* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hyphae spores
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
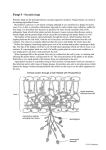
1. Chitin:____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 2. Hyphae: ________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3. Mycelium:_________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 4. Fruiting Body:______________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 5. Mycorrhizae:_______________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 6. Sporangia:________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 7. Lichen:___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 1. Describe how fungi use hyphae to obtain their food. 2. Describe a typical fruiting body of sac fungi, bread mold, and club fungi. 3. Sporangia are formed during the life cycle of a typical bread mold. At what stage are they formed? 4. Draw a flowchart showing the sequence of steps in the reproduction of yeast, a single celled fungus. 5. The mycelium of a fungus grows underground. In what ways might this be helpful for the fungus? 1. How do fungi contribute to the balance of an ecosystem? 2. What are three reasons lichens are useful to humans? 3. Draw a Venn diagram comparing lichens and mychorrhizae. Include terms such as roots, photosynthesis, and mutualism. 4. Some antifungal medications can damage the patient’s own tissues. Why doesn’t this problem occur with antibiotics? 1. Multicellular 1. Multicellular a. With the exception of yeast 2. Nucleus 2. Nucleus a. Can be more than one 3. Cell Wall a. Made of Cellulose 4. Absorb Water and Nutrients a. Roots 5. Contain Chlorophyll a. Autotrophic 3. Cell Wall a. Made of Chitin 4. Absorb Water and Nutrients a. Hyphae 5. Do Not Contain Chlorophyll a. Heterotrophic: -Saphrophytes -Parasites 1. __________________ Multicellular a. _______________ Except yeast 2. __________________ Eukaryotic 3. __________________ Have Cell Walls a. _______________ Made of Chitin 4. __________________ Heterotropic MYCELIUM _______________: underground network of hyphae that have grouped together. Produce ____________________ which FRUITING BODY is a reproductive structure of a fungus and grows above ground. Fruiting Body THREAD-LIKE _____________________ chains of ___________ CELLS that form the _______ of a fungus BODY and ____________________ MYCELIUM Hyphae Mycelium ENZYMES Hyphae secrete ________________________ to break down dead/living NUTRIENTS material. Once the material is broken down into simpler _________________, HYPHAE the food is absorbed through the fungus’ ___________________ Pieces of _____________________ can ____________________ and form into BREAK OFF HYPHAE new fungi. (ASEXUAL _________________________________ REPRODUCTION) FUSE Hyphae can _________________ together and create ____________________. _________________________________ (SEXUAL REPRODUCTION) NEW HYPHAE REPRODUCTIVE STRUCTURES -________________________ that grow into new organisms. -Adapted for dispersal and _____________ SURVIVING for extended period of time in unfavorable conditions . SACS SPORANGIA CLUB-SHAPED PARTS PRIMITIVE FUNGI _______________ Chytridiomycota SAC FUNGI _________________ Ascomycota SP0RANGIA FUNGI ________________ Zygomycota 1. 1. Smallest/Simplest 1. Form a sac called ascus 2. Mostly aquatic 2. 3. Spores with Flagella Ascus contains spores for 2. reproduction Sporangia produce spores for reproduction 4. Decomposers or parasites 3. Yeasts, Penicillium, morels, truffles 5. Chytrids Range for molds on 2. spoiled food to fungi used to ferment foods 3. 3. Contain sporangia CLUB FUNGI _______________ Basidiomycota 1. Contain club-shaped parts that produce spores for reproduction. Club parts produce spores for reproduction Contain mushrooms, puffballs, shelf (bracket) fungi. Also include rusts and smuts _______________ HYPHAE FROM DIFFERENT FUNGI JOIN TOGETHER _________________ THEN GROW INTO SPORANGIA __________________ THAT RELEASE __________________, SEXUAL SPORES (COMBINED _________) DNA HYPHAE ____________ break apart, and form new fungi SPORES ____________ are released by fungi and form new fungi SPORES •Produce _____________ in saclike structures called __________________. ASCI BUDDING •Reproduce by _______________ & SPORES ____________________ •Useful to humans •Bread •Alcohol •Penicillium •Blue Cheese YEASTS TRUFFLES MORELS PENICILLIUM CUP MILDEW HYPHAE ____________ break apart, and form new fungi SPORANGIA DNA SPORES ____________ are released by fungi and form new fungi •Branch out and feed with hyphae ________________ •Reproduce by producing spores in ________________________ sporangia •Sporangia are structures, found on the tips of hyphae that make __________ spores CAP GILLS STIPE •Form Branches of MYCELIUM ____________________ underground HYPHAE (MYCELIUM) •Have gills under their _________________ that house the CAP CLUB LIKE PARTS _________________________ that produceSPORES _____________ for __________________. REPRODUCTION •Spores are found IN BETWEEN GILLS __________________________ _________________________________ ON CLUB LIKE PARTS! PARASITES 1. _______________________________: PATHOGENIC DISEASE a. Can be _____________________ and cause ______________ * In Plants: DUTCH ELM DISEASE caused by sac fungus - _______________________ FRUIT - Destroy ___________________ crops * In Humans: ATHLETE’S FOOT - ___________________ - ___________________ NAIL FUNGUS RING WORM - ___________________ - ___________________ YEAST INFECTIONS DECOMPOSERS 2. _____________________________: (____________________) SAPHROPHYTES ONCE LIVING THINGS a. Break down ___________________________ LOGS LEAVES ANIMALS b. _______________, _________________, _______________ c. Helpful: MINERALS NUTRIENTS * Return ___________________ and _______________ back into the soil. ‘HARD’ * Break down _______________ plant materials that cannot be used without first being broken down by decomposers. d. Harmful: • Deteriorate __________________ WOODEN houses, boats, etc • REPRIATORY ILLNESS Causes __________________________ MYCORRHIZAE ______________________: Partnerships between _______________ and FUNGUS CERTAIN PLANTS roots of ________________ Fungus help plants to ‘FIX’ NITROGEN ______________________, Plants provide FOOD _____________ for the fungus. LICHEN ______________________: Partnerships between _______________ and FUNGUS ORGANISM WITH CHLOROPHYLL ______________________ Fungus supplies organism WATER with chlorophyll _________ And HABITAT ______________________, Plants provide FOOD _____________ for the fungus. C