* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AST 207 7 Homew
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
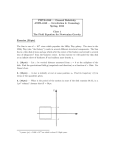
AST 207 7 Homew work 5 Due 18 Octoober 2010 at beginningg of class. No laate papers. H mod del of a star. Imagine that you have maade “stars” ouut of hot platees and you aree 1. Hot-plate pllotting them on o a Hertzsprrung-Russell diagram d a. (3 pts.) How can yo ou make two hot h plates witth the same sppectral class aand differing absolu ute magnitudee? Chang ge the hot plattes size. For all a parts, the kkey idea is thaat the H-R diaagram is a ploot of absolu ute magnitudee or luminosity aand temperatuure. b. (3 pts.) If you moveed the hot plaate to a greaterr distance, hoow would its pplace on the H HR diagram change? It wou uld not, the HR R diagram deepends on the absolute maggnitude, not oon the apparennt magnitude or the stars distance from f us. c. (3 pts.) If you turneed the setting on the hot plaate from “higgh” to “mediuum,” how wouuld its i the HR diagram change?? place in It wou uld move to th he right and down. Doing this would firrst, decrease tthe temperatuure, thus reeddening the star s and moviing it to the riight, and secoond, decrease its luminositty. Movin ng it down. 2. Life L on Deneb b. Here you will w find out wh hat it means tto live near a ggiant like Denneb. Recall thhat the lu uminosity of a star , where T is its temperaature and R iss its radius. Abs. mag. Diistance (pc) Appp. Mag. A Star a. In classs we found th hat a star 10 Sun -2 6.74 4.83 1/2200,000 times fainter f has a magnitude m Deneb 1.225 -77.3 5000 +2.5 greater. g This relationship betweeen the flux fA and fB of two staars A and B and a their magn nitudes can bbe expressed m mathematicallly as mA–mB= –2.5 log(fA/ fB). (3 pts.) How much brrighter is Denneb than the suun if both aree placed at thee same distancce? (2 pts.) What W quantity y makes this ccomparison inn the most dirrect manner? mA–mB= –2.5 log(ffA/ fB), where mA will be Deeneb, and mB will be the sun, solving foor the ratio of o their fluxes, we get fA 10 fB ( m A mB ) 2 .5 10 ( 7.3 4.83) 2 .5 71000 Deneb b is 71000 tim mes as bright at a the sun. Absolu ute magnitudee makes this comparison c inn the most dirrect way. If yyou used appaarent magnitude, you wou uld have to acccount for disstance. 00K, and the ttemperature oof Deneb is 98800K. (2 pts.)) How b. The temperature of the sun is 570 l is Deneeb than the su un? (3 pts.) Exxplain the prinnciple(s) that you use and w where much larger you go ot the values. We kn now . Use the raatio of the lum minosity of Deeneb to that oof the sun. 2 Thereffore: 71000 R Deneb TDeeneb 2 RSun TSunn Solvin ng for the radiii ratio we gett: 4 2 4 R Denebb (9800) 4 2 RSun (5700) 4 AST 207 7 Homew work 5 Due 18 Octoober 2010 at beginningg of class. No laate papers. 2 2 TSun RDenebb 57000 71000 71000 90 RSun 98000 TDeneb Deneb b is 90 times the radius of the t sun. To ansswer this we needed n to kno ow the ratio oof luminosities from part a,, and luminossity’s relationship to the radius r and tem mperature of a star. The tem mperatures caame from the data given. btends ½ degree in the sky. If Deneb repplaced the sunn, what angle w would c. (2 pts.)) The sun sub our rep placement sub btend? (2 pts..) Explain thee principle(s) that you use aand where yoou got the vallues. The haalf-angle of th he sun is / , where R is its radiuus and D is its distance. If D Deneb replaceed the sun, thee radius is larger by a factoor of 90. Thereefore the anglle subtended bby the replaceement sun is 90 0.5° 45°. The raadius was from m part b. M Figure 1 is the Hertzssprung-Russelll diagram off the star clustter M15. 3. M15. gnitude of thee hottest mainn-sequence staars? a. (2 pts.) What is the absolute mag t HR diagraam, the hottesst main sequeence stars are about 3.5 From the b. (3 pts.) Why are theere no hotter main-sequenc m ce stars? m sequencce because theey all already used up theirr There are no hotter stars on the main gen cores and d left the main n sequence. H Hotter stars usse up their fuel faster. hydrog c. Stars with w a color B-V=0.6 span a range of 5 m magnitudes. (22 pts.) What pproperty of thee stars accoun nts for this ob bservation? (3 3 pts.) What iss the range off this propertyy? Their size s (or radius) accounts fo or this range iin observationn. Since color is relateed to temperrature, the temperratures are thee same. nitudes is two o steps 5 magn of 2.5 mag, which is i two factorss of 10 in lumino osity, or 102, or o 100. So if lu uminosity (L)) increasses by a facto or of 100, an nd temperaturre (T) stays constant, c then n using , 100 = R2, or R=10. Thereffore the radius coverss a factor of 10. The radius of the giants is ten times that t of the dw warfs. Fig gure 1 Hertzsprrung-Russell ddiagram of the sstar cluster M115. B-V is a meeasure of color.. The vertical sscale on the lefft is apparent m magnitude, and the scaale on the rightt is absolute maagnitude.



![[ ] ò](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003342726_1-ee49ebd06847e97887fd674790b89095-150x150.png)