* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD IN TRANSITION
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
State church of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
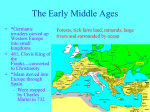
WORLD IN TRANSITION BYZANTINE EMPIRE BYZANTINE EMPIRE: The Beginning o Eastern part of the former Roman Empire o Constantinople is the capital o Strong for 1000+ years o Most speak Greek and are Christian o Byzantine Empire protected Western Europe from attack by Persians, Arabs, Seljuk Turks, and the Ottomans until they took control BYZANTINE EMPIRE: Justinian o Emperor in 527 to 565 o Conquers much of entire old Roman Empire o Wife, Theodora is very influential in his reign, coEmperor BYZANTINE EMPIRE: Justinian Code o Goes through all of the old Roman Laws and simplifies o Creates JUSTINIAN CODE: Single, uniform code of about 5,000 laws o Covers every aspect of Byzantine Life o Marriage, slavery, property, inheritance, criminal justice, women’s rights o Used for 900 years o Justinian & the entire Byzantine Empire preserves Greek and Roman (GrecoRoman) culture o Emphasis on education – Greek and Latin grammar, philosophy, literature, science o Former western part of the Roman Empire grows “dark” and doesn’t really preserve the past. Byzantine Empire does. BYZANTINE EMPIRE: Justinian’s Other Accomplishments o Constructed many public buildings in Constantinople o Rebuilt fortifications (walls) around Constantinople o Passion for Church building o Hagia Sophia o Built baths, aqueducts, law courts, schools, hospitals BYZANTINE EMPIRE: The Decline & Fall o Declining population o Bubonic Plague hits o542 AD: 10,000 people die each day o Attacked by many different invaders over time making Empire smaller o 1453: Constantinople fell to Ottoman Turks o Led by Mehmed – Ottoman Sultan o Mehmed changes Constantinople to Istanbul and makes it the capital of Ottoman Empire FEUD OVER RELIGION CHRISTIANITY o Made the official religion of both Roman and Byzantine Empires o Christianity different in Byzantine Empire o Differences in styles of: oWorship oRole of Emperor & church leaders oOpinions on various issues (use of icons vs no icons) FIRST SPLIT IN CHRISTIAN CHURCH o 1054: Christianity splits into TWO 1. Roman Catholic: Western part of former Roman Empire 2. Eastern Orthodox: Byzantine Empire o Major Cause: Role of the Pope o Roman Catholic Church: Pope is the leader; infallible o Eastern Orthodox Church: Pope equal to everyone including Emperor THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE o 1359 – 1922 o Officially became an Empire in 1453 when Constantinople fell o Last Sultan: Mehmen Vi Vahdetin (Nov. 1, 1922/Turkish War of Independence o Arabic and Muslim o Protectors of education, fueled the Renaissance o Algeria, Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, the United Arab Emirates, the West Bank, and Yemen The Ottoman Empire 1359-1683 THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE: Suleiman o Sultan of Ottoman from 1520 – 1566 o Known as “ The Magnificent” in Europe, “The Lawyer in Muslim world o Expands Empire to include Austria Hungary o Creates law code for civil and criminal cases o Simplifiers taxes o Makes government more efficient by reducing bureaucracy o Allows for religious freedoms for non-Muslims THE ARAB EMPIRE THE ARAB EMPIRE o Muslims armies were well disciplined and also too advantage of weak surrounding empires (Byzantine) o Religious tolerance o Umayyads: came into power, made capital Damascas, changed ways from simple to extravagant causing a divide o Abbasids: overthrew the Umayyads, moved capital to Baghdad – ideal location from trade CHINA THE QIN DYNASTY o Ruled by Emperors “divine authority” o Unifies states into country o 4,000 miles of highways – trade o Universal system of writing, laws, currency, weights and measures o High taxes and repressive government – force labor (Great Wall) o Falls apart with death of son THE HAN DYNASTY o Central government o Lower taxes and punishments o Expands west o Structured society o Rich: Emperor and other state officials o Poor: peasants, merchants, soldiers, and lastly slaves o Peasants paid taxes in form of crops, owed a month of military service or labor to the government each year o Labor used to expand Great Wall and build canals, roads, and irrigation ditches HAN DYNASTY COMES TO AN END o Large gap between rich and poor o Tradition held that land was divided between male heirs o As time went on, family land got smaller and smaller o Eventually hard to grow food to sell and even for family o Take out loans at high interest rates to buy more land o Large land owners didn’t have to pay taxes o Government needed money so small land owners needed to pay more o Time of social unrest o By 220 CE, dissolves into kingdoms EUROPE THE STORY SO FAR o Effects of Constant Invasions and Warfare o Germanic invaders overrun western Roman Empire in 400s o Fighting disrupts trade and government, people abandon cities o Marks the beginning of the Middle Ages – from 500 to 1500 o The Decline of Learning- Dark Ages – 500 to 700 AD o As cities are abandoned, level of learning declines o Knowledge of Greek language and culture almost lost o Loss of Common Language o Introduction of German language changes Latin; dialects develop GERMANIC & EUROPEAN KINGDOMS GERMANIC KINGDOMS o 400-600 o Germanic kingdoms replace Roman provinces o Continual wars change borders between kingdoms o The Church provides order and security o Government o Germans held together by family ties/loyalty, no government o Small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions o Warriors pledge loyalty to their chief; live in lord’s hall THE FRANKS o Clovis Rules the Franks o Hold power in Roman province of Gaul o Clovis, leader of the Franks, converts to Christianity in 496 o Leads warriors against other Germanic armies o Unites Franks into one kingdom with Church’s help by 511 GREGORY I o 590, Gregory I becomes Pope o Under Gregory I, Church becomes secular – a political power o Pope’s palace center of Roman government o Uses Church money to raise armies, care for poor, negotiate treaties o Establishes a Christendom – churchly kingdom spreading out from Rome EUROPEAN KINGDOMS o The Franks control largest and strongest kingdom o By 511, Frankish rule extends over present day France o Charles Martel Emerges o Most powerful official in kingdom omajor domo – mayor of the palace o In 719, he becomes more powerful than king o Son, Pepin, begins Carolingian Dynasty – family ruled from 751 - 987 ENTER CHARLEMAGNE o Pepin dies in 768, leaves kingdom to two sons o One son dies, leaving second son, Charlemagne, to rule o Charlemagne’s armies reunite western Europe, spread Christianity o In 800, Charlemagne travels to Rome to protect Pope Leo III from mobs o Pope crowns Charlemagne emperor; gives him title-”Roman Emperor” o This act united Germanic power, the Church, and heritage of Roman Empire CHARLEMAGNE o Charlemagne strengthens his royal power by limiting nobles power through royal agents o Royal agents sent out to keep counts in check, confirm that they’re treating their counties justly o Encouraged learning, opens palace school, and orders monks to open schools for future monks/priests o Died in 814, son Louis rules poorly o Louis’ three grandsons fight for control of the empire o In 843 they divide empire into three kingdoms; sign Treaty of Verdun o Divide of Empire leads to lost power and lack of central authority, leads to feudalism FEUDALISM o 850 to 950 FEUDALISM emerges: political system based on land control THE FEUDAL PYRAMID King served by nobles Nobles served by knights Peasants served at bottom o Lord: landowner who gives fiefs (land grants) in exchange for services o Knights: Horsemen, defend their lord’s land in exchange for fiefs o Vassals: People who receive fiefs, become powerful landowners SOCIAL CLASSES o Three Social Groups Those who fight: nobles and knights Those who pray: monks, nuns, leaders of the Church Those who work: peasants - horseless, weaponless, powerless Social class is usually inherited; majority of people are peasants Most peasants are serfs; people tied to place of birth by law Serfs aren’t slaves, but what they produce belongs to their lord MANORIALISM MANOR LIFE o The Lord’s estate, a manor, has an economic system (manor system) Serfs and free peasants maintain the lord’s estate, give grain The lord provides housing, farmland, protection from bandits Manors include lord’s house, church, workshops, village Cover a few square miles of land, are largely self-sufficient MANOR LIFE Peasants pay taxes to use mill and bakery; to get married; pay a tithe to priest Tithe: a church tax; equal to one-tenth of a peasant’s income Serfs live in crowded cottages with dirt floors, straw for beds Daily grind of raising crops, livestock; feeding and clothing family Poor diet, illness, malnutrition make life expectancy 35 years Serfs generally accept their lives as part of God’s plan THE CRUSADES PROBLEMS IN THE CHURCH o Problems in the Church o Some Church officials marry even though against Church o Some officials selling of religious jobs (simony) o Kings used non-ordained men as bishops oChurch believed they should be the only ones to appoint bishops o Response: Spiritual Revival o Monasteries help bring about a spiritual revival o Reformers help restor and expand Church power THE CRUSADES o In 1093, Byzantine emperor wanted to prevent the Muslim Turks from taking Constantinople o Pope Urban II issues a call for a CRUSADE, a “holy war” o Goals of the Crusades o Reclaim Jerusalem and reunite Christendom o Kings can get rid of knights who cause trouble o Younger sons want land and glory by fighting o Merchants join to gain wealth through trade THE FIRST & SECOND CRUSADES o Pope promises Crusaders who die place in heaven o First Crusades: Three armies gather at Constantinope in 1097, capture Jerusalem two years later o Captured lands along coast divided into four o Muslims take back territory. o Second Crusade: Retake Jerusalem again. o In 1187, Jerusalem falls to Muslims lead by Saladin THE THIRD CRUSADES o Started by three powerful rulers: o Philip II (France) o Frederick I (German) o Richard the Lion-Hearted (England) fought to regain Holy Land from Saladin o After many battles, Richard and Saladin agree to truce o Saladin keeps Jerusalem but Christian pilgrims could enter city SPANISH CRUSADES o Most of Spain controlled by Moors, Muslims o Reconquista: Christians drive Muslims from Spain, 1100 - 1492 o Inquisition: Attempt reunite Christians, suppress heresy (slander against church) & expel non-Christians RESULT OF THE CRUSADES o Crusades show power of Church o Convince thousands to fight o Women manage estate & business affairs o Merchants expand trade o Southwest Asia o Failure of later crusades weakedns Pope and nobles, strengthens kings o Create lasting bitterness between Muslims and Christians MEANWHILE IN ENGLAND COMMON LAW & THE MAGNA CARTA o Henry II 1154-1189 o Formed common law: basis of many Englishspeaking countries today including the US o John, Henry’s son, o King after the death of his father and brother o Terrible military leader o Cruel to subjects; constant taxing o Nobles revolted; forced John to sign MAGNA CARTA: guaranteed basic political rights, safeguarded feudal rights and limited king’s powers THE GREAT SCHISM THE PLAGUE HUNDRED YEARS WAR THE GREAT SCHISM Pope and King Collide In 1300, Pope Boniface VIII asserts authority over France’s Philip IV, Kings must obey pope. Philip has him imprisoned; Pope dies soon after Avignon and the Great Schism 1305, French Pope is chosen; moves to Avignon, city in France 1378, two Popes chosen, one in Rome, one in Avignon Each declares the other false, causing split called Great Schism 1417, Council of Constance ends schism, chooses Martin V as pope THE PLAGUE Origins and Impact of the Plague 1300s, Euope suffers bubonic plague, extremely deadly disease Begins in Asis; spreads to Italy and other countries over trade routes via fleas on rats Abour 1/3 of Europe’s population dies Effects of the Plague Town populations fall, trade declines, prices rise Some serfs leave manors for paying work Many Jews blamed and killed; Church status weakened THE HUNDRED YEARS WAR 1337-1453, between England and France English king Edward III claimes French throne Fighting continues over trade and land Effects: Marks the end of medieval society Established borders of France and England England a mess- begins War of Roses- 2 families fight for the throne