* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Early Middle Ages: Germanic Kingdoms Unite under
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Carolingian art wikipedia , lookup
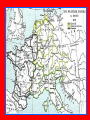
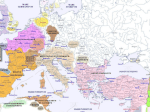
The Middle Ages The Early Middle Ages: Germanic Kingdoms Unite under Charlemagne What Happened to Rome?? th 5 • By the end of the century, Germanic invaders had destroyed the Roman Empire… What Happened to Rome?? • The Impact of Invasion: • Disruption of Trade • Downfall of Cities • Population Shifts • Decline of Learning • Loss of Common Language What Happened to Rome?? • BUT, there was one institution that survived the fall of Rome… The CHURCH!! Germanic Kingdoms Emerge Germanic Kingdoms Emerge • Between AD 400 & 600 small Germanic Kingdoms replaced large Roman provinces • What impact did these small kingdoms have on government? Germanic Kingdoms Emerge • In GAUL, a Germanic people called the FRANKS held power • Influential Frankish Ruler: • Clovis Germanic Kingdoms Emerge • CLOVIS: • Converted to Christianity • Gained support of the Church in Rome • United Franks into one kingdom Europe & the Muslim World Europe & the Muslim World • 622: The development of Islam… • The Muslims built a huge empire & began to overrun Christian lands Europe & the Muslim World • Battle of Tours (732): • Frankish ruler, Charles Martel defeated a Muslim raiding party from Spain Europe & the Muslim World • Important victory for European Christians • Made Charles Martel a Christian hero The Family Tree • Charles Martel • Martel’s SON: • Pepin the Short • Pepin’s SON: • CHARLEMAGNE (Charles the Great) Charlemagne Charlemagne’s Empire • Empire included: • 2/3 of Italy • All of present day France • Small part of Spain • All of German Saxony Charlemagne, the Hero? • Spread Christianity through his conquest of other lands • AD 800 – Pope Leo III called Charlemagne to Rome in order to crush an unruly mob • SUCCESS!!! Charlemagne, the Hero? • In gratitude, the Pope crowned Charlemagne & called him the “Roman Emperor” Charlemagne, the Hero? • Significance? • A Christian Pope crowned a German king as the successor to the Roman Emperors • Legitimized Charlemagne’s rule over the former Roman Empire Charlemagne, the Hero? • Revived the ideal of a UNITED CHRISTIAN COMMUNITY • Also paved the way for future power struggles between Roman Catholic Popes and German Emperors Charlemagne’s Accomplishments • Government: • Appointed nobles to rule over local regions • STRONG, EFFICIENT & ORDERLY! Charlemagne’s Accomplishments • Learning: • Wanted to make a “second Rome” in Aachen • Revived Latin learning Charlemagne’s Accomplishments • Curriculum included grammar, rhetoric, logic, arithmetic, geometry, music & astronomy • Became the EDUCATIONAL MODEL for Medieval Europe Charlemagne’s Heirs • A year before his death, Charlemagne crowned his only surviving son, Louis the Pious, as emperor Charlemagne’s Heirs • Louis was an INEFFECTIVE leader, but had 3 sons: • Lothair, Charles the Bald & Louis the German • Fought for control of the empire… Charlemagne’s Heirs • Civil War ended in 843 with the TREATY OF VERDUN • Divided Charlemagne’s Empire into 3 Kingdoms Charlemagne’s Legacy • Despite the breakdown of the empire, Charlemagne left a lasting legacy… 1. Extended Christian civilization into N. Europe Charlemagne’s Legacy 2. Further blended Greek, Roman & Christian traditions 3. Educational model 4. Strong, efficient gov’t – example for later medieval rulers