properly. How will this affect the heart? If the valve is not functioning properly, there will be some backflow of blood in the heart. 5. Explain why the muscle of the left ventricle is thicker than the muscle of the right ventricle. The muscle on the left side of the heart is much thicker than the right side of the heart because it has to pump blood out of the heart with enough force to reach all the parts of your body. 6. What is blood pressure? Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the artery walls when the heart contracts. OR Blood pressure is caused by the force in which your heart contracts and pushes blood against your artery walls. a. If your heart has to contract harder to force the blood out into the arteries, how will that affect blood pressure? Your blood pressure will increase or be higher if your heart has to contract harder.