* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Classification
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
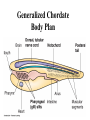
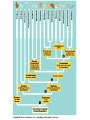
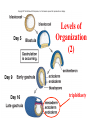
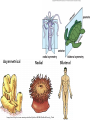
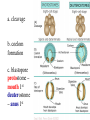
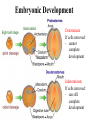
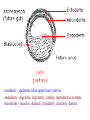
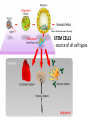
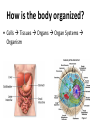
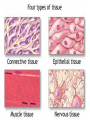
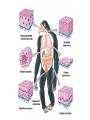
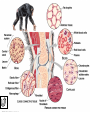
Animal Classification Pictorial References Page # 368 370 371 386 Figure# 18.1B 18.3A-D 18.4 18.15 Diagram Gastrulation Body Plans Animalia Phyl. Tree Chordates Phyl.Tree 9 Animal Phyla 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminths Nematoda Mollusca 6. Annelida 7. Arthropoda 8. Echinodermata 9. Chordata Major Body Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Digestion* 6. Immune Respiration* 7. Hormone Circulation* 8. Reproduction Excretory* 9. Skeletal Nervous/Senses* Generalized Chordate Body Plan Questions to Answer 1. What is the function of this organ/system? 2. What is the relationship of structure to function? (i.e. how does the shape of this structure assist in its function?) 3. How does this system show adaptations to the animal s environment? Phylogenetic Tree (p.371) Criteria for Classification a. b. c. d. level of organization – no. of germ layers symmetry – shape of body body cavity – type of body cavity embryonic development – formation of digestive tract e. support – internal/external skeleton f. segmentation – compartments to body Levels of Organization Day 1 " (1) Day 2" Day 3" Day 4" Day 5" Day 5" Levels of Organization (2) Day 9" Day 16" triploblasty Body Symmetry (2) 1) Asymmetry – no symmetry *sponges 2) Radial symmetry – can be divided into equal parts from top orientation *starfish 3) Bilateral symmetry – can be divided into halves lengthwise *worms, insects, mammals Image from : http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookDiversity_7.html Body Cavity (3) • acoelomate – no coelom (solid mesoderm) • pseudocoelomate – coelom surrounds cavity (hydroskeleton) • coelomate – mesoderm surrounds cavity (guts are separated) Image from : http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookDiversity_7.html Body Support (4) 3 Types of Skeletons: 1. hydrostatic – water-filled body cavity *sea anemone 2. exoskeleton – muscles attach to outer covering made of chitin *crustaceans, insects 3. endoskeleton – muscles attach to inner bones *vertebrates a. cleavage b. coelom formation c. blastopore protostome – mouth 1st deuterostome – anus 1st Protostome Spiral Cleavage Schizoceoly Deuterostome Radial Cleavage Enterocoely Embryonic Development Determinate If cells removed: - cannot complete development Indeterminate If cells removed: - can still complete development endoderm – diges,ve & respiratory organs mesoderm – muscles, skeleton, circulatory & reproduc,ve & urinary organs, connec,ve ,ssue ectoderm – skin, CNS ectoderm – epidermis (skin upper layer) nerves endoderm – digestive, respiratory, urinary, reproductive systems mesoderm – muscles, skeletal, circulatory, excretory, dermis STEM C______ ELLS…. Inner cell mass becomes the baby STEM CELLS -‐ source of all cell types How is the body organized? • Cells à Tissues à Organs à Organ Systems à Organism Animal Classification Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. blastula gastrula blastopore acoelomate coelomate pseudocoelomate germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm) characteristics & examples of each: • porifera • nematode • cnidarian • mollusk • platyhelminth • annelid 8. radial & bilateral symmetry 9. protostome 10. deuterostome 11. radial or spiral cleavage 12. segmentation 13. amniote 14. cephalization 15. tissue organization • echinoderm • arthropod • chordate