* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CLASSICAL civilization in the mediterranean
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
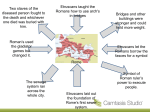
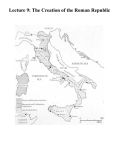
ROME 509 BCE – 476 CE The Roman empire ruled large parts of Europe, North Africa and the Middle-East for hundreds of years. This made it very influential to the cultures/societies of these places. Roman developments in government – having a written constitution and clear laws that protect people’s rights, representative government; having a government that balances power between different people/groups have a big influence on our government Romans believed their citystate was found in 753 BCE (pictured being fed by a wolf) In truth, the ancestors of the Romans were IndoEuropean nomads know at LATINS that settled the area around 2000 BCE 3 The Romans shared Italy with other people like Greeks and Etruscans. The Romans borrowed a lot of ideas and technologies from the Etruscans & Greeks. The Etruscans were Originally from Anatolia Colonized Roman regions in 9th or 8th c. Society declines late 6th c. BCE due to Greek maritime attacks Celtic invasions from north Absorbed by Romans 4 How did the Etruscans influence Rome’s development? Romans probably learned about monarchy from them. Etruscans ruled Rome for a while and helped the development of city – engineering to drain wetlands around city, how to build arches, walls, roads, administration Brought in trade Arts – Taught Romans sculpture, terracotta, jewelry, pottery Religion – Romans borrowed some gods and religious practices Monarchy through 7th6th c. BCE under Etruscans Major center of trade routes made it increasingly wealthy & important. 7 In 509 BCE the Romans overthrow the last Etruscan king & created an aristocratic republic. The Senate was created (like our Senate/Congress) to make laws for the republic Only patricians (upper-class aristocrats with lots of land) could be in it. They elected 2 consuls every year to lead the city (like our president) By having two and only letting them serve for 1 year they hoped to prevent consuls from getting too much power & becoming like kings. Senate could also appoint DICTATORS with complete control of government for 6 month during emergencies. 8 Like in Athens, as the city grew, regular people like artisans, merchants, and farmers also wanted a say in the government. To prevent riots by these PLEBEIANS (average citizens) The PATRICIANS started making the government more democratic. IN 450 BCE they published all the laws in the Twelve Tables so people would know their rights 9 IN the 4th century BCE, the plebeians gained the right to elect TRIBUNES that represented them in the government and could VETO, or block, laws passed by the senate. Eventually, plebeians could also be voted consuls. Dominated and conquered Etruscan and Greek city-states through war and diplomacy (alliances) By 270 BCE they controlled most of the Italian Peninsula Expansion via military threat and incentives Conquered areas treated justly If people accepted Roman rule, paid taxes, and supplied soldiers, they could keep their customs and local laws Eventually could become citizens equal to Romans 11 After conquering Italy, Rome came into more contact with Carthaginian Empire. Carthage was a city-state in North Africa started by Phoenician traders. They controlled many cities in north Africa, Spain, and Sicily. Rome and Carthage fight 3 major wars between 264-164 BCE – The PUNIC WARS. Mostly fighting over territory like Sicily that provide grain for food. 12 Led by Hannibal who invades Rome during the 2nd Punic War, Carthage almost wins. Rome eventually comes back and destroys Carthage and sells its people into slavery Later conquers Greece. Rome dominates Mediterranean by middle of 150 BCE 14 The Expansion of the Roman Empire, 133 B.C.E. 16