* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Korean War
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Germany wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
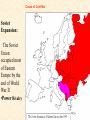
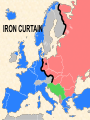
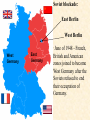
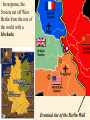
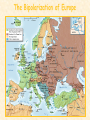
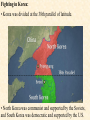
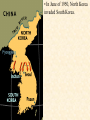
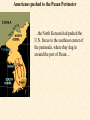
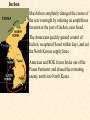
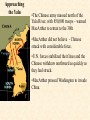
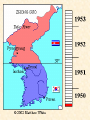
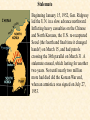
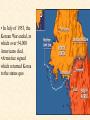
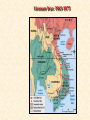
Objective: To examine the causes of the Cold War. Big Three: •Yalta Conference •Potsdam Conference •Division of Germany, war time trials, reparations? • http://www.mrallsophistory.com/fire.html Cold War Historiography • Orthodox School – Blamed Soviets • Revisionists – US the aggressor • Realist – Less moralistic; pragmatic politics WWII and Cold War • Pre-War Relations • Second Front • Yalta Conference (Feb 1945) – US needs Russian help in Japan – Eastern Europe’s fate left unclear • Truman and the Bomb – Potsdam Conf. (July 1945) – Unconditional surrender – Timing and message to Soviets Cold War Heats Up • • • • Future of Germany Atomic Diplomacy Iron Curtain Speech Kennan’s Telegram (1946) – Birth of Containment Policy Differing World Visions Cause of Cold War • United States – Saw stable and secure world by spreading American ideas and values – Must be internationally active • Soviets shaped by invasions – WWII losses – Seek secure border – Demand buffer zone Battle of Stalingrad Cause of Cold War Soviet Expansion: · The Soviet Union occupied most of Eastern Europe by the end of World War II •Power Rivalry After World War 2, many government and economic systems changed! • Many countries became communist after World War 2 including: - Czechoslovakia (1948) - Poland (1947) - Hungary (1947) - China (1949) Free Elections as promised? - Cuba (1959) - North Korea (1945) • In 1946, Winston Churchill correctly warned that the Soviets were creating an “iron curtain” in Eastern Europe. Winston Churchill giving the “Iron Curtain” address at Westminster College on March 5, 1946 IRON CURTAIN Peep under the Iron curtain March 6, 1946 • USSR wanted to spread its ideology of communism worldwide; US wanted to spread its ideology worldwide. • Question of who controlled atomic bombs. • Both countries feared an attack from each other. • Division of Europe – Eastern Europe became Communist.. due to free elections? • Truman did not personally like Josef Stalin. • USSR “reparations” policy in the part of Germany it had occupied. Focus on Berlin • Germany divided into four zones French, British, American, and Soviet troops. Occupation zones after 1945. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone. Soviet blockade: East Berlin West Berlin West Germany East Germany ·June of 1948 - French, British and American zones joined to become West Germany after the Soviets refused to end their occupation of Germany. · In response, the Soviets cut off West Berlin from the rest of the world with a blockade. Eventual site of the Berlin Wall Berlin Airlift: · President Truman decided to avoid the blockade by flying in food and other supplies to the needy people of West Berlin. · At times, over 5,000 tons of supplies arrived daily. Marshall Plan and the Berlin Airlift Germany remains divided: · In May of 1949, Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union ended the blockade. · The Soviet zone of Germany, including East Berlin, became known as the nation of East Germany. October, 1949 · By 1948, every Eastern European country was under communist control. American Response: · Truman Doctrine – statement of President Truman that promised military and economic support to nations threatened by communism • In 1947, the U.S. gave $400 million to Greece and Turkey in order to help them put down communist revolts. The domino effect • USSR influence on other communist countries. • US worried about USSR power. • Domino effect (one country becomes communist, then another, then another etc) Cold War Heats Up • Truman Doctrine (1947) – Implements containment policy • Marshall Plan (1947) – Helps US economy – Undermines conditions for communism • NSC-68 Aid for Europe: · Secretary of State George Marshall toured Western Europe and witnessed widespread homelessness and famine. Children in a London suburb, waiting outside the wreckage of what was their home. September 1940. German bombers set the whole inner city of Rotterdam ablaze, killing 800-900 of its inhabitants.” * Aerial view of the ruins of Rotterdam. Jewish children in the Warsaw Ghetto in 1942 · Weak countries in ruins were considered easy prey for Communist. To prevent, US would send aid to rebuild economy in what became known as the Marshall Plan. Nuremberg, Germany, April 20, 1945 * The U.S. gave over $12 billion in aid to European countries between 1948 and 1952, helping to improve their economies and lessen the chance of communist revolutions. Mao’s Revolution: 1949 Who lost China? – A 2nd Power! Communist NSC-68 policy WHY? • • • • Soviets explode their first atomic bomb China goes Communist Conflict is unavoidable Cannot trust Soviets WHAT? • Expanded military expenses from $13 b to $50 b per year The Bipolarization of Europe North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) Mutual defense alliance United States Luxemburg Belgium Netherlands Britain Norway Canada Portugal Denmark 1952: Greece & Turkey France Iceland Italy 1955: West Germany 1983: Spain OAS – Organization of American States • US in theory gives up policeman role in Western Hemisphere to the OAS Warsaw Pact (1955) } U. S. S. R. } East Germany } Albania } Hungary } Bulgaria } Poland } Czechoslovakia } Rumania • United States of America and the Soviet Union built up huge arsenals of atomic weapons and ballistic missiles….arms race. • The military blocs - NATO and The Warsaw Pact • Destructive conflicts like the Korean and Vietnam Conflicts. • Point Four Program – 3rd world countries • Huge spy programs • Education expansion in the United States • Space Race Sputnik I (1957) The Russians have beaten America in space—they have the technological edge! Politics, Cold War, and Science Fiction Space Exploration The Korean War 1950-1953 The Korean War: A “Police Action” (19501953) Korea divided at the end of WW II at the 38th parallel Kim Il-Sung Syngman Rhee “Domino Theory” Fighting in Korea: • Korea was divided at the 38th parallel of latitude. • North Korea was communist and supported by the Soviets, and South Korea was democratic and supported by the U.S. • In June of 1950, North Korea invaded South Korea. Korean War • Origins of Divided Korea – First “Hot” War • North Korea Invasion – Kim Il Sung • “Korea is the Greece of the Far East” – UN Police Action • China and MacArthur • Stalemate – 38th Parallel • The U.N. sent an international force to Korea in order to push the North Koreans out of South Korea. United Nations forces in Seoul, South Korea. • U.S. General Douglas MacArthur led the U.N. force, approximately 80% of which were U.S. soldiers. Americans pushed to the Pusan Perimeter …the North Koreans had pushed the U.N. forces to the southeast corner of the peninsula, where they dug in around the port of Pusan… Inchon MacArthur completely changed the course of the war overnight by ordering an amphibious invasion at the port of Inchon, near Seoul. The Americans quickly gained control of Inchon, recaptured Seoul within days, and cut the North Korean supply lines. American and ROK forces broke out of the Pusan Perimeter and chased the retreating enemy north into North Korea. Approaching the Yalu •The Chinese army massed north of the Yalu River, with 850,000 troops – warned MacArthur to retreat to the 38th •MacArthur did not believe - Chinese struck with considerable force. •U.N. forces stabilized their lines and the Chinese withdraw northward as quickly as they had struck. •MacArthur pressed Washington to invade China. An Entirely New War •Chinese struck again with roughly 300,000 Chinese troops •Overwhelmed the U.N. forces. •MacArthur.. "We face an entirely new war." •MacArthur pushed back down the peninsula. •Seoul changed hands yet again on January 5. Stalemate Beginning January 15, 1952, Gen. Ridgway led the U.N. in a slow advance northward. Inflicting heavy casualties on the Chinese and North Koreans, the U.N. re-recaptured Seoul (the fourth and final time it changed hands!) on March 15, and had patrols crossing the 38th parallel on March 31. A stalemate ensued, which lasting for another two years. Not until nearly two million more had died did the Korean War end, when an armistice was signed on July 27, 1953. Ending the War: • U.N. troops regained South Korea by March of 1951. • Gen. MacArthur wanted to attack China with support of Chinese nationalists. • President Truman disagreed with MacArthur about attacking China. “the wrong war, at the wrong place, at the wrong time” • In July of 1953, the Korean War ended, in which over 54,000 Americans died. •Armistice signed which returned Korea to the status quo Why US settled for this solution and results? • Waning public enthusiasm for the war • Full consumer production war • US lost face in Russian eyes – Russians doubted the commitment of the US • US emerges largely undamaged Eisenhower and the Cold War • Wanted relaxation of tensions with USSR • Concerned about defense budget - $50 billion under Truman • “new look” for American defense • Cut back on army and navy • Relied on Air Force and nuclear striking power • -$40 billion John Foster Dulles – Sec of State • Massive retaliation – use of nuclear weapons to halt communist aggression that threatened vital US interests anywhere in world The Eisenhower Doctrine Buildup of nuclear capacity to serve as a deterrent Why massive retaliation failed? • Proves to be more costly – defense consumes 50% of national budget • Eisenhower warns country of the power of a “military-industrial complex” • Reduced our ability to fight limited wars • Lacked credibility – did we ever use it? - Hungarian revolt of 1956 – no US response - Polish uprising of 1956 – “ - Middle East – Suez Crisis and Lebanaon – “ - Southeast Asia – “ Eisenhower’s plan for regional collective security • SEATO – 1954 • CENTO - 1959 The Vietnam War c.1963-1975 Indochina crisis • US aid to France in war against communist guerrillas led by Ho Chi Minh • Chinese assistance to Vietminh who surrounded French at Dien Bien Phu • Ike refused help – would have compromised American “tradition of anti-colonialism” • Dien Bien Phu fell and Indochina divided at 17th parallel – communist in North and French in south US took over for French New government headed by Ngo Dinh Diem, Vietnamese nationalist and Catholic “Domino theory” The Suez Crisis: 1956-1957 Egyptian leader Nasser seized the canal British and French invaded to regain control The Hungarian Uprising: 1956 Imre Nagy, Hungarian Prime Minister } Promised free elections. } This could lead to the end of communist rule in Hungary. Nixon-Khrushchev “Kitchen Debate” (1959) Cold War ---> Tensions <--- Technology & Affluence U-2 Spy Incident (1960) Col. Francis Gary Powers’ plane was shot down over Soviet airspace. Paris, 1961 Khrushchev & JFK meet to discuss Berlin and nuclear proliferation. Khrushchev thinks that JFK is young, inexperienced, and can be rolled. The Berlin Wall 1961 Ich bin ein Berliner! (1963) President Kennedy tells Berliners that the West is with them! Khruschev Embraces Castro, 1961 Bay of Pigs Debacle (1961) The Cuban Missile Crisis 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) Vietnam War: 1965-1973 The Vietnam War c.1963-1975