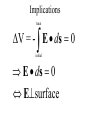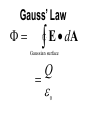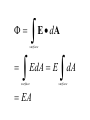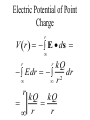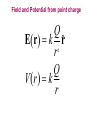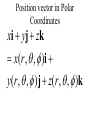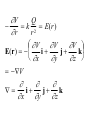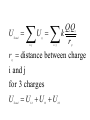* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download r - Personal.psu.edu
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrocommunication wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
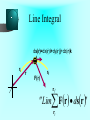
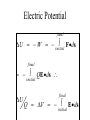
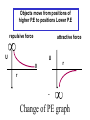
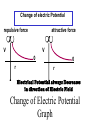
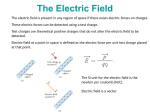
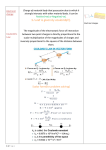
LESSON 25 Electric Potential Definition Comparison to Potential Energy Equipotential Surfaces Electric Potential due to point charge Electric Potential due to many charge Electric Potential Energy of Interaction Work done by a force F on moving object from initial point to final point final W F ds initial Line Integral ds(r)=dx(r)i+dy(r)j+dz(r)k ri r F(r) rf rf "Lim Fr dsr " ri Potential Energy Work done by a conservative force on an object is equal to the negative of the change of Potential Energy of the object Thus equal to the change of Kinetic Energy of the object Capacitor Electric Potential final Fds U W initial final QEds initial U final Eds Q V initial Electric Potential Difference The change of electrical P.E. per unit charge between an initial point and a final point is called the Potential Difference between the points It is the change of electric potential between the two points. Potentials at a point By definition the P.E. at a point infinite distance from the source of a force is zero Thus the electric potential at a point infinite distance from the source of an electric field is zero Electric Potential at point r Formula r V r E ds S.I. Units [U]/[Q] = J/C= V (Volts) Objects move from positions of higher P.E to positions Lower P.E repulsive force U attractive force U 0 r r - Change of PE graph Change of electric Potential repulsive force V attractive force V 0 r 0 r Electrical Potential always Decreases in direction of Electric Field Change of Electric Potential Graph Movement of Charge Negative charge moves in opposite direction to electric field Positive charge moves in the same direction as an electric field Equipotential Surface Equipotential Surface is A connected set of points that all have the same electric potential Potential Difference between points is 0 volts. Work done on Surface No work is done when moving charge from one to point to another point on such a surface As change of P.E. between points on surface is 0 Joules Implications final V = - E ds 0 initial E ds 0 Esurface Field lines and Equipotential Surfaces +3C -2C Gauss’ Law Review of Gauss' Law I The Electric Flux through a surface enclosing a charge is equal to the Charge enclosed divided by the permittivity The Electric Field outside of a spherical charged object is the same as if object were a point charge Gauss’ Law Review of Gauss' Law II E dA Gaussian surface Q 0 Review of Gauss' Law III E dA surface EdA E surface EA dA surface Implications Surface of an isolated conductor in electrostatic equilibrium must be an isopotential surface Electric Potential of Point Charge r V r E ds kQ Edr 2 dr r r kQ kQ r r r r Field and Potential from point charge Electric Potential of Point Charge IIQ Er k r Q V r k r 2 rˆ Picture r point where electric field and potential is evaluated unit vector Charge Polar Coordinates V(r) V(x, y, z) V(r, , ) V(r) Definitions of coordinates z (x,y,z) r Phi y Theta x Position vector in Polar Coordinates xi yj zk x(r, , )i y(r, , )j z(r, , )k Electric Field and Potential V Q for k Point E(r ) Charge r r2 V V V E(r) i j k x y z V i j k x y z radius of conductor Graphs = Electric Potential = Electric Field Magnitude distance from center of charged conductor Spherical Charge Electric Field and Electric Potential outside of spherical charged conductor is the same as the field and potential obtained from a point charge that has the same charge Electric Potential due to Electricmany Potential at a point due to Sources many source charges r (r) V(r ) V(r)dr= k dr r V(r0) Vi (r0) i i Qi k r0 i 0 charged body charged body Potential Energy of Potential Energy of Interaction Interaction I Fixed source charge Q0 and fixed charge Q F QE U QV Potential energy of interaction between source charge of electric field and the charge Q Potential Energy of Interaction II P.E. of interaction between Q and Q0 (source charge) - positive work is done on the charges in bringing them together if they repel or negative work if they attract If one brings another charge to a fixed position work will be done (either positive or negative) by the forces due to Q and Q0 U Potential Energy of Interaction III Q Q Total U ij i j i j k i r j ij r distance between charge ij i and j for 3 charges U U U U Total 12 13 23