* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric & Gravitational Fields and Electric Potentials
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
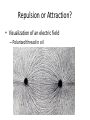
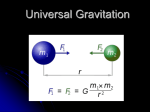
Warm Up 3 • 36 The illustration shows the transcription process. What is the main purpose of the structure labeled W? • F Carrying instructions for protein synthesis • G Transforming into a protein • H Replacing damaged DNA • J Passing traits to offspring Electric & Gravitational Fields and Electric Potentials Gravitational vs Electrical Force Discussion 1. Gravitational Force acts between 2 _____. 2. Electrical Force acts between 2 _____. 3. In which direction does the gravitational force act? How about the electrical force? 4. Does gravity get stronger or weaker from the center of a mass? How about electrical force? 5. Do these 2 forces seem similar? Gravity and Electricity Gravitational Force Electrical Force Force between 2 masses Attraction only Weaker over distance Cause things to orbit Force between 2 charges Attraction & Repulsion Weaker over distance Cause electrons to orbit Gm1m 2 F 2 d kq1q2 F 2 d G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 k = 8.99 x 109 Nm2/C2 Force Fields in Physics • Force Fields are just areas with forces. – Gravitational Field – Area where the force of gravity pulls on an object – Electric Field – Area where an electric force can push or pull an object Repulsion or Attraction? • Visualization of an electric field – Polarized thread in oil Attraction or Repulsion? • Line model Force Fields in Physics • Force fields are drawn with lines – The lines represent the direction positive charge would accelerate if placed in the field. – The result is lines start from a positive charge and end at a negative charge Force Fields in Physics • Force fields are drawn with lines – The density of lines represent magnitude Electrical Potential Energy • Think about trying to bring together 2 magnets at their North poles. • How much force does it take for you to bring them together? At the beginning versus when they are really close? Electrical Potential Energy • Electrical Potential Energy – Energy required to keep a charge from moving in an electric field. • Strong field + strong charge + short distance = high Electrical Potential Energy • When the charge is released, that potential energy is transformed to kinetic energy Electric Potential • Electric potential = “electric potential energy”/”charge” • SI unit for Electric Potential is the “volt”, V J V C Misconceptions of the Volt • High Voltage is deadly – Van de Graaff generators can easily generate 50,000 V – High potential energy but very little charge Sample Problem • If 20. J of work is required to move 4.0 C of charge in a uniform electric field, the electric potential will be _____. • • • • A) 80. V B) 5.0 V C) 0.0 V D) 100 V Exit Ticket 2 • Consider two charged objects. One carries a charge of 1.8 x10-6 C When the two are separated by a distance of 0.9m, there is a force of 2.7 N between them. What is the charge on the second object? Warm Up 4 Electric Potential Energy • Electric Potential Energy (ePE) is due to a charge’s location in an electric field • ePE is the amount of work needed to move a charge to that location – Similar to gravitational potential energy depends on the height of an object • The amount of charge you are moving does not matter Lightning • High Electric Potential is created by friction and air currents in the clouds • Clouds become polarized, usually bottom of the cloud is negative • Polarized cloud induces the ground to be polarized • Lightning occurs to neutralize the charge imbalance Electric Shielding • Why is it safe to drive stay inside a car during a lightning storm? • Excess charges only coat the surface of an object – Object’s normal electrons force the extra electrons to stay outside • Inside of the car remains neutral – Same with the inside of a Van de Graaff generator Lab – Mapping Electric Potential • Groups of up to 3 • You will measure the electric potential difference with a volt meter • Measure 36 (6 x 6) points around the positive terminal • Measure 6 points from the negative terminal to the positive terminal • Draw contour map at 0.5 V intervals • Turn in drawing