* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 32 - Workforce Solutions
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Animal locomotion wikipedia , lookup
Animal cognition wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Animal communication wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
Animal coloration wikipedia , lookup
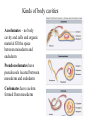
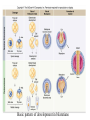
Chapter 32 Overview of Animal Diversity General features of Animals • • • • • Animals are heterotrophs and multicellular Muscle and nervous system (high mobility) Diverse in form and habitat Sexual reproduction Characteristic pattern of embryonic development Five key transitions in animal evolution • Evolution of tissues allowed specialization • Evolution of different forms of symmetry (radial or bilateral) • Evolution of body cavity • Evolution of different patterns of development • Evolution of segmentation or repeated units in body Tissues evolved allowing specialized functions • Parazoa – lack definite symmetry and lack tissues and organs. Example-sponges can differentiate and dedifferentiate • Eumetazoa – have well-defined symmetry and well defined tissues and differentiation is irreversible Radial or Bilateral Symmetry Symmetry - arrangement of body parts Kinds of symmetry: • Radial symmetry (Parts of body arranged around a central axis and any plane passing through axis can divide the organism to form mirror images). Phylum Cnidaria • Bilateral symmetry have dorsal and ventral surfaces have anterior and posterior ends show cephalization - concentration of nervous tissue at the anterior end of an organism Phylum Chordata Three germ layers (except sponges) • In most animals – ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm • Outer ectoderm develops into body coverings and nervous system • Middle mesoderm develops into skeleton and muscles • Inner mesoderm develops into digestive organs and intestines Kinds of body cavities Acoelomates – no body cavity and cells and organic material fill the space between mesoderm and endoderm Pseudocoelomates have pseudocoels located between mesoderm and endoderm Coelomates have coelom formed from mesoderm What led to development of circulatory systems? • Development of a coelom created problems with circulation of nutrients and removal of wastes. Coelomates developed Circulatory systems • Open circulatory systems – the blood passes from vessels into sinuses where it mixes with body fluids before it returns to the vessels • Closed circulatory systems – blood flow is continuous through vessels separated by body fluids Basic pattern of development in bilaterians Embryonic development of Protostomes and Deuterostomes • Protostomes • Embryonic cells cleave in spiral pattern • Exhibit determinate development • Blastospore becomes animal’s mouth • Coelom originates from mesodermal split • Deuterostomes • Embryonic cells cleave in radial pattern • Exhibit indeterminate development • Blastospore becomes animal’s anus • Coelom originates from invagination of archenteron Segmentation • Segmentation is convergent • Allows redundant organ systems • Allows for more efficient and flexible movement • Found in annelids, arthropods and chordates but now segmentation is common in many other animals. Taxonomy: Kingdom Animalia • contains well over 30 phyla • basic categories: invertebrates - animals without a backbone vertebrates - animals with a backbone Role of Molecular Biology in evolution of animals • Molecular Biology is helping scientists understand the origins of animal clades • Rapid diversification (due to evolution of Hox genes) of animals started in beginning of Cambrian period – Cambrian explosion This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against any individual in the United States, on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age disability, political affiliation or belief; and against any beneficiary of programs financially assisted under Title I of the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 (WIA), on the basis of the beneficiary’s citizenship/status as a lawfully admitted immigrant authorized to work in the United States, or his or her participation in any WIA Title I-financially assisted program or activity. “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.”