* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Molecules and Simple Reactions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
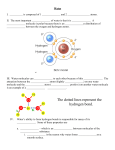
Organic Molecules and Simple Reactions Name: Background Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are three major groups of organic compounds found in living things. They are composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. In proteins, nitrogen is also present. The skeletons of carbohydrates, fat, and protein molecules are chains of carbon atoms to which hydrogen atoms are bonded. Compounds composed entirely of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons differ from one another by the number and arrangement of the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Other organic compounds are formed from hydrocarbons when one or more different kinds of atoms are substituted for a carbon or hydrogen atom. The group of substituted atoms is called a functional group. The chemical properties of a molecule are often determined by its functional groups. Organic molecules can be illustrated in several ways. A molecular formula shows the types and numbers of atoms in a molecule. A structural formula shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Molecules can also be illustrated with the use of molecular models. Procedures and Observations Part I: Functional Groups The functional groups contribute to the chemical properties of organic molecules. In many cases it is a functional group that becomes involved in a chemical reaction. a. Table 1 shows the number of chemical bonds formed by some atoms. Using this information, draw the structural formula for each of the functional groups in Table 2. The unattached bond in each formula shows where the functional group can be bonded in a molecule. The structural formula for the methyl group has been filled in as an example. Name Methyl Chemical Formula --CH3 Hydroxyl --OH Carboxyl --COOH Ethyl --CH2CH3 Amino --NH2 Atom Hydrogen (H) Carbon (C) Nitrogen (N) Oxygen (O) Number of Bonds 1 4 3 (or 4) 2 Structural Formula b. Use a molecular kit to make a three-dimensional representation of each functional group. Part II: Organic Molecules Ethane is a hydrocarbon that has the molecular formula C2H6. a. Draw the structural formula for ethane b. How many carbon – hydrogen bonds does ethane have? ______________ c. How many carbon-carbon bonds does ethane have? ______________ d. Make a model of ethane. e. Draw the structural formula for each organic molecule in Table 3. Use the model kits for help. Name Ethyl alcohol Chemical Formula CH3CH2OH Acetic acid CH3COOH Water H 2O Glycine NH2CH2COOH Glycerol CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH2(OH) Structural Formula Part III Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Dehydration Synthesis is a type of chemical reaction in which molecules of substances bond together to form more complex substances. Water (H2O) is released in this type of reaction. For example two molecules of glucose can join together, with the release of H2O to form maltose, a disaccharide. See figure 1 below. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Figure 1 a. Complete the dehydration synthesis reactions of the following molecules using structural formulas. The hydrogen and oxygen atoms that combine to form water are marked. Hydrolysis is the breaking down of large molecules into smaller molecules. Water is used in a hydrolysis reaction. For example, maltose and water react to form two molecules of glucose. See Figure 3 on the next page. Figure 3 b. Complete the hydrolysis reaction of the following molecule. Use structural formulas. The places where the –H and –OH of a water molecule are added to break apart the molecule are marked. Conclusions and Applications 1. Why are functional groups important in organic chemistry? 2. What is the difference between a molecular formula and a structural formula? Which tells you more about a molecule? 3. As growth occurs in the body, new substances must be synthesized. By what type of chemical reactions are molecules joined together to form more complex molecules? 4. What type of chemical reaction is involved in the breakdown of large molecules, such as those found in food, into smaller molecules.