* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography Skills
Diver navigation wikipedia , lookup
Celestial navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
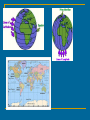
Geography Skills I. Movements of the Earth A. The Earth revolves around the sun in a nearly circular pattern(orbit). One Revolution takes 365 ¼ days B. As it orbits the sun, it also spins on its axis. One Rotation takes 24 hours C. The tilt in the Earth’s axis causes sunlight to strike different parts of the Earth at different timesCreating seasons (tilt is 23.5 degrees) 1. Spring-March 20-21 2. Summer- June 21-22 3. Fall –September 22-23 4. Winter-Around December 21 II. The Globe A. Scaled model of the Earth B. Shows actual size, shape, and locations of landmasses and bodies of water drawn to a scale C. Shows the 7 continents and 4 oceans Continents and Oceans III. Hemisphere A. The globe is in the shape of a sphere B. You see only one half at a time- Hemi means half (easier to study one half at a time) C. Geographers divide the globe into 4 hemispheres to study D. An imaginary line known as the Equator divides the Globe into the Northern and Southern hemispheres IV. Latitude and Longitude A. B. C. To locate places on a map or globe, we use the global grid. This grid is made up of lines known as latitude and longitude. Latitude lines, or parallels run east to west. *They measure the distance north or south of the equator. Longitude lines, or meridians run north to south.*They measure the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian which runs through Greenwich, England. D. Latitude and Longitude are measured in degrees. When writing a location the latitude measurement is written first. ( 30 N, 90 W) V. Maps A. Shows regions on a flat surface B. Difficulty is showing correct size and shape. (making something flat that is meant to be round) C. Mapmakers use different types of projections to fix the distortions. Try to choose the map with the least distortion D. Types of projections (M6-M7) 1. Same shape maps-accurately shows land but distorts the size and distance between 2. Mercator Projection- accurately shows shape of land and direction but distorts the distance and size 3. Equal-area map-shows the correct size of land but distorts the shape of the land especially at the edges 4. Robinson map-Keeps size and shape relationships of most oceans and continents. Polar areas are distorted. overall view is good VI. Using maps There are five major parts to every map: 1. Title-states subject of the map (read!!!!) 2. Compass rose- shows direction Cardinal directions-N, S, E, W 3. Key-Shows what the symbols and colors used on the map mean 4. Locator-Shows where location is on a globe 5.Scale bar-Helps to find the actual distance between areas on the map VII. Types of maps A. Political map-shows the cities, states, countries, or other political features B. Physical map-shows a region’s physical features (hills, mountains, deserts, etc) 1. Elevation map-uses color 2. Relief map-uses shading C. Special purpose maps 1. Climate maps 4. Human migration 2. Language map 5. world land use 3. Religion maps 6. Historical maps VIII. Themes of Geography 1. Place-description of what an area is like based on natural and human features 2. Location- where is it? Absolute location-use latitude and longitude Relative location-where one place is in relation to another 3. Region-an area with common features that set it apart from others 4. Movement-Movement of goods, people, and ideas around the world. How this affects the people and the area’s development 5. Human/environment interaction-relationship between people and the land they live on