* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download congress - Cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Filibuster in the United States Senate wikipedia , lookup
Electoral reform in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Article Five of the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
History of the United States Congress wikipedia , lookup
Powers of the President of the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
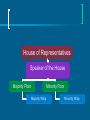
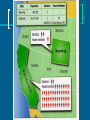
CONGRESS Why Bicameralism? Compromise Checks & Balances Congressional Reapportionment & Redistricting Reapportionment – The reallocation of the number of representatives each state has in the HR Why is it important? 1. increases or decreases the number of seats 2. more Rep’s more influence 3. electoral votes Redistricting – the drawing/redrawing of congressional district lines Gerrymandering Why? To enhance political party strength Protect incumbents Who is in Congress? Personal & Political Backgrounds WASP Mid 50’s (middle-aged) Married w/ children Table 11.1: Blacks, Hispanics, and Women in Congress, 1971-2002 Many were lawyers Held previous positions in government Many make careers out of office Do members represent their voters? Demographically: No Republican members more conservative than avg. Americans Democrat members more liberal than avg. Americans Yes: If they want to get elected Congressional Elections Incumbents usually win Why? Advertising – name recognition Credit Claiming - Pork Barrel & casework Safe districts - Gerrymandering Table 11.2: Incumbents in Congress Reelected by 60 Percent or More Figure 11.2: Percentage of Incumbents Reelected to Congress Source: Harold W. Stanley and Richard G. Niemi, Vital Statistics on American Politics, 1999-2000 (Washington, D.C.: Congressional Quarterly Press, 2000), table 1-18. Job Benefits Power Pay $162,000 YR & Retirement Office space Congressional Staff Travel allowances & Franking Privileges Powers of Congress Legislative examples include: to collect taxes, borrow money, to declare war, and to “make all laws necessary and proper” Non-legislative powers oversight of the executive branch appointments impeachment Essay Practice # 1 A. Discuss two reasons why the framers created a bicameral legislature B. Identify one power unique to the House of Representatives and explain why the framers gave the House that power C. Identify one power unique to the Senate and explain why the framers gave the Senate that power. Leadership in Congress House of Representatives Speaker of the House- Boehner 1. Presides over the House 2. Appoints select & conference committees 3. Appoints the rules committee 4. Assigns bills to committees 5. Second in line for the presidency Speaker of the House– John Boehner (R) Majority & Minority Leader 1. Partisan position picked by individual parties 2. Floor leader & legislative strategist Majority – Cantor Minority - Pelosi Majority Leader – Eric Cantor Minority Leader Party Whips 1. Assistant floor leader 2. Inform party leaders on the “mood” of the House 3. Keep nose count on important votes Senate Vice President - Biden 1. President of the Senate 2. Presides over the Senate 3. Votes in case of tie Joseph Biden President pro Tempore 1. Ceremonial job 2. Presides when the VP is absent 3. Third in line for the presidency after the Speaker – Dan Inouye Majority Leader 1. True leader in the Senate 2. Recognized first for all debates 3. True leader of the Majority party Majority – Reid Minority - McConnell Harry Reid (D-NV) Minority Leader – Mitch McConnell Types of Committees Standing Committee Formed to handle bills in different policy areas 2-3 committees and 4-7 subcommittees per member Joint Committees Made up of members of both houses to meet about a specific issue and report back their findings – Example - Library of Congress Select Committees Temporary - set up to study specific issues Conference Committees Temporary Members from both houses hammer out differences in a bill Caucuses Associations of members of Congress created to advocate on behalf of an ideology, constituency, or regional and economic interest Types- Intraparty, Personal interest, Constituency concerns Table 11.5: Congressional Caucuses How Things Work: How a Bill Becomes Law Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Total Members Determined By Qualifications Length of Term Special Powers Senate Congress The United States Congress House Senate Total Members 435 Members 100 Members Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Total Members Determined By Qualifications Length of Term Special Powers 435 Members Senate 100 Members Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Senate The state’s population: Two from each state, no Determined By the more people living in matter what the size of the the state, the more state’s population Representative the state will have. Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Total Members 435 Members Senate 100 Members The state’s population: the more Two from each state, no matter Determined By people living in the state, the what the size of the state’s more Representative the state will population have. Qualifications Length of Term Special Powers Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Senate ▪ Must be 25 years old ▪ Must be 30 years old Qualifications ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 7 ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 9 years years ▪ Must be resident of state ▪ Must be resident of state Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Total Members 435 Members Senate 100 Members The state’s population: the more Two from each state, no matter Determined By people living in the state, the what the size of the state’s more Representative the state will population have. Qualifications Length of Term Special Powers ▪ Must be 25 years old ▪ Must be 30 years old ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 7 years ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 9 years ▪ Must be resident of state ▪ Must be resident of state Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Length of Term 2 years Senate 6 years Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Total Members 435 Members Senate 100 Members The state’s population: the more Two from each state, no matter Determined By people living in the state, the what the size of the state’s more Representative the state will population have. Qualifications Length of Term Special Powers ▪ Must be 25 years old ▪ Must be 30 years old ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 7 years ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 9 years ▪ Must be resident of state ▪ Must be resident of state 2 years 6 years Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Senate ▪ Impeaches federal officials ▪ Conducts impeachment Special Powers ▪ Introduces money bills trials ▪ Selects a President if the ▪ Approves Presidential Electoral College fails to appointments do so ▪ Ratifies (approves) treaties Congress The United States Congress House of Representatives Total Members 435 Members Senate 100 Members The state’s population: the more Two from each state, no matter Determined By people living in the state, the what the size of the state’s more Representative the state will population have. Qualifications Length of Term ▪ Must be 25 years old ▪ Must be 30 years old ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 7 years ▪ Must be U.S. citizen for 9 years ▪ Must be resident of state ▪ Must be resident of state 2 years ▪ Impeaches federal officials Special Powers ▪ Introduces money bills ▪ Selects a President if the Electoral College fails to do so 6 years ▪ Conducts impeachment trials ▪ Approves Presidential appointments ▪ Ratifies (approves) treaties Journal topic Members of Congress tend to have a particular demographic profile. Is this a matter of concern? Does the preponderance of a particular demographic and professional group compromise the quality of representation provided by the U.S. Congress? HOW MEMBERS OF CONGRESS VOTE REPRESENTATIONAL VIEW(Delegates) - MEMBERS VOTE TO PLEASE THEIR CONSTITUENTS ORGANIZATIONAL VIEW (Partisan) - MEMBERS OF CONGRESS VOTE TO PLEASE COLLEAGUES Logrolling ATTITUDINAL VIEW (Trustees)- IDEOLOGY AFFECTS A LEGISLATURES VOTE The U.S. Congress: The U.S. Congress House of Representatives Speaker of the House Majority Floor Majority Whip Minority Floor Minority Whip Senate President of the Senate Majority Floor Majority Whip President pro Temp. Minority Floor Minority Whip Bills & Resolutions Bills 10,000 proposed laws a session About 6% become law Two Types 1. Public – entire nation 2. Private – certain people or places Resolutions Three types – Joint resolution, concurrent resolution and Resolution Joint Resolution Has the force of law May be used to appropriate money & propose constitutional amendments Concurrent Resolution State position Example – Foreign matters Resolutions Used for such things as the adoption of a new rule or procedure Riders to Bills Riders are provisions not likely to pass on its own merit Attached to an important measure certain to pass “Christmas Tree” bill – many riders attached Court Cases Buckley v. Valeo 1976 Political spending is protected by the 1st Amendment. However, there is sufficient public interest in establishing a level playing field to justify limits Wesberry v. Sanders 1964 Court ruled that each district must represent approximately the same number of people as all others Shaw v. Reno 1993 Ruled against racial gerrymandering Pork barrel legislation- the practice of legislators obtaining funds through legislation that favors their home districts – ex. Highway Bill - Don Young (R-AK) $1 billion to his home state - $231 million to build a bridge to a sparsely inhabited marshland Named “Don Young’s Way”