* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparative Psychology
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cyberpsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
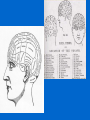
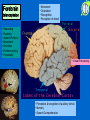
Biological Psychology 303 Fall 08 Lecture 1 You have been entrusted with the care and feeding of the most extraordinary and complex creation in the universe… Home to your… Thoughts, personality, cherished memories, future hopes… It orchestrates the symphony of consciousness that gives you purpose and passion, motion and emotion But what do you really know about it? I get no respect… Egyptians Indian Chinese Greeks Aristotle - necessary for life - emotion HB Hippocrates (460-370 B.C) Galen (130-200 A.D) Will the human brain ever completely understand its own workings? 3 major debates • Nature of neural communication • Localism vs Holism (Neurons) • Mind vs Brain (monism/dualism) 3 major debates • Mind vs Brain (monism/dualism) Mind-Body Question Dualist: mind separate from body Mechanist: Body is like a machine Mind controls the machine Body tells mind about the environment Rene Descartes (1596-1650) Pipes = nerves Water = fluids in body Hidden Value = Pineal Control Valve: Pineal Gland “Seat of the Soul” First technical model for the NS Innervation of the Pineal Dependent on the Light/Dark Cycle Debate: Mind vs Brain Mind vs Brain??? Monism: Dualism: Mind is product of brain Brain is physical mind is not Mind-Body Question..are you a monist or a dualist? 3 major debates • Mind vs Brain (monism/dualism) Still up for debate… Next Debate: Nature of Neural Communication: Settled Luigi Galvani (1596-1650) Italian Physician Physicist Electrical Stimulation of frog legs Contraction of the muscles “Animal Electricity” "While one of those who were assisting me touched lightly, and by chance, the point of his scalpel to the internal crural nerves of the frog, suddenly all the muscles of its limbs were seen to be so contracted that they seemed to have fallen into tonic convulsions. “ Doctrine of specific nerve energies All nerves carry electrical signals Different nerves = different outcomes Johannes Muller (1801-1858) German Physiologist Debate: Neural Communication Camillo Golgi (1843-1956) Italian Physician: Santiago Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) Spanish Histologist Silver Staining Method – continuous mass of tissues…one cytoplasm (holism) Labeled Cells “neuron doctrine” – discrete entities Nobel Prize 1906: Research on structure of the nervous Debate: Nature of Neural Communication Debate: Nature of Neural Communication 1. Neurons are discrete and autonomous cells that can interact 2. Synapses are gaps that separate neurons 3. Information is transmitted in one direction from dendrites (input) to the axon (output) 3 major debates • Nature of Neural Communication Settled… Next Debate: Localism vs Holism brought Anatomy & Psychology together discrete regions of brain controls specific functions = mental state localization Phrenology (personology) Franz Joseph Gall (1757-1825) German Physician Neuroanatomist Forebrain telencephalon • Movement • Orientation • Recognition • Perception of stimuli • Reasoning • Planning • Speech Produce • Movement • Emotions • Problem solving • Personality • Visual Processing • Perception & recognition of auditory stimuli • Memory • Speech Comprehension Wilder Penfield (1891-1976) American-Born Canadian Neurosurgeon: • Greatest neurosurgeon of all times • mapped the brain • direct stimulation of the brain •“Grandmother Cell" • Localism vs holism? Most Valuable Player “The Organization of Behavior” (1949) First comprehensive theory on how psychological phenomena might be produced by BRAIN ACTIVITY Donald O. Hebb (1904-1985) perceptions emotions thoughts memories Canadian Psychologist A large brain, like large government, may not be able to do simple things in a simple way. Donald O. Hebb “Cell Assemblies” Synaptic transmission Material basis mental associations “Connectionism” LTP Hebb based his theories •humans and animals •clinical case studies •logical arguments = eclectic approach became a hallmark of biopsych http://www.psych.ualberta.ca/~tcpeters/great_can_ws/dhebb.html 3 major debates • Localism vs Holism a little of both going on… Watson & Crick ( 1953) discovered chemical structure of DNA Nature 171, 737-738 (1953) Molecular structure of Nucleic Acids WATSON, J. D. & CRICK, F. H. C. Medical Research Council Unit for the Study of Molecular Structure of Biological Systems, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge. A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid New debate Nature vs Nurture New debates Nature vs Nurture <> (0.11 seconds) Francis Collins Human Genome Project (NIH) www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/seq/ “NCBI Genome Project” Sequencing of the human genome: “the book if life” J. Craig Venter Celera Genomic Neuroscience Biopsychology: the study of the biological basis of behavior the study of : Neuroanatomy: structure of NS Neurochemistry: chemical bases of neural activity Neuroendocrinology: interactions btw NS & endocrine system Neuropathology: disorders of NS Neuropharmacology: drugs effects on NS – neural activity Neurophysiology: function & activity of the NS Divisions Biopsychology Physiological Psychology: neural mechanisms of behavior by direct manipulation of the brain (Experimental) Psychopharmacology: neural activity and behavior with drugs (Experimental & Applied) Neuropsychology: psychological effects of brain damage in humans (Applied) Psychophysiology: relation bwt physiological activity & psychological processes in humans – non invasive (Experimental..also Applied) Comparative Psychology: compare behavior btw species, evolutionary level (experimental) Cognitive Psychology: non invasive study of brain, cognition, information processing (Applied, Experimental)