* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Emirate of Crete wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Constantinople wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine–Arab wars (780–1180) wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine dress wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
State church of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
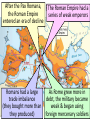
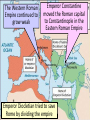
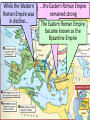
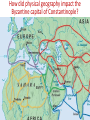
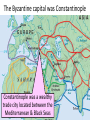
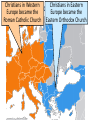
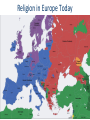
■Essential Question: –What is the significance of the Byzantine Empire? What happened to the Roman Empire by 500 A.D.? AfterThe the Pax Romana, The Roman Empire had a Fall of the Roman Empire the Roman Empire series of weak emperors entered an era of decline Romans had a large As Rome grew more in trade imbalance debt, the military became (they bought more than weak & began using they produced) foreign mercenary soldiers The Western Roman Empire continued to ■ Textgrow weak Emperor Constantine moved the Roman capital to Constantinople in the Eastern Roman Empire Emperor Diocletian tried to save Rome by dividing the empire By 476,The barbarians Fall ofconquered the Roman Empire the Western Roman Empire The Western Roman Empire fell into the Middle Ages (“Dark Ages”) from 500 to 1300 A.D. What happened in the Eastern Roman Empire? While the …the EasternEmpire Roman Empire TheWestern Fall of the Roman Roman Empire was remained strong in decline… The Eastern Roman Empire became known as the Byzantine Empire How did physical geography impact the Byzantine capital of Constantinople? ■ Text The Byzantine capital was Constantinople Constantinople was a wealthy trade city located between the Mediterranean & Black Seas Byzantine Capital of Constantinople The Byzantine Empire ■Citizens in the Byzantine Empire thought of themselves as Romans & they shared some similarities with the Roman Empire: –The Byzantine Empire kept alive Greco-Roman culture –Constantinople was a center for learning where schools taught philosophy, medicine, Greek and Latin grammar, geometry The Byzantine Empire ■Citizens in the Byzantine Empire thought of themselves as Romans & they shared some similarities with the Roman Empire: Roman Pantheon How was architecture similar? Byzantine Hagia Sophia The Byzantine Empire ■Citizens in the Byzantine Empire thought of themselves as Romans & they shared some similarities with the Roman Empire: –Constantinople used Roman-style architecture such as arches & domes –Byzantine cities had forums for trade & arenas to entertain citizens One of the most impressive architectural buildings in the Byzantine Empire was a Christian cathedral called the Hagia Sophia The Byzantine Empire ■Citizens in the Byzantine Empire thought of themselves as Romans & they shared some similarities with the Roman Empire: –The official language was Latin, but most Byzantines spoke Greek The Byzantine Empire ■Citizens in the Byzantine Empire thought of themselves as Romans & they shared some similarities with the Roman Empire: Religion in the Byzantine Empire Religion in the late Roman Empire How was religion similar? Because of its location close to Judea, most Byzantines had converted to Christianity before those in the Western Roman Empire The Byzantine Empire ■Citizens in the Byzantine Empire thought of themselves as Romans & they shared some similarities with the Roman Empire: –Both the Roman & Byzantine Empires were ruled by Byzantine Roman emperors who had absolute government government power over the empire –Justinian was the most How was famous Byzantine Emperor government similar? About 50 years after the fall of Rome, Byzantine Emperor Justinian came to power & began reconquering Roman territories In addition to empire building, what else did Emperor Justinian value? The Justinian Code ■ To oversee his new empire, Justinian ordered legal experts to consolidate old Roman laws into a single law code –The Justinian Code served as the legal basis for criminal justice, marriage, property, slavery, & women’s rights –The law code became one of the most important legacies of the Byzantine Empire & served as the basis for laws for the next 900 years Justinian ■ In addition to expanding the empire & creating a uniform set of laws, Emperor Justinian also began large building projects –He ordered the construction of the Hagia Sophia to show the importance of the church –He built hospitals, aqueducts, public baths, schools, & courts Empress Theodora ■ Justinian’s wife Theodora had a lot of power & influence in the Byzantine Empire: –She met with & wrote to foreign leaders –She advised Justinian & helped him pass laws –She encouraged building of Christian cathedrals The Division of Christianity ■ Because of the distance & lack of contact between Byzantine Empire & Western Europe, Christianity developed differently –All Christians based their faith on Jesus & the Bible –But they had different practices to show their faith The Division of Christianity ■ Christians were organized the same way: –Archbishops & bishops oversaw regions where Christianity was practiced –Priests led individual churches ■But, Christians in the East & West disagreed over leadership of the Church The Division of Christianity ■ Christians in Western Europe: –Believed that there should be a Pope to oversee bishops & give authority to all Christians –Christians in Western Europe accepted the authority of the Pope The Division of Christianity ■ Christians in Eastern Europe: –Believed that the Byzantine Emperor had authority over issues involving Christianity –Byzantine emperors relied on a Patriarch to oversee the church, but the emperor had final authority –Christians in the Byzantine Empire did not accept the authority of the Pope The Division of Christianity ■One of the biggest controversies among Christians was the use of icons: –Icons were religious images to help Christians in their prayers & worship –Some Christians thought this was “idol worship” –In 730, the Byzantine Emperor banned icons & many Christians rioted Emperor Leo III ordered the destruction of icons in the Byzantine Empire Riots broke out between people who wanted icons & iconoclasts (those who wanted to ban icons) The Pope in Western Europe supported the use of icons & called the Byzantine Emperor a heretic (a believer of false ideas) The Pope excommunicated the emperor (kicked him out of the church) The Division of Christianity ■These disagreements led to deep divisions among Christians & the Great Schism (split) occurred in 1054: Christians in Western Christians in Eastern The Division of Christianity Europe became the Europe became the Roman Catholic Church Eastern Orthodox Church The Division of Christianity Roman Catholics & Eastern Orthodox Christians practice their regions differently: Religion in Europe Today