* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The US and the First World War
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Armistice of 11 November 1918 wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
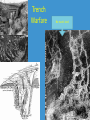
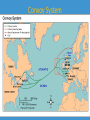
The US and the First World War Mr. Pagliaro Seymour High School @PagsAPUSH Part 1 World War I Begins • Objectives: –Identify the long-term causes and the immediate circumstances that led to World War I. –Describe the first two years of the war. –Summarize U.S. public opinion about the war. –Explain why the United States entered the war. Key terms • • • • • • • Allies (Triple Entente) Central Powers Franz Ferdinand “no man’s land” Trench warfare Lusitania Zimmerman Note Causes: The Dual Alliance • Pact between Germany & AustroHungarian Empire – Negotiated by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck • Linked empires of Kaiser Wilhelm II (G) and Emperor Franz Joseph (A-H) • Led to Central Powers The Austro-Hungarian Empire Triple Entente - 1907 • Alliance among France, Britain, and the Russian Empire led by: – Raymond Poincaré President of France – Georges Clemenceau Prime Minister of France – Tsar Nicholas II of Russia – King George V, GB Nicholas II George V Allied powers, pre-World War I June 28, 1914 • Serb Gavrilo Princip assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand – Possible Anarchist conspiract; The Black Hand – started chain reaction – Led to first World War. Belligerents Allied (Entente) Powers France British Empire Russian Empire(1914–17) Italy (1915–18) Japan Belgium Serbia Romania (1916–18) Greece (1917–18) Portugal (1916–18) Montenegro (1914–16) Brazil (1917–18) United States (1917–18) • Central Powers German Empire Austria-Hungary Ottoman Empire Bulgaria (1915–18) American Neutrality • Wilson announced American neutraility – Consistent w/ American tradition – Demanded neutrality be respected on high seas • Americans sided w/ England & France Trench Warfare No man’s land Air warfare U-Boats • 1915-Lusitania disaster – 1,198 killed; 128 Americans • 1917-Germany declared unrestricted submarine warfare Zimmerman Note • 1917-Germay wanted alliance w/ Mexico vs. USA – Offered return of lands taken in Mexican-American War • Intercepted by British • Wilson’s Response – Violated American Free Shipping • Killed Americans • Interfered w/ Mexico – American crusade: • …to make the world safe for democracy! Part 2 American Power Tips the Balance • Objectives – Describe how the United States mobilized for war. – Summarize U.S. battlefield successes. – Identify the new weapons and the medical problems faced in World War I. – Describe U.S. offensives and the end of the war. Key Terms • • • • • • • Selective Service Act Convoy system Sgt. Alvin York Conscientious objector Mechanized warfare Capt. Eddie Rickenbacker John J. Pershing Selective Service • May 18, 1917 • Males, 21-30, required to register for draft –1918, expanded to 18-45 • Total enrollees: 24 million –2 million drafted by lottery »1/5 foreign born American Recruitment • Use of Uncle Sam Minority groups in Military • Women – non-combatant military position – 13,000 enrollees – Navy, Marines = ; Army treated women < men • African-Americans – Segregated units – 1st black officers – Proportionally, twice as many in Army vs. US pop. “Building the Bridge to France” Government promoted ship building 1. Exempted ship builders from draft 2. Promoted ship building 3. Assembly through fabrication 4. Converted/commandeered all new ships for war Convoy System Convoy System American Expeditionary Force • John J. Pershing – “Black Jack” – Led Buffalo soldiers on Great Plains – Hunted Pancho Villa in 191617 – Led AEF in Europe • Fought separate of Allies in 1918 American Expeditionary Force • American Soldiers – “Doughboys” • Over there, over there, Send the word, send the word over there---That the Yanks are coming! • “Lafayette, we are here!” American Expeditionary Force • Sgt. York – Attempted conscientious objector – “Hero” took German machinegun nest • “single-handedly” Captured 32 guns & 132 Germans, killed 28 American Expeditionary Force • Eddie Rickenbacker – American “Ace” End of the War • Early 1918-Russia withdrew due to Revolution • October 1918 - American aggression – Allies defensive war • November 1918-Germany “mutiny” • 11/11/1918 – Armistice – Only other truces: Christmas Truces, 1914 End of the War World War I Results Part 3: The Homefront • Key Objectives: – Explain how business and government cooperated during the war. – Show how the government promoted the war. – Describe the attacks on civil liberties that occurred. – Summarize the social changes that affected African Americans and women. Key Terms • • • • • • War Industries Board (WIB) Bernard M. Baruch George Creel Committee on Public Information Espionage and Sedition Acts Great Migration War Industries Board • Led by Bernard M. Baruch – Encouraged mass production – Industrial output increased 20% • Fuel Administration – Gasless Sundays – Daylight savings National War Labor Board • Led by Taft – 6,000 Strikes • “Work or fight” – Promoted regulating working conditions Committee on Public Information • American Propaganda • Machine • Led by George Creel • Promote support –Encouraged buying war bonds –Portrayed Germany as murderous Food Administration • Led by Herbert Hoover – Food conservation for war effort – Gospel of the Clean Plate • Meatless Mondays • Wheatless Wednesdays – Victory Gardens Food Administration Propaganda Espionage & Sedition Acts – 1917 & 1918 • No speaking out against America or Allies • Against: – Socialists – IWW members • Extremely reactionary – Clarence Waldron • Minister • Preached pacifism – Sentenced 15 years The Great Migration • 20% of African-Americans moved North • Causes: – Jim Crow laws – Need for labor in war industry Exodus from South • 1915-majority of African-Americans in South – Moved to Midwestern & Northern cities # of African Americans in Southern States after Civil War Estimated African American population of Southern States; Multiply x 1000 Part 4: Wilson Fights for Peace • Key Objectives: –Summarize Wilson's Fourteen Points. –Describe the Treaty of Versailles and international and domestic reaction to it. –Explain some of the consequences of the war. Key Terms • • • • • • Fourteen Points League of Nations Treaty of Versailles reparations war-guilt clause Henry Cabot Lodge The Peace Process The following telegram was sent through the Swiss government and arrived in Washington, D.C., on 5 October 1918: • The German Government requests the President of the United States of America to take steps for the restoration of peace, to notify all belligerents of this request, and to invite them to delegate positions for the purpose of taking up negotiations. The German Government accepts, as a basis of peace negotiations, the Programme laid down by the President of the United States in his message to Congress of 8 January 1918, and his subsequent pronouncements, particularly in his address of 27 September 1918. In order to avoid further bloodshed the German Government requests to bring about the immediate conclusion of an armistice on land, on water, and in the air. • —Max, Prince of Baden, Imperial Chancellor Negotiating Peace • Wilson had offered since 1914 to broker peace – Developed Fourteen Points Peace Plan • Incorporated into 1919 Treaty of Versailles Treaty of Versailles • Wilson’s Fourteen Points called for: Open international diplomacy No secret alliances Freedom of the Seas Creation of League of Nations Preserve peace & security of members Arms reduction Consideration and nationalism for all ethnic groups League of Nations League of Nations Creation of Weimar Germany • New Borders, post-WWI to Nations created by Treaty • • • • • • • • Poland Czechoslovakia Yugoslavia Iraq Syria Lebanon Israel Jordan Weaknesses of Treaty 1. Humiliation of Germany-militarily, politically, economically 2. Exclusion of new Bolshevik Russia 3. International instability due to treatment of colonial peoples Stripping Germany’s Power • Germany required to pay $33 billion reparations • Demilitarization • War-guilt clause – Blamed Germany alone for war • Kaiser Wilhelm II considered war criminal Senate opposed Treaty • Senate had power to approve treaties – Henry Cabot Lodge leads Republicans against ratification • Lodge Amendments – Changed treaty regarding US and League of Nations – Senate did not ratify Treat • US signed separate peace w/ Germany -1921 – Never joined L.o.N.