* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4. Electrostatics and Conductors
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
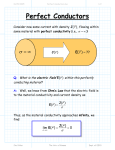
4. Electrostatics with Conductors General statements about E(x) in or near a conductor • E is 0 inside the conducting material. • E is normal at the surface. • The surface charge density is = 0En . • The conductor is an equipotential. (Explain why each statement must be true.) G L Pollack and D R Stump Electromagnetism 1 4. Electrostatics with Conductors The Method of Images • The image of a charge q in a planar conducting surface is a charge q = – q located at an equal distance on the opposite side of the surface. • The image of a charge q in a conducting sphere of radius a is a charge q= – qa/r located at the conjugate point, i.e., at radius r = a2/r. (Explain why the image charge is not real but a useful fiction.) G L Pollack and D R Stump Electromagnetism 2 4. Electrostatics with Conductors In some simple, azimuthally symmetric problems involving a spherical conducting boundary, the potential in a charge-free region takes the form A B cos V ( r , ) C D r cos 2 r r where A, B, C, D are constants that will be determined by the boundary conditions. Then the electric field is E = V . (Section 4.3) G L Pollack and D R Stump Electromagnetism 3