* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon and nitrogen cycles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
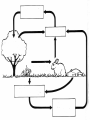
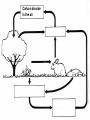
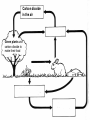
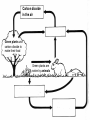
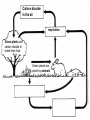
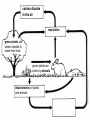
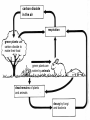
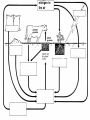
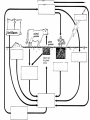
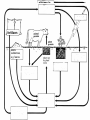
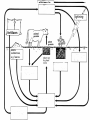
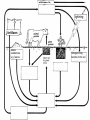
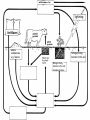
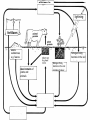
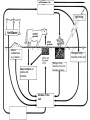
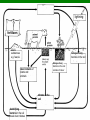
Food Production and the Environment The Carbon Cycle Carbon dioxide in the air Carbon dioxide in the air Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food Carbon dioxide in the air Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food Green plants are eaten by animals Carbon dioxide in the air respiration Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food Green plants are eaten by animals carbon dioxide in the air respiration green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food green plants are eaten by animals dead remains of plants and animals carbon dioxide in the air respiration green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food green plants are eaten by animals dead remains of plants and animals decay by fungi and bacteria Decay Fungi and bacteria are responsible for the decay of dead organisms. Decay In order to be able to carry out decay, fungi and bacteria need: 1. Oxygen 2. Moisture 3. The correct temperature The Nitrogen Cycle nitrogen in the air nitrogen in the air fertilizers fertilizers nitrogen in the air fertilizers fertilizers waste substances e.g. faeces nitrogen in the air lightning fertilizers fertilizers waste substances e.g. faeces nitrogen in the air lightning fertilizers fertilizers waste substances e.g. faeces Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil nitrogen in the air lightning fertilizers fertilizers waste substances e.g. faeces Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the root nodules of clover nitrogen in the air lightning fertilizers fertilizers waste substances e.g. faeces Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil dead remains of plants and animals Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the root nodules of clover nitrogen in the air lightning fertilizers fertilizers waste substances e.g. faeces Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the root nodules of clover dead remains of plants and animals nitrates in the soil lightning fertilizers fertilizers waste substances e.g. faeces Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the root nodules of clover dead remains of plants and animals nitrates in the soil denitrifying bacteria in the soil break down nitrates The nitrogen cycle Living things need nitrogen to make protein. They can not use the nitrogen in the air The nitrogen in the air must be changed to nitrates before plants can use it. The nitrogen cycle Animals get their nitrogen by eating plants. The nitrogen cycle The roots of some plants (e.g. clover, pea & beans) have swellings called root nodules on them. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria living in these nodules change nitrogen in the air into nitrates. The nitrogen cycle The nitrogen-fixing bacteria are essential to maintain the fertility of the soil. Without them food yields would rapidly fall.