* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 15.2 Single - Factor (One - Way) Analysis of Variance
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Strategic management wikipedia , lookup
Channel coordination wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Target costing wikipedia , lookup
Business process wikipedia , lookup
False advertising wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
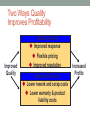
Dimensions Of Product Quality (Garvin) 1. Core Performance •basic operating characteristics 2. Features •“extra” items added to basic features 3. Reliability •probability product will operate, even in strenuous conditions 4. Convenience •Amount of effort required to use the product 5. Durability •life span before replacement 6. Serviceability •ease of getting repairs, speed & competence of repairs 7. Aesthetics •look, feel, sound, smell or taste 8. Safety •freedom from injury or harm 9. Personal image •subjective perceptions based on brand name, advertising, design labels, etc Additional Dimensions of Service Quality 1. Time & Timeliness •customer waiting time, completed on time 2. Accessibility & Convenience •ease of obtaining service 3. Face-to-Face interaction •treatment by employees 4. Accuracy •performed right every time e The Meaning of Quality Producer’s Perspective Quality of Conformance Production •Conformance to specifications •Cost Consumer’s Perspective Quality of Design •Performance quality •Product’s bundle of attributes & specifications •Price Fitness for Consumer Use Marketing Two Ways Quality Improves Profitability Sales Gains via Improved response Flexible pricing Improved Quality Improved reputation Reduced Costs via Lower rework and scrap costs Lower warranty & product liability costs Increased Profits Cost Of Quality • Control Costs (cost of achieving good quality) •Prevention •Appraisal • Failure Costs (cost of poor quality) •Internal failure costs •External failure costs Japanese vs US Quality Costs (1980s) 70 60 % of quality effort 50 40 Japan 30 USA 20 10 0 Design Product Produce Product Rework Product Resolve Customer Problems Quality And Productivity • Productivity = output / input • Fewer defects increase output • Quality improvement reduces inputs Quality Philosophies • Joseph Juran • Focus on actions and mind-set of managers; believed an organization’s culture is the root cause of quality problems • W. Edwards Deming • Developed statistical process control techniques • Six Sigma • Focus on reducing defects to achieve stable and predictable process results through statistical approaches and problem-solving • Total Quality Management • Management philosophy that advocates participation of every member in organization is part of effort to improve quality Total Quality Management 1. Customer defined quality and satisfaction 2. Top management leadership 3. Quality as a strategic issue 4. All employees responsible for quality 5. Continuous improvement 6. Shared problem solving/ Cross-discipline system approach 7. Statistical quality control: measurement of results 8. Mutually beneficial supplier relations Options to Improve Quality of Conformance • Consumer Education: product labeling, instructions, online resources • Follow-up Service: Recalls, extended warranties, replacements • Inspection of Work and Product • Preventative Procedures Preventative Procedures • Improve Quality of Design: Design product/process for robustness, poka-yoke, Taguchi Statistics • Implement Six Sigma • Involve Employees: Training, empowering, soliciting input • Form strategic supplier partnerships • Remove safety nets: carrying JIT inventory and requiring minimal lead times