* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Communication
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
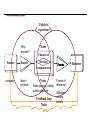
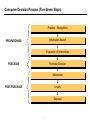
The communication process Fields of experience Why encode? Source Encode Noise Channel of Message Receiver Communication company Idea-> symbols Frame of Sales person, media, reference: public relations Attitudes, Noise Feedback loop Noise 1 values, beliefs Consumer Decision Process (Five-Seven Steps) Problem - Recognition Information Search PRE-PURCHASE Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Decision PURCHASE Satisfaction POST-PURCHASE Loyalty Disposal 2 Four Steps in the Book Awareness Exploration Commitment Dissolution 3 Evolution of Customer Buying Process Buying Process Awareness Traditional Market Communication Early Web Market Communication Informative Ads tv, radio, mags, outdoor. PR Sales promos: Free trial, deals, rebates Word-of-mouth buttons banners sponsorships Consideration Comparative ads Personal Selling Banners Links Preference Source: Forrester Research, Monitor Analysis 4 Comparative ads Personal Selling microsites brochureware web site Purchase point-of purchase promotions direct marketing daily specials sweepstakes first-time order incentives Loyalty Reminder Ads product experience buyers’ clubs e-mail alerts newsletters Microsites Microsites are communications tools that enable targeted information exchanges. Microsite work is a typical need for a corporation that already has a large-scale, fully-functional presence on the internet, but wishes to fulfill specific marketing campaign or business goals involving customer and prospect cultivation. Strategically focused, high impact and brand intense, microsites provide a vehicle for micro-targeted communication to a key audience. Microsites are agenda-based web solutions that serve a strategic purpose. Product and service announcements software demos event marketing (trade shows, seminars) prospect qualification & sales public relations customer cultivation branding enhancement 5 Four categories of Marketing Communications Strategies Individualized Customized Personalized Traditional Mass Marketing General Approaches Off-line On-line Audience Focus Broad Communication Media 6 The Four Categories of Communications Customized Personalized Permission Marketing—freebies Personalized Recommendations (rule-based, collaborative filtering) Personalized Advertisements Personalized Web Pages Personalized E-commerce (e-stores) Personal selling Direct Marketing General Approaches Traditional Mass Marketing Public relations Sales promotion Television Radio Magazines Newspapers Billboards 7 Web sites Banner Ads Search engines and shopbots Interstitials E-Mail (junk) Viral Marketing (Hotmail, NYTimes) Portal Sponsorship/Exclusive Agreements Associate/Affiliate Programs (directing to) On-line and Off-line Partnership: Full range Provide Information to Entice Customers Leverage Customer Base – reputation and trust Mass communication Banner ads CPM – Cost per thousand impressions – Rates vary by popularity and reach If millions view site – weekly flat fee Click-through rate -- # times viewers go to advertiser’s website. Slotting fees – for premium position, exclusivity in category, etc. Ad clicks, impressions, click-through, CPC (cost per click), CPM, Unique users (cookies), visits (30 minute time out). Interstitials– runs between pages on a website On main page In new smaller pages (pop-ups, pop-unders) Rich media Interruptive and hated but better brand recall and click-though rates 8 Communication Objective 1. Build brand awareness, recall, knowledge, preference, liking 2. Lead to purchase – promotions, coupons, sweepstakes For each marketing message, have a corresponding objective http://www.pepsi.com/pepsipromoscur/index.php http://www.sunnydelight.com/ http://www.snapple.com/home.asp www.cnn.com advertiser links 9 The Media Plan 1. Communication Criteria: Objectives, Budget, Segments 2. Media Criteria: Appropriate for objectives, segments, and budget Possible objectives: Brand awareness, consideration, preference, purchase, loyalty Increasing knowledge about a particular offering (Could fit in the first three stages) Making the brand more hip Reaching a new target 3. Media mix. Combine media to achieve consistency and efficiency 4. Allocate spending across media and over time 5. Evaluation and control (are objectives being met) 1 Ebay Case, p. 381 Awareness – Offline levers (ambassadors; alliances); Online Levers (Furby) Exploration– Offline Levers (ads on West Wing); Online Levers (keywrds on Google) Commitment– eBay stores Dissolution– kicking out bad users 1 www.monster.com 1 Monster.com 1 Monster.com discussion 1. What was the rationale for spending 15% of 1999 advertising budget on a single super-bowl 30 second spot? 2. The Monster.com-AOL allicance. America Online (AOL) and TMP Worldwide reached a content and marketing agreement on Dec. 1, 1999 that called for Monster.com to be the exclusive provider of career search services over seven AOL brands, including Digital City (which has a contract with HotJobs.com). Monster.com will create co-branded sites allowing AOL members and visitors to search for jobs, apply online, research companies and choose personalized geographic areas to help with their job searches. As part of that deal, TMP agreed to pay $100 million over the length of the fouryear contract. 1 Monster.com discussion 3. How else is Monster.com building its brand? 4. How and why is Monster.com building communities? 5. How might Monster.com strengthen its franchise given Jeff Taylor’s options: building its brand launching vertical extensions increasing geographical expansion 1