* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 05WHAT
Forensic anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Western European marriage pattern wikipedia , lookup
Ethnicities of the Philippine Cordilleras wikipedia , lookup
Descent from antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural differences in decision-making wikipedia , lookup
Intercultural competence wikipedia , lookup
Matrilineality wikipedia , lookup
Post-processual archaeology wikipedia , lookup
American anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Tribe (Internet) wikipedia , lookup
Political economy in anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness in humans wikipedia , lookup
Ethnography wikipedia , lookup
Structural anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Social Bonding and Nurture Kinship wikipedia , lookup
Ethnoscience wikipedia , lookup
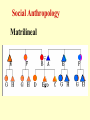
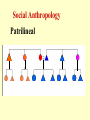
Cultural Anthropology Ethnography Ethnology Social Anthropology Linguistics Ethnography (ethnos, a people+graphos, a writing) An attempt to give an accurate, objective, valid, reliable account of the way of life of a specific group of people. This is the basic descriptive level of cultural anthropology. Participant Observation is major feature. Laura Tamakoshi’s (above) work in New Guinea is another. Margaret Mead’s work with the Samoans is a good example. (Margaret Mead also worked in New Guinea.) Ethnology (ethnos, people+logos, word) An attempt to give an accurate, objective, valid, reliable account of the way of life of a larger set of people. A higher level of generalization…. E.B. Tylor The Science of Culture. Ethnologists try to find patterns of behavior that are common to the various groups under investigation. The Comparative Method is an important tool. Cultural Universals…cultural traits manifest in kinship systems religion some way in all cultures under study. language Social Anthropology Area of anthropology most like sociology. Differs mainly on areas of emphasis and the professional identification of the individual. Social Anthropology Social anthropologists been Sociologists have been have concerned concerned mainly with mainly with own society. Kinship and Descent traditional society. Social Anthropology Kinship and descent are Cultural Universals. Genealogical Space – Space that contains all human beings. Social Anthropology Genealogical Space Descent Males Females Marriage affinal consanguineal Generation consanguineal Social Anthropology The investigation of kinship terminology begins with a distinction between kin types and kin terms. Kin types refer to the basic uncategorized relationships that anthropologists use to describe the actual contents of kinship categories. They are supposedly culture free, etic components. Kin terms are the labels for categories of kin that include one or more kin types. They are emic structures and vary across cultures. Social Anthropology Kin Types Primary components and letter symbols Mother [M] Father [F] Sister [Z] Brother [B] Daughter [D] Son [S] Husband [H] Wife [W] Social Anthropology Social Anthropology Social Anthropology Rules of Descent Bilineal (Bilateral) Unilineal Matrilineal Patrilineal Social Anthropology Bilineal Eskimo Kinship Similar to “American” system Social Anthropology Matrilineal Social Anthropology Patrilineal Social Anthropology Comparison of Patrilineal with Matrilineal Descent Patrilineal Matrilineal Strong marriage Brittle marriage Patrilocal residence Matrilocal residence Strict sex rules Lax sex rules No marriage rule X-cousin marriage Prescribed Proscribed Social Anthropology Rules of Residence Neolocal Associated with bilineal descent Matrilocal Associated with matrilineal descent Patrilocal Associated with patrilineal descent Ambilocal Associated with bilineal descent Social Anthropology Forms of Marriage Rules of Marriage Monogamy Endogamy - Marriage within group One spouse Polygamy Exogamy - Marriage outside group Multiple spouses Polygyny Multiple wives Polyandry Multiple husbands Social Anthropology Family relatives Nuclear families Extended families Four functions of families Nurturance Sex control Economic foundation Enculturation Linguistics Study of Language Language is a system of vocal symbols by means of which human beings interact in terms of their culture. Linguistics !Kung Study of Language The three S’s of language: Sound No Phonology, languagePhonetics, uses all sounds Phonemics Phonemes “packets” of similar humans can-make. sounds recognized as same sound. Shape Grammar; - of rules to put Morpheme -syntax basic of sound Morphology stydyunit shape of to sounds togetherhas been attached. which meaning language Sense All languages make sense(meaning). to the Semantics study of sense Sapir-Whorf peopleHypothesis who use them…They are equal in this regard. Linguistics Chronemics Olfactics Haptics Kinesics Proxemics Oculesics In many other cultures, time is Time The study in USof is meanings, a sequence….a usagecommodity time is experienced polychronically to be communication spent, used, wasted…. and of time. rather than sequentially. Concerned with systems of smell Communication through the skin….i.e. Touching by Ashley Montague Bodily movement, facial expression, etc. Ray Birdwhistell is pioneer Communication by use of space…. Edward T. Hall’s work, for example Communication involving the eyes Includes paralanguage… It’s not what you say, it’s Metalanguage/Vocalics the way you say it.