* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography Skills Powerpoint
Ordnance Survey wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
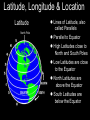
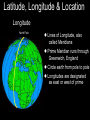
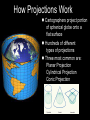
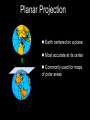
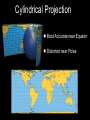
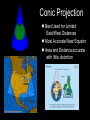
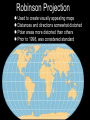
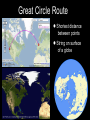
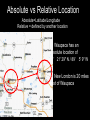
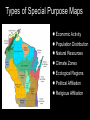
Introduction to Geography Skills for Learning Geography Skill Examples Tools Asking Geographic Questions Why is there traffic on this road? Why are people moving south? Where should we build hospital? Maps, Globes, Internet Remote Sensors News Media Acquiring Geographic Information Compare satellite photos over time Design a traffic survey Collect data on hunting Field Observation Interviews, GPS Satellite Imagery Organizing Geographic Information Create a population density map Summarize interview information Create a map w/resources shown Maps, Databases, Graphs, Charts Summaries, etc Analyzing Geographic Information Draw conclusions about resources Compare information from maps Compare traffic surveys Maps, Databases, GIS Spreadsheets Charts, Diagrams Answering Geographic Questions Present results of survey to govt. Suggest location for hospital Decide to increase hunting limits Maps, Reports Presentations, Papers Speeches, etc Latitude, Longitude & Location Latitude North Pole Lines of Latitude, also called Parallels Parallel to Equator High Latitudes close to North and South Poles Low Latitudes are close to the Equator North Latitudes are above the Equator South Latitudes are below the Equator Latitude, Longitude & Location Longitude North Pole Lines of Longitude, also called Meridians Prime Meridian runs through Greenwich, England Circle earth from pole to pole Longitudes are designated as east or west of prime Latitude, Longitude & Location The Global Grid North Pole Every location on earth can be defined by latitude and longitude Latitude North or South of Equator Longitude East or West of Prime Meridian Degrees, Minutes, Seconds Absolute Location From Globes to Maps From 3D to 2D Globe: Scale Model of Earth Map: Symbolic Representation of part of planet on paper Surface of Earth like peel of an orange Cartographers use projections to make maps from globes How Projections Work Cartographers project portion of spherical globe onto a flat surface Hundreds of different types of projections Three most common are: Planar Projection Cylindrical Projection Conic Projection Planar Projection Earth centered on a plane Most accurate at its center Commonly used for maps of polar areas Cylindrical Projection Most Accurate near Equator Distorted near Poles Conic Projection Best Used for Limited East/West Distances Most Accurate Near Equator Area and Distance accurate with little distortion Problems with Projections Curved surface of Earth cannot be accurately displayed on the flat surface of a map Every projection stretches or breaks the surface of the Earth in some way as it is flattened Depending on projection: distance, direction, shape or area may be distorted Cartographers have developed different projections for different purposes Winkel Tripel Projection Minimizes distortion to Area, Distance and Direction 1998: Adopted as standard by National Geographic Society Robinson Projection Used to create visually appealing maps Distances and directions somewhat distorted Polar areas more distorted than others Prior to 1998, was considered standard Goode's Interrupted Equal Area Projection True Size and Shape Distances distorted Mercator Projection One of earliest projections, 1569 Gerardus Mercator Distances and size increasingly distorted the further away from the equator Accurate shape and direction, good for sea travel Great Circle Route Shortest distance between points String on surface of a globe Geographic Information Systems Computer Systems accept data from a variety of sources Geographers can quickly access & use Often organized in layers Map Scale Small Scale Large Scale Large Area Less Detail Small Area Greater Detail Absolute vs Relative Location Absolute=Latitude/Longitude Relative = defined by another location Waupaca has an absolute location of 44° 21' 29" N / 89° 5' 9" W New London is 20 miles east of Waupaca Types of Maps: General Purpose Political Physical/Topographical Types of Maps: Special Purpose Black Bear Habitat Population Density Correlation vs Cause & Effect Types of Special Purpose Maps Economic Activity Population Distribution Natural Resources Climate Zones Ecological Regions Political Affiliation Religious Affiliation Other Tools used by Geographers Line Graphs Excellent for measuring changes over time Bar Graphs Good for comparing Items to each other University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Circle/Pie Graphs Good for comparing items to a total or to other items Charts & Tables Used to organize data for convenient display, comparison & understanding Continent Population Land Area 810 Million 11.6 Million Square Miles No Permanent 5.5 Million Square Miles Asia 3.7 Billion 12.2 Million Square Miles Australia 19 Million 2.9 Million Square Miles Europe 727 Million 8.8 Million Square Miles North America 491 Million 8.7 Million Square Miles South America 350 Million 6.8 Million Square Miles Africa Antarctica Diagrams Show the relation of objects or ideas to each other The Five Themes of Geography Location: Position on the Earth's Surface (Absolute/Relative). Place: Physical and Human Characteristics of the location. Human/Environment Interactions: Shaping the Landscape. Movement: Humans Interacting on the Earth. Regions: How They Form and Change.