* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War
Mutual assured destruction wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Cuban Missile Crisis wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
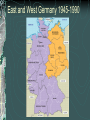
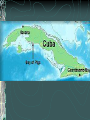
The Cold War: 1947-1991 Clash of communist Soviet Union and democratic United States Post World War II United Nations- formed after WWII An international peacekeeping association formed in 1945 to provide international security USA, USSR, Britain, China, France, etc. (50 countries) The Cold War The Big 3 (Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin) met to determine the make-up of post-WWII Europe at the Yalta Conference in USSR in 1945 USSR was given control of E. Europe until free elections could be held Germany was divided into U.S., France, England & USSR zones Results of the Yalta Conference E. European nations became satellite states of USSR Germany was split into East (communist) and West (democracy) East and West Germany 1945-1990 Iron Curtain Term coined by Churchill Used to described the division of Europe East and West Berlin 1945-1990 Berlin was divided into East (Commie) and West (Democracy) Stalin and Eastern Europe He created “buffer states” between USSR and the West Cold War Policy of US and the West Soviets (totalitarianism and communism) Vs US and West (democracy and capitalism) US saw Soviets as a threat to spread communism throughout Europe Containment Policy of US and West was to “contain” (stop) the spread of Communism: Truman Doctrine 1947 – Pres. Truman’s economic and military aid program to help people resist communist aggression Domino Theory If one country “falls” to communism, soon after its neighbor will also become communist Then the next neighbor will “fall” … and so on This was used to justify U.S. involvement in Europe The Marshall Plan US feared poor countries of Europe would come under Soviet control MP offered eco aid to “any country that needed it” to lessen appeal of communism North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) Includes US, Canada and most of W Europe Warsaw Pact – Defensive alliance between the Soviet Union and its satellites Formed in response to NATO NATO (Green) and Warsaw Pact (Red) Berlin – The Wall After the split of Germany and Berlin, thousands of Germans fled to W Berlin to escape communist E Germany 1961 – E Germany built a wall to stop the flow The wall symbolized the Cold War “Checkpoint Charlie” Brinkmanship US Pres. Eisenhower threatened to “retaliate instantly” to any Soviet aggression This led to an arms race Both sides threatened to use all-out nuclear war Bay of Pigs Unsuccessful action by a CIA-trained force of Cuban exiles to invade southern Cuba An attempt to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro The rebels were defeated and taken as prisoners Important Results: Gave Soviets the feeling that the US couldn’t stop them in the Western Hemisphere This will eventually lead to the Cuban Missile Crisis Cuban Missile Crisis A thirteen-day confrontation between the Soviet Union and Cuba on one side and the United States on the other JFK vs Nikita Khrushchev The Cuban and Soviet governments began to build bases in Cuba for medium-range and intermediate-range ballistic nuclear missiles (MRBMs and IRBMs) with the ability to strike most of the continental United States. On the brink of a nuclear war for many days Confrontation ended when Soviets decided to remove missiles from Cuba and US privately removed their missiles from Turkey and Italy and pledged to not invade Cuba Gorbachev Leader after Kruschev during the Reagan years Glasnost- liberalized political landscape Gov’t should be more honest Perestroika- allowed for more private ownership of land, make socialism more effective Cold War Thaws Gorbachev and Reagan begin meeting at the “Geneva Summits” Allows the Cold War to eventually end Symbol- destruction of the Berlin Wall