* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
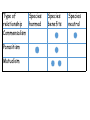
Ecology • Study of ecology • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F-0rTICAT_c • Intro to ecology • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GlnFylwdYH4 Words to consider 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Ecosystem Biotic Abiotic Commensalism Mutualism Parasitism Producer 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Consumer Decomposer Biodiversity Pollution Renewable resources Non- renewable resources Population Definition: Synonym/examples: Antonym/non-examples: Sentence: Sketch: Lexipedia Merriam-Webster Visual Dictionary http://www.visualdictionaryonline.com/ Shahi http://blachan.com/shahi/ Snappy Words http://www.snappywords.com/ The Science Dictionary https://www.thesciencedictionary.com/ Ecology WHAT IS ECOLOGY? Ecology- the scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environments, focusing on energy transfer Ecology is a science of relationships Ecosystem - populations in a community and the abiotic factors with which they interact (ex. marine, terrestrial) WHAT DO YOU MEAN BY ENVIRONMENT? The environment is made up of two factors: • Biotic factors- all living organisms inhabiting the Earth • Abiotic factors- nonliving parts of the environment (i.e. temperature, soil, light, moisture, air currents) Symbiotic Relationships Commensalismone species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped Ex. orchids on a tree; polar bears and cyanobacteria Epiphytes: A plant, such as a tropical orchid or a bromeliad, that grows on another plant upon which it depends for mechanical support but not for nutrients. Also called aerophyte, air plant. Symbiosis • http://sp11symbiosis.providence.wikispaces.net/Sh ark+symbiosis+with+Pilot+and+Remora+fish Symbiotic Relationships Mutualismbeneficial to both species Ex. cleaning birds and cleaner shrimp, lichen Symbiotic Relationships Parasitismone species benefits (parasite) and the other is harmed (host) • Parasite-Host relationship Symbiotic Relationships Parasitism- parasite-host Ex. lampreys, leeches, fleas, ticks, tapeworm Type of Species relationship harmed Commensalism Parasitism Mutualism = 1 species Species benefits Species neutral Feeding Relationships Producer- organisms such plants, they trap energy from the sun • Bottom of the food chain Feeding Relationships Consumer- all heterotrophs: they ingest food containing the sun’s energy Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Decomposers Feeding Relationships CONSUMERS Herbivores • Eat plants • Secondary, tertiary … consumers • Eat animals Feeding Relationships ConsumerDecomposers • Breakdown the complex compounds of dead and decaying plants and animals into simpler molecules that can be absorbed Biodiversity • The variety of life in an ecosystem. Pollution • Any substance that contaminates any part of an environment • The presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance or thing that has harmful or poisonous effects. Natural resources = substances and energy sources needed for survival • Renewable resources: • products that are constantly being replaced • Perpetually available: sunlight, wind, wave energy • Renew themselves over short periods: timber, water, soil • These can be destroyed • Nonrenewable resources: can be depleted, resources that are used more quickly than they are replaced • Oil, coal, minerals POPULATION a group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time that interbreed And Compete with each other for resources (food, mates, shelter, etc.)