* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
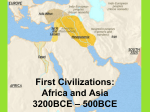
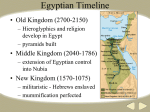
First Civilizations: Africa and Asia 3200BCE – 500BCE Ancient Kingdoms of the Nile I. Geography of the Nile River - “Gift of the Nile” – without the Nile, Egypt would be swallowed up by desert - Nile flows from south to north- Yearly Floods - Rain in the spring at the source of the Nile in Central Africa caused a yearly flood of the Nile. - The yearly flood covered the land with silt (nutrient rich soil) - Upper Egypt – located in the South, stretched from the first cataract (waterfall) to within 100 miles of the Mediterranean - Lower Egypt covers the delta region - Delta – a triangular region of marshland formed by deposits of silt at the mouth of the river - Menes, king of Upper Egypt, united Upper and Lower Egypt II. Old Kingdom (2700 BCE – 2200 BCE) - Pharaohs – Egyptian rulers often thought to be a god - Pharaohs in the Old Kingdom organized a strong central government - Pharaoh’s job to instill justice and order - Vizier – chief minister who advised the Pharaoh about official matters A. Pyramids - Built at Giza during Old Kingdom - Great Pyramid was tallest structure in world until Eiffel Tower was built around 4000 years later - Pyramids symbolized the wealth of Ancient Egypt because of the cost, resources, and organization it took to construct - Farmers often worked on the Pyramids when not planting/harvesting III. Middle Kingdom (2050 BCE – 1800 BCE) - Power struggle, crop failure, and cost of pyramids led to fall of Old Kingdom - Characterized by inconsistent floods from the Nile and turbulent politics IV. New Kingdom (1550 BCE – 1100 BCE) - At height of New Kingdom, empire stretched to the Euphrates River - Hatshepsut was a woman who ruled as Pharaoh from 1583 BCE – 1482 BCE - Ramses II was the most powerful ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into decline and fell to invaders from Assyria, Persia, Greece, and Rome. V. Egypt and Nubia - Nubia (also known as Kush) bordered Egypt to the south and the two empires were trading partners and also fought each other occasionally. - During a 100 year period, Nubia even conquered Egypt. Egyptian Civilization I. Egyptian Religion - Amon-Re – The chief god of the sun. - Pharaoh was closely linked to the sun god and was the only one who could conduct ceremonies to Amon-Re - Osiris – Murdered by brother Set - Isis – Wife of Osiris - Set – God who murdered his brother, Osiris - Horus – Falcon headed god - Anubis - Jackal headed god - Ankh – a cross like symbol that symbolized good health II. Belief in Afterlife - After death, the soul would be tested by Osiris. Osiris would weigh the heart (thought to be the soul in Ancient Egypt) would be weighed against a feather (which was the symbol of truth and justice). If the scale balanced, the soul would pass on to the afterlife, if there was imbalance, the soul would face annihilation - Book of the Dead – a book written that was full of instructions, spells, and charms to guide a person on their journey through the afterlife. - Mummification – the preservation of the dead - People were often buried with objects they would need for the afterlife - Mummification was very expensive and typically reserved for Pharaohs or those who could afford the process. III. Egyptian Society - Most Egyptians were farmers, who in the off-season would serve the Pharaoh as builders or warriors. - Egypt grew in trade, artisanship, and warfare with other cities – both brought new ideas, money, and riches (jewelry, furniture, and fabrics). - Women – could inherit property, enter business deals, buy and sell goods, obtain a divorce, work outside the home (textiles, priests), etc. IV. Egyptian Learning - Hieroglyphics – picture writing on stone that became more complex (from pictograms to ideograms - symbolized actions or ideas). - Then they moved to demotic (simpler, everyday writing style) on papyrus (Nile based plant). - Rosetta Stone – Greek, demotic, and hieroglyphic on one black stone that helped decipher the languages. - Decoded in the early 1800’s by Jean Champollion – helps us read all Egyptian artifacts now. - Skilled in medicine through mummification (knew how the body worked) - Also, developed a calendar (similar to ours) and mathematics (pyramids). V. Arts and Literature - Paintings –bodies forward and eyes looking sideways with pharaohs larger. - Architecture – Pyramids, Great Sphinx, Karnack (Romans). - Literature – hymns, prayers, proverbs to Gods, poems, folk tales (The Tale of Sinuhe). City-States of Ancient Sumer I. Geography of the Fertile Crescent - Mesopotamia – “between the rivers” area with terrible floods - The Epic of Gilgamesh – narrative poem where a great flood destroyed (4,900 yrs ago flood evidence) - 3200BCE – Sumerian Cities emerge (south) – clay bricks were building blocks for the cities. - Sea and river traders and land traders (invented wheeled vehicles!). II. Sumerian Civilization - The ruler was in charge of maintaining city-walls and irrigation systems, leading armies, leading religious ceremonies, serving gods, and enforcing laws. - Scribes collected taxes and kept records. - Hierarchy – system of social ranks (ruling family, officials, priests – merchants, artisans – peasant farmers, slaves). - Women shifted from honored and independent to dependent on men, but kept some rights such as trading and property ownership. - Gods were polytheistic that acted like humans (ate, married, had families). - To keep gods happy, each city built a ziggurat (pyramid temple) for ceremonies and sacrifices. - Afterlife was seen as a pessimistic place (dust, mud, blackness). III. Advances in Learning - Writing – Cuneiform – wedge shaped marks on clay tablets used for goods records and became more complex for poems, treaties, contracts, etc. - Scribes/scholars developed basic algebra and geometry, hour system, 360 degrees system, and calendars. - Passed on culture and developments to Greece and Rome! Invaders, Traders, and Empire Builders I. Ruling a Large Empire - 2300 BCE – Sargon of Akkad (middle) invaded Sumer – first empire! - The empire died with Sargon but he started a movement to unite all of Mesopotamia under one ruler. - 1790 BCE – Hammurabi of Babylon united much of Meso. – created the Code of Hammurabi (300 laws on a stone pillar) – first to codify laws (set down in writing). - Criminal law – eye for an eye, life for a life! - Civil law (private rights) – protect the powerless (women and children) - Hammurabi also improved irrigation, trained an army, encouraged God (Marduk) over all other gods. II. Warfare and the Spread of Ideas - Conquerors uprooted the defeated and helped to spread ideas! - 1400 BCE – Hittites moved into Mesopotamia and learned to extract iron from ore to make cheaper, stronger, and more weapons than others – tried to hide their discovery - 1200BCE – secret is revealed and brings about the Iron Age! - 1100 BCE – Assyrians became fiercest warriors with a well-organized society. - Women were confined and heavily clothed, extensive laws of lifestyles, and huge palaces were built. - King Assurbanipal – first library with a collection of stone cuneiform tablets. - 612 BCE – Nebuchadnezzar revived Babylonian empire – built the Hanging Gardens to please his homesick wife. III. Persian Empire - 539 BCE – Cyrus the Great conquered Asia Minor to India and promoted tolerance (respect all customs and traditions in the empire). - 522-486 BCE – Darius set up satraps (governor of a province). - Moved from a barter to money economy (use of coins or bills for payment). IV. Phoenician Sea Traders - Became known for manufacturing and trade – glass, purple (tyrian) dye. - To promote trades, they set up colonies (territory settled and ruled by people from another place). - known as Carriers of Civilization! – came up with the first alphabet (22 consonant sounds/symbols).