* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Policy Model for Analyzing Macroprudential and Monetary Policies Sami Alpanda Gino Cateau
Household debt wikipedia , lookup
History of the Federal Reserve System wikipedia , lookup
Life settlement wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Fractional-reserve banking wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Bank of England wikipedia , lookup
A Policy Model for Analyzing Macroprudential and
Monetary Policies
Sami Alpanda
Gino Cateau
Cesaire Meh
Bank of Canada
October 2014
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
1 / 19
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors. No
responsibility should be attributed to the Bank of Canada.
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
2 / 19
Motivation
Recent global …nancial crisis was a reminder that the real economy
and the …nancial system are closely linked
…nancial system can be a source of shocks
amplify/propagate shocks originating elsewhere
Theoretical front: renewed interest in incorporating real-…nancial
linkages into DSGE models
Policy front: new emphasis on the role of macroprudential
regulations
more targeted than MP to achieve …nancial stability
MP may at times face tradeo¤s: e.g. low in‡ation and high HH debt
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
3 / 19
In this paper
We build a medium scale, small-open-economy DSGE model with
real-…nancial linkages: balance sheet positions of banks, HHs, and
…rms a¤ect funding/lending conditions and the real economy
macroprudential policies: capital requirements; LTV
nominal and real frictions: monetary policy and propagation
We use the model to analyze
transmission of …nancial shocks (e.g. exuberance, risk premium)
e¤ects of macroprudential policies on real and …nancial variables
Main …nding: LTV most e¤ective and least costly in reducing HH
debt, followed by capital regulations and MP.
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
4 / 19
Literature: Balance sheet and bank capital channels
Firm and HH leverage key determinant of borrowing conditions
Carlstrom and Fuerst (1997), Bernanke, Gertler and Gilchrist (1999),
Kiyotaki and Moore (1997), Iacoviello (2005)
ampli…cation due to "…nancial accelerator"
Firms/HHs
Assets
Liabilities
Capital
Bank loans
Housing Net worth
Assets
Loans
Securities
Banks
Liabilities
Funding
Equity
Capital position of banks key for funding and lending conditions
Holmstom and Tirole (1997), Meh and Moran (2010), Gertler and
Karadi (2010), Davis (2010), Gerali et al. (2010)
further ampli…cation due to "adverse feedback loop"
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
5 / 19
Model
Small-open-economy DSGE model with …nancial frictions
HH lending to banks, and bank lending to HHs/…rms involve
monitoring costs (Curdia and Woodford, 2011)
spreads in funding/lending rates depend on bank and borrower
leverage (Bernanke et al., 1999; Davis, 2010)
macroprudential policies feed into spreads
…nancial shocks (e.g. capital quality; spreads; exuberance)
Other key features
nominal frictions: price/wage stickiness; indexation
real frictions: habit formation; utilization and investment adj. costs
open economy: extended UIP condition; partial pass-through
monetary policy: Taylor rule
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
6 / 19
Brief overview of the model
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
7 / 19
Banks
Use deposits and bank capital to fund lending to impatient
households and entrepreneurs
PI ,t bI ,t + PE ,t bE ,t = Dt + At
Pay dividends to patient HHs; dividend smoothing based on adj. costs
(Jermann and Quadrini, 2012)
Bank loans are modeled as perpetuities with exponentially decaying
coupon payments (Woodford, 2001)
bank loan issued in t 1 priced in period t as (δ/π t ) PI ,t ; allows
recursive formulation for banks’cash-‡ow (ABS)
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
8 / 19
Monitoring costs and lending rates
Banks incur monitoring costs based on market value of bank
assets/lending (Curdia and Woodford, 2011)
captures "bad loans"/default; cost of purchasing default insurance
costs increase with borrower leverage ) spread similar to BGG
Monitoring costs for bank lending to HHs and bank funding are
modeled similarly
modeling choice captures main themes in literature while avoiding
technical issues (long-term borrowing; risk-averse borrowers)
Bank borrow short-term, lend long-term (modeled as perpetuities
with exponentially decaying coupon payments as in Woodford, 2001)
long-term lending rates depend on: current and future policy rates
and bank/borrower leverage
bI ,t =
R
1
δI
RI
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
∞
∑
s =0
δI
RI
s
h
i
bt + s + Ψ
b d ,t +s + Ψ
b I ,t +1
Et R
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
9 / 19
Macroprudential policy and spreads
Regulatory LTV policy feeds into monitoring costs on household loans
ΨI ,t = f
(1
mt ) qh,t hI ,t
nI ,t
monitoring costs increase as equity falls short of regulated equity
translates quantity restrictions into spreads
Similarly, bank capital regulations impact funding spread
Ψd ,t = f
γt [ω I PI ,t bI ,t + ω E PE ,t bE ,t ]
At
regulations do not necessarily bind in the short-run
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
10 / 19
Calibration
Main targets for steady-state:
3% risk-free rate; 14 bps. funding spread
240 and 200 bps. overall spread on HH and business loans
mortgage debt / impatient HH housing = 95% (bI /hI )
mortgage debt / total housing = 30% (bI /h )
business debt / entrep. capital = 0.5 (bE /kE )
business debt / total capital = 0.25 (bE /k )
bank capital ratio = 10%
Parameters determining dynamics:
nominal and real frictions: ToTEM
…nancial frictions: HRAM; MAG report (BIS)
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
11 / 19
Tightening in regulatory LTV: transmission mechanism
Increase in current and future monitoring costs of banks, ΨI ,t +k "
lending rate to HHs, RI "
impatient HH borrowing, bI #; demand for housing and consumption #
house price, qh #; residential investment #
Spillover to non-residential sector and ampli…cation
demand for non-res. investment #, capital price, qk #
bank capital # =) bank funding/lending rates "
Moderating factors
π # ) policy rate, R #
patient HH increase demand: cP , hP , kP "
currency depreciation ) exports "
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
12 / 19
Tightening in regulatory LTV
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
13 / 19
Transmission mechanism for capital req. and MP
Increase in bank capital requirements
direct impact on borrowing cost of entrepreneurs as well as HHs
larger decline in business loans and non-res. investment
"broad" tool to reduce HH debt
Increase in policy rates
adverse impact on patient HH consumption demand and exports
"blunt tool" to reduce HH debt
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
14 / 19
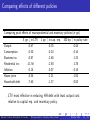
Comparing e¤ects of di¤erent policies
Comparing peak e¤ects of macroprudential and monetary policies (in pp)
Output
Consumption
Business inv.
Residential inv.
In‡ation
House price
Household debt
5 pp # in LTV
-0.67
-0.50
-0.87
-11.56
-0.14
-5.54
-7.60
1 pp " in cap. req.
-0.35
-0.10
-2.68
-2.58
-0.07
-1.21
-1.37
100 bp " in policy rate
-0.44
-0.16
-1.35
-1.78
-0.16
-1.50
-0.50
LTV most e¤ective in reducing HH debt with least output cost;
relative to capital req. and monetary policy.
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
15 / 19
Optimal LTV policy and policy coordination
Scenario: low π ("external headwinds") and high HH debt
("exuberance")
Optimal regulatory LTV ratio: slightly higher than 0.95
what’s the …nancial stability concern?
pecuniary externality: spreads depend on aggregate variables
"exuberance shocks": a¤ect expected return on assets
Instead consider high impact event (crisis) due to high HH debt
HH debt level after 5 years determines shock intensity
optimal policy: MP loosening and LTV tightening
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
16 / 19
Alternative modeling of long-term mortgages
Debt accumulation:
Dt = ( 1
κ ) Dt
1
+ Lt
Average borrowing rate on outstanding mortgages, RtM :
Dt RtM = (1
Φ ) ( Dt
Lt ) RtM 1 + [Lt + Φ (Dt
Lt )] RtF ,
where Φ : share of existing loans re…nanced at current …xed rate, RtF
New borrowing:
Lt = φPt qh,t ihI ,t + γ [Pt qh,t (1
δh ) hI ,t
1
(1
κ ) Dt
1 ] + εl ,t
If κ = 1 and γ = φ, then constraint becomes similar to Iacoviello
(2005)
Dt = φPt qh,t hI ,t
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
17 / 19
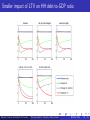
Smaller impact of LTV on HH debt-to-GDP ratio
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
18 / 19
Conclusion
Small open-economy DSGE model with nominal, real and …nancial
frictions
captures main themes in RFL literature while keeping model tractable
can be used to analyze e¤ects of macroprudential policy
Related work/possible extensions:
‡ow vs. stock of HH debt
small probability/high impact event
default and risk-taking channel of MP
term-premium vs. credit risk (QE)
Some …nal thoughts on policy implications:
MP tightening may increase HH debt-to-GDP ratio (in SR)
signi…cant tightening in LTV required to reduce HH debt
Alpanda, Cateau, Meh (Bank of Canada)
()Macroprudential - Monetary Policy Model
October 2014
19 / 19